This page provides information on the Override Material.
Overview
The VRayOverrideMtl is a utility material provided with the V-Ray renderer. It allows a surface to look different depending on whether it is seen through reflections, refractions, or GI.
With this material you can get a fine control over the color bleeding, reflections, refractions, and shadows of the objects.
The example image by Linda Ferroni demonstrates the reflect material override option. Notice that the yellow bottle and brown pot are reflecting as entirely different materials in the mirror.
Parameters
Base material – The material V-Ray uses while rendering the object.
GI material – The material V-Ray uses while calculating the GI solution.
Reflect material – The material V-Ray uses to render the object with, when the object is seen in reflections. For more information, see Using the Reflect material example below.
Refract material – The material V-Ray uses to render the object with, when the object is seen in refractions. For more information, see Using the Refract material example below.
Shadow material – The material that is used to render shadows cast from the object.
Example: Using the GI material
This example shows how the use of a GI material affects the rendering.
This simple interior scene represents a room lit by two rectangle VRayLights - one hidden top light and another back fill light - as well as by three disc VRayLights for the pendant lamps above the sinks.
A wooden VRayMtl from the Chaos Cosmos library is applied on the floor, and a default VRayMtl with Diffuse color (128, 128, 128) is applied on the rest of the scene objects, except for the glass objects (mirror and pendant lamp plafonds).
In the first image, it is visible that all walls, objects, and the ceiling are rendered in some light brown color, despite having a light-gray material assigned to them. This is due to the color bleeding, generated by the GI calculations.
In the second image, the scene is rendered with a VRayOverride GI material assigned to the floor. The VRayOverrideMtl contains in itself the initial two V-Ray materials: the wooden VRayMtl as base and the default VRayMtl as GI material. The rest of the scene objects keep the default gray VRayMtl. So now V-Ray knows that while calculating the GI it has to use the GI material (in this case: VRayMtl with Diffuse color (128, 128, 128) and during rendering it uses the Base material (in this case: the wooden VRayMtl). The result of that is quite different from the previous render as the Color Bleeding is gone. Of course this depends entirely on your choice for the GI material. For instance, if you had chosen a bluish colored material, the final result would also be tinted slightly to blue, like in the first render with the pale brown colors.
For a much more complex scene, with lots of different geometry, shaders, textures, etc., using the VRayOverride material can be very helpful.
Example: Using the Reflect material
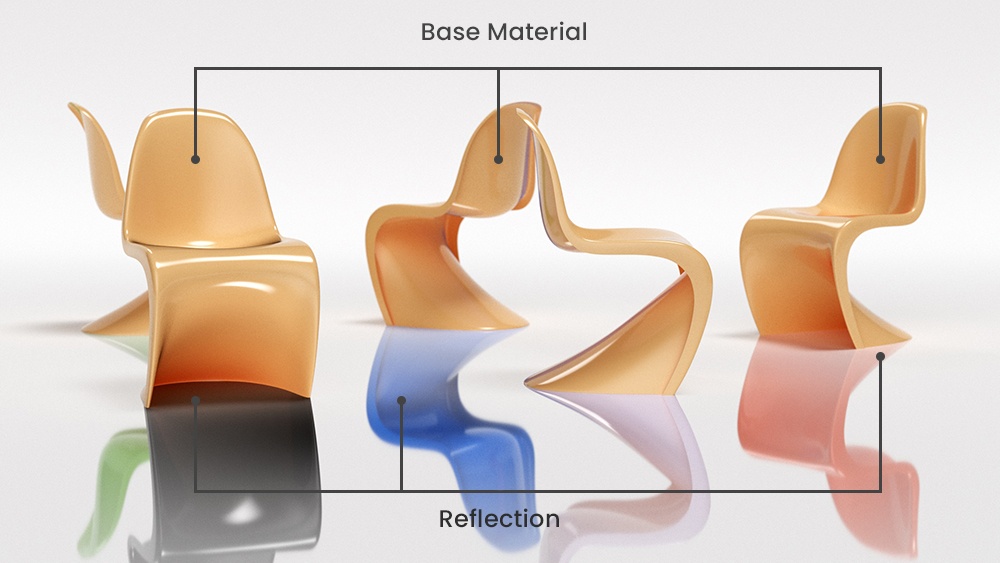
The scene used in the following examples is very simple and contains five chairs and a light source in a studio type environment. Each chair has a VRayOverride material assigned, but only the Base material is active. The rendered chairs are the same in their diffuse colors and reflections.
Now each of the chairs has a different material assigned in their VRayOverride Reflect material. The first one has a green diffuse color, the second one has black, the third one has blue, the fourth - purple, and the fifth has a red diffuse color. V-Ray uses those materials when the objects are seen in reflections. In this scene, the environment is actually a reflective surface, so the chairs are being reflected. On the other hand, you can also notice that the base material of the chairs is also reflective, and the fourth chair is seen with its Override Reflect material in the middle chair.
Example: Using the Refract material
The next render is even more complex as the chairs' Override Refract material is activated as well. From left to right follow: a blue and a red diffuse color. Those materials are set so that when seen through refraction, V-Ray considers and renders the objects with them. As you can see the Reflect materials are still affecting the render image.
If you take a closer look at the glass chairs' edges you will notice the green reflection, which is actually the reflect material of the right chair. While V-Ray had been tracing the rays on the chairs' surfaces, those polygons on the edges had first captured a reflection, so that's why there are green traces.
Notes
- Since V-Ray 3.0 the V-Ray Override material doesn't support the 3ds Max Standard material.