This page provides information about the V-Ray C4DBake utility texture.
Overview
VRayC4DBake is a utility texture that helps you render native Cinema 4D shaders with V-Ray at a higher quality.
V-Ray does not support native Cinema 4D shaders and sometimes they might lack the needed detail.
For greater control over the quality, use the VRayC4DBake texture. V-Ray internally bakes the shader while rendering, so the results are accurate.
UI Path: Texture > V-Ray > VRayC4DBake
Workflow
- Create a V-Ray material and assign it to the object.
- Select the VRayC4DBake texture from the Texture slot.
- Go to the VRayC4DBake parameters and from the Shader options, select the desired Cinema 4D shader.
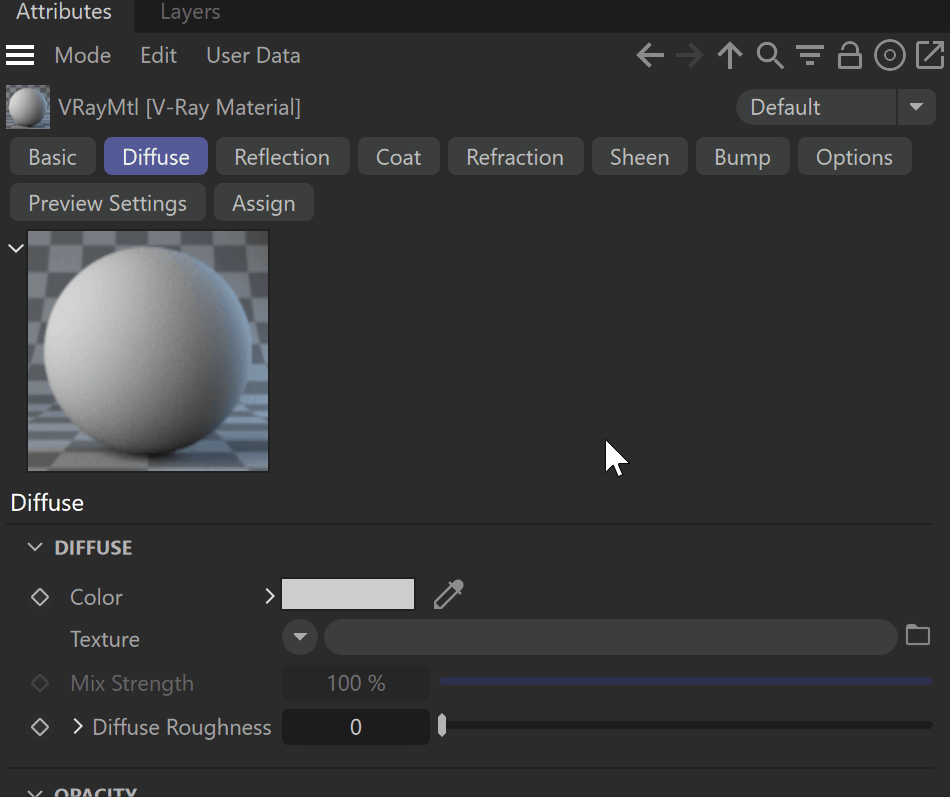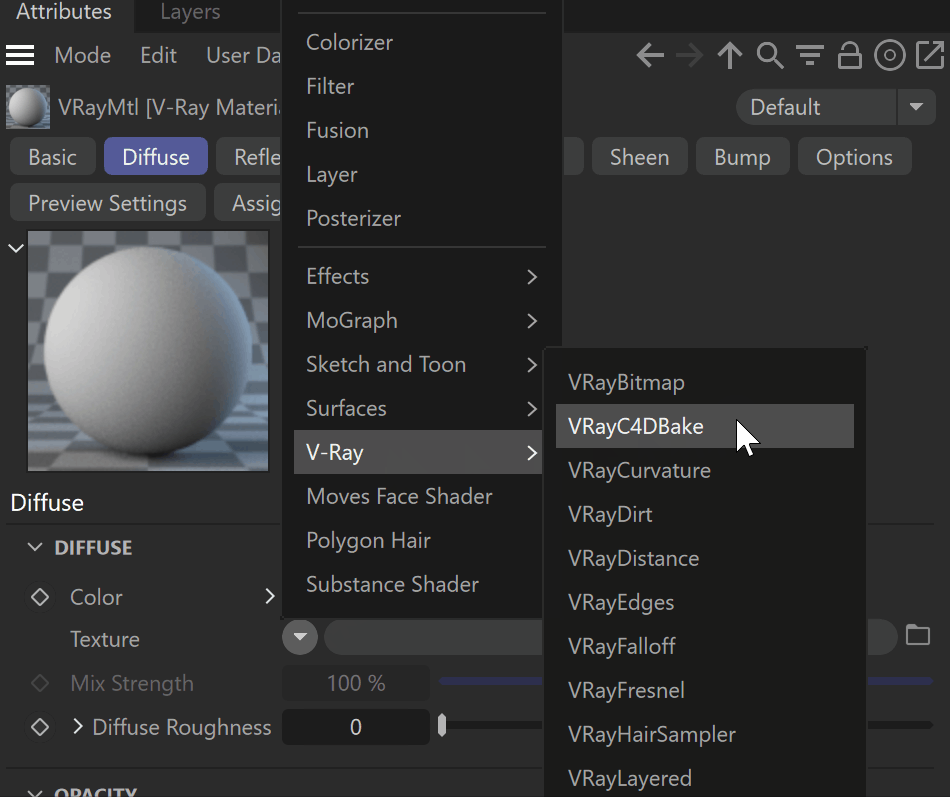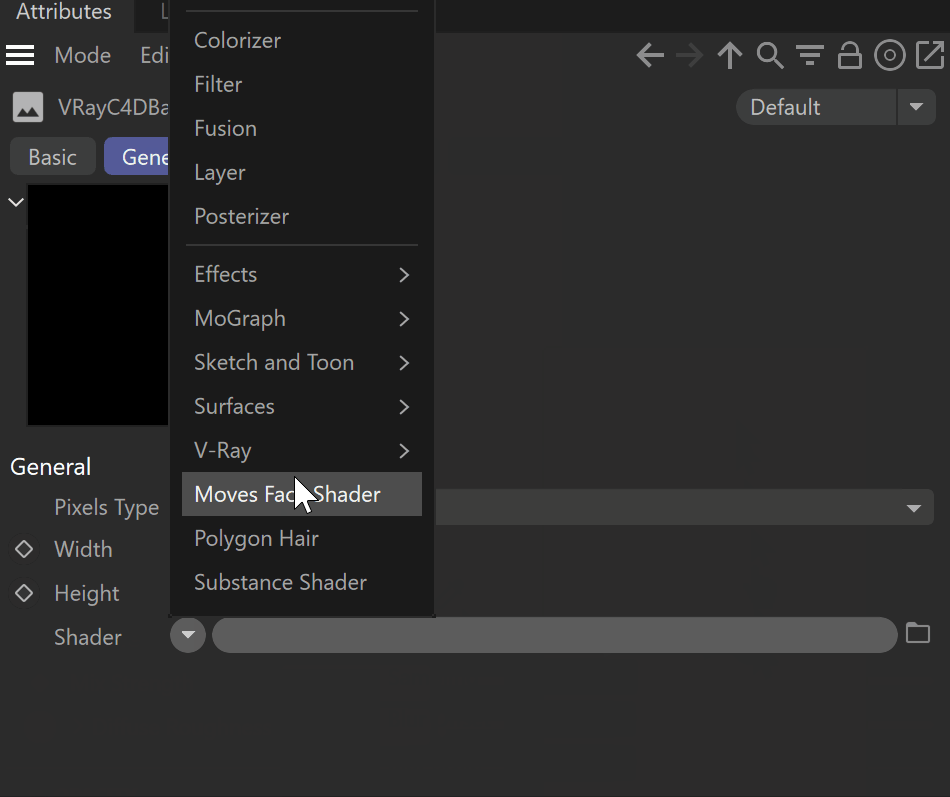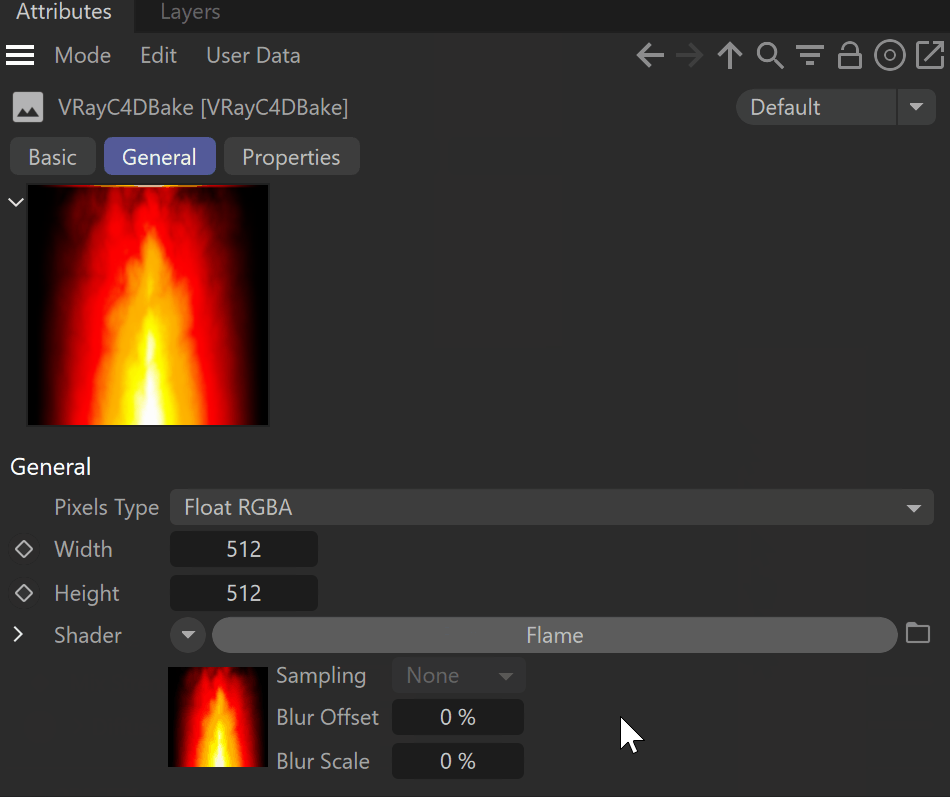
General
Pixels Type – Specifies how to bake the pixel of the texture:
8-bit RGBA
Float RGBA
16-bit RGBA
8-bit RGB
Float Grayscale
8-bit Grayscale
Width/Height – Specifies the resolution of the baked texture.
Shader – Specifies the Cinema 4D texture you want to render.
You can further edit the loaded shader using the options that appear in the Shader submenu .
Properties
Filter Type – Specifies the type of filtering to apply to the image.
Nearest – The nearest texel from the map is taken, without any interpolation.
No Filtering – Does not apply any filtering.
Mip-Map Filtering – Applies a mip-map filter.
Summed Are Table Filtering – Pyramidal MIP-map filtering is used to compute the texture color. Can be blurry for textures seen at grazing angles.
Elliptical Filtering – High quality anisotropic MIP-map texture filtering that reduces blurring and aliasing artifacts.
Sharp Mip-map Filtering – Sharper and more accurate version of the Summed Are Table Filtering. Produces results that are closer to the results with disabled filtering but with less AA samples required.
Filter Blur – Specifies the filter blur. The higher the value, the more blurred the texture renders and the less render time it takes, and vice versa. A value of 0.01 means no filtering, but leads to increased render times.
Transfer Function – Specifies the color space for the loaded image file. The value is automatically selected when loading a new file by looking for the strings "_lin_srgb", "_srgb" and "_raw" in the file name. It also considers the file extension. You can manually modify the value.
None – No correction is applied.
Gamma corrected – The color space is controlled through the Gamma parameter.
sRGB – The loaded image is considered in sRGB color space.
Gamma – Specifies the gamma correction to be applied.
Allow Negative Colors – If disabled, negative colors are clamped. Enable to allow negative colors.
Interpolation – Determines how the image is interpolated from the pixel values.
Bilinear – Image values are interpolated from four pixels in the bitmap. This is the fastest interpolation method, but the result is not continuous (non-smooth) and may produce artifacts when the map is used for displacement or bump mapping.
Bicubic – Image values are interpolated from sixteen pixels in the bitmap. This is the slowest method, but the results are smooth, without too much blur.
Biquadratic – Image values are interpolated from nine pixels in the bitmap. This method is faster than the Bicubic interpolation, but may smooth the image too much.
From 3ds Max – Interpolation type is chosen automatically, depending on the bitmap, format to match the behavior of the standard texture. For HDR and EXR images, the interpolation is Bilinear, and for all other formats - Bicubic.