Page History
...
| Section | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Column | | ||||||||||
|
when the camera mode is set to Video cam. |
| Column | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| Column | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
...
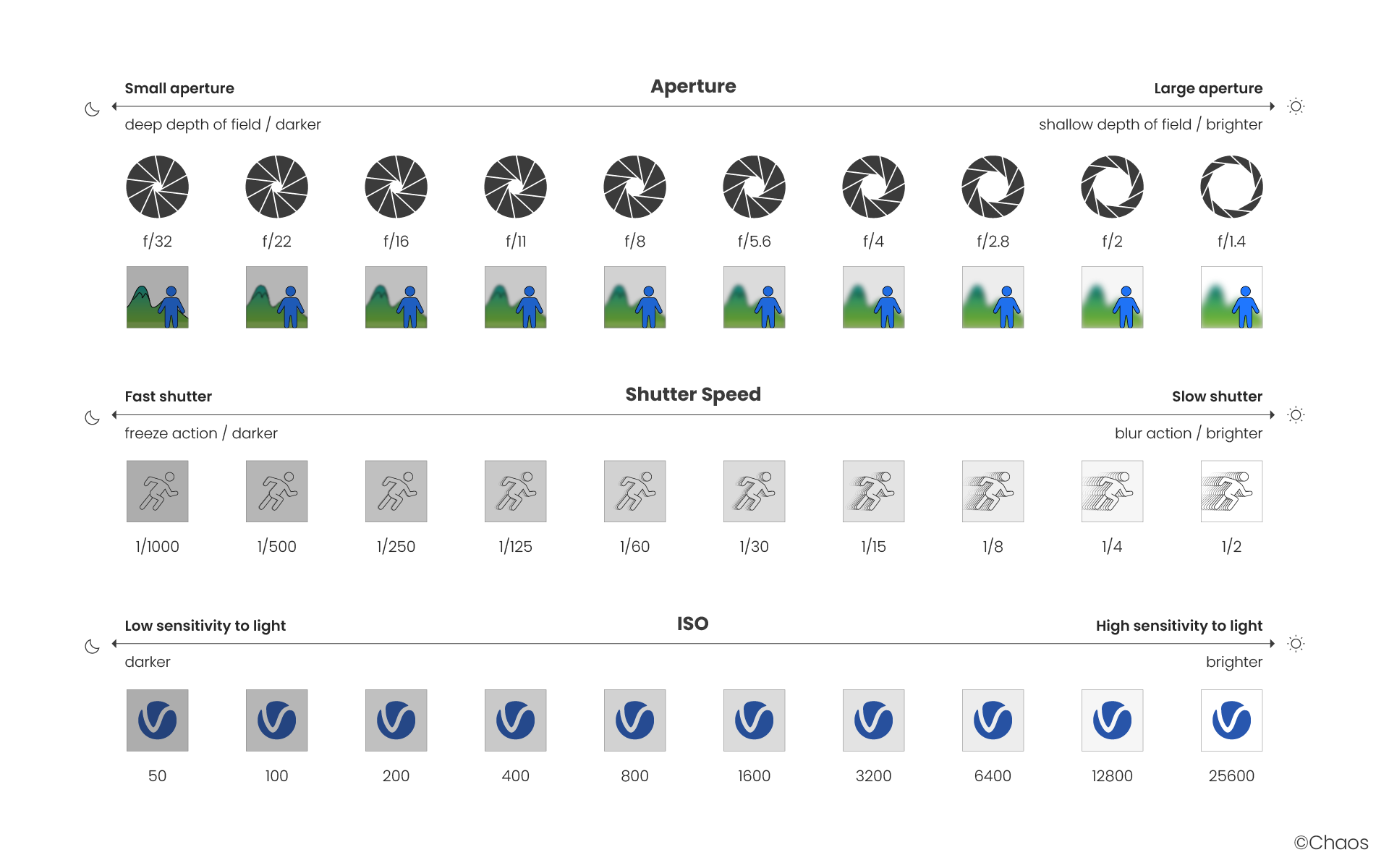
Aperture F-number vs Shutter Speed vs ISO
Cheat Sheet
The main options that control the brightness of a V-Ray Physical camera are Aperture F-number, Shutter Speed and ISO. They affect each other and you need to balance their values according to your scene. Keep in mind that these settings do not correspond to those of a real-life camera. They apply only to the V-Ray Physical camera.
| Fancy Bullets | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Anchor DOFMotion DOFMotion
DoF & Motion blur
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...