Page History
This page provides information on the V-Ray User-defined Scalar Map.
Overview
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Parameters
...
| Section | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Examples
...
For In the examples below we use a user attribute to several objects. The attribute value is read with a userScalar texture that passes the value , user attributes are assigned to different objects with different values. A VRayUserScalar texture reads the values and passes them to a shader at render time. This way we can pass different shader values that are controlled at the object level, allowing us to share the shader between all objects.
...
Note that alembics coming from other applications, e.g. Houdini, with custom attributes already baked in, can be read in the same way as the user attributes. See the the Houdini to Maya Alembic Workflow tutorial for more information.
...
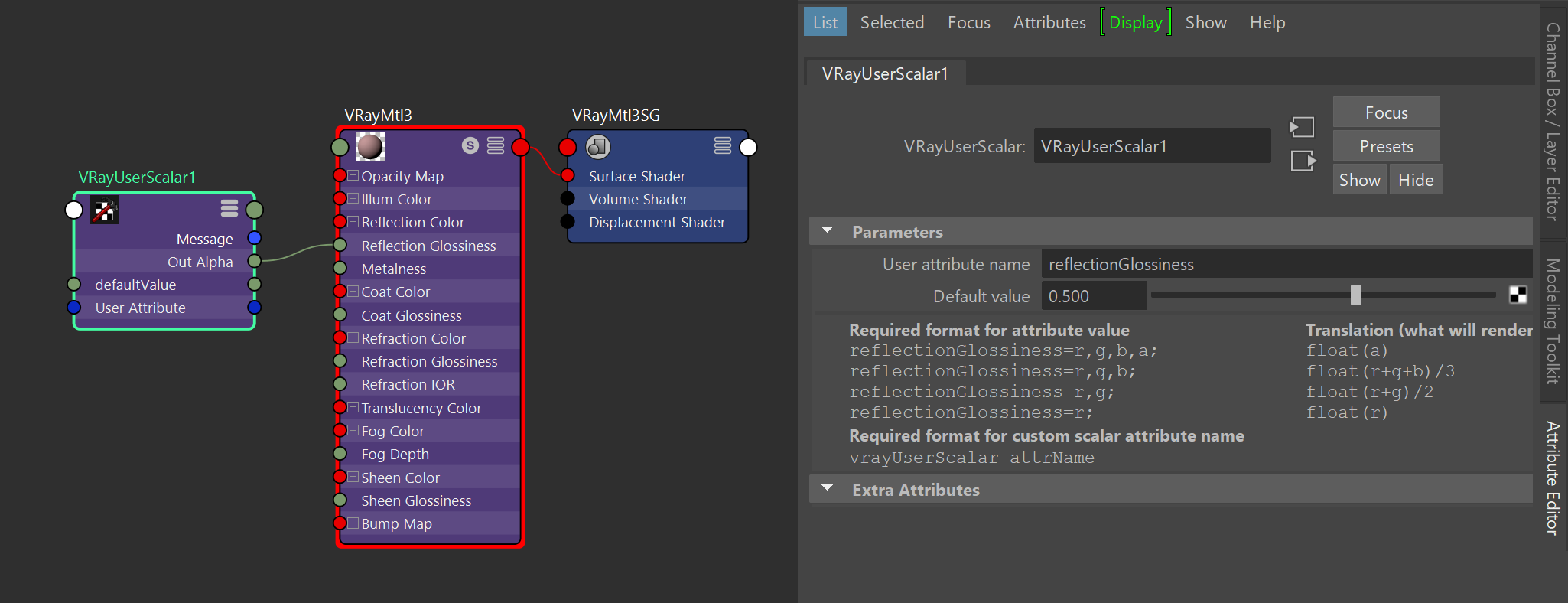
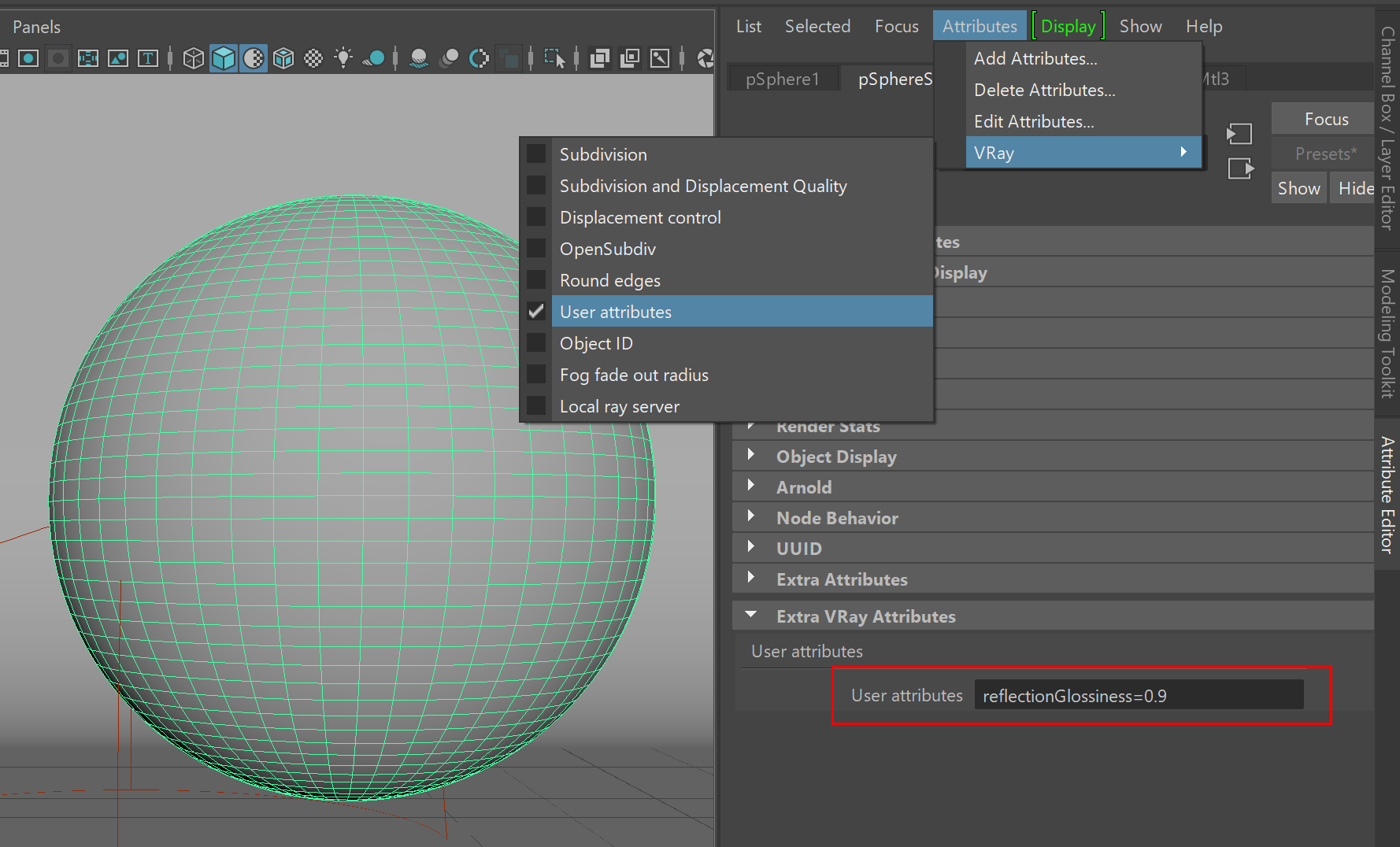
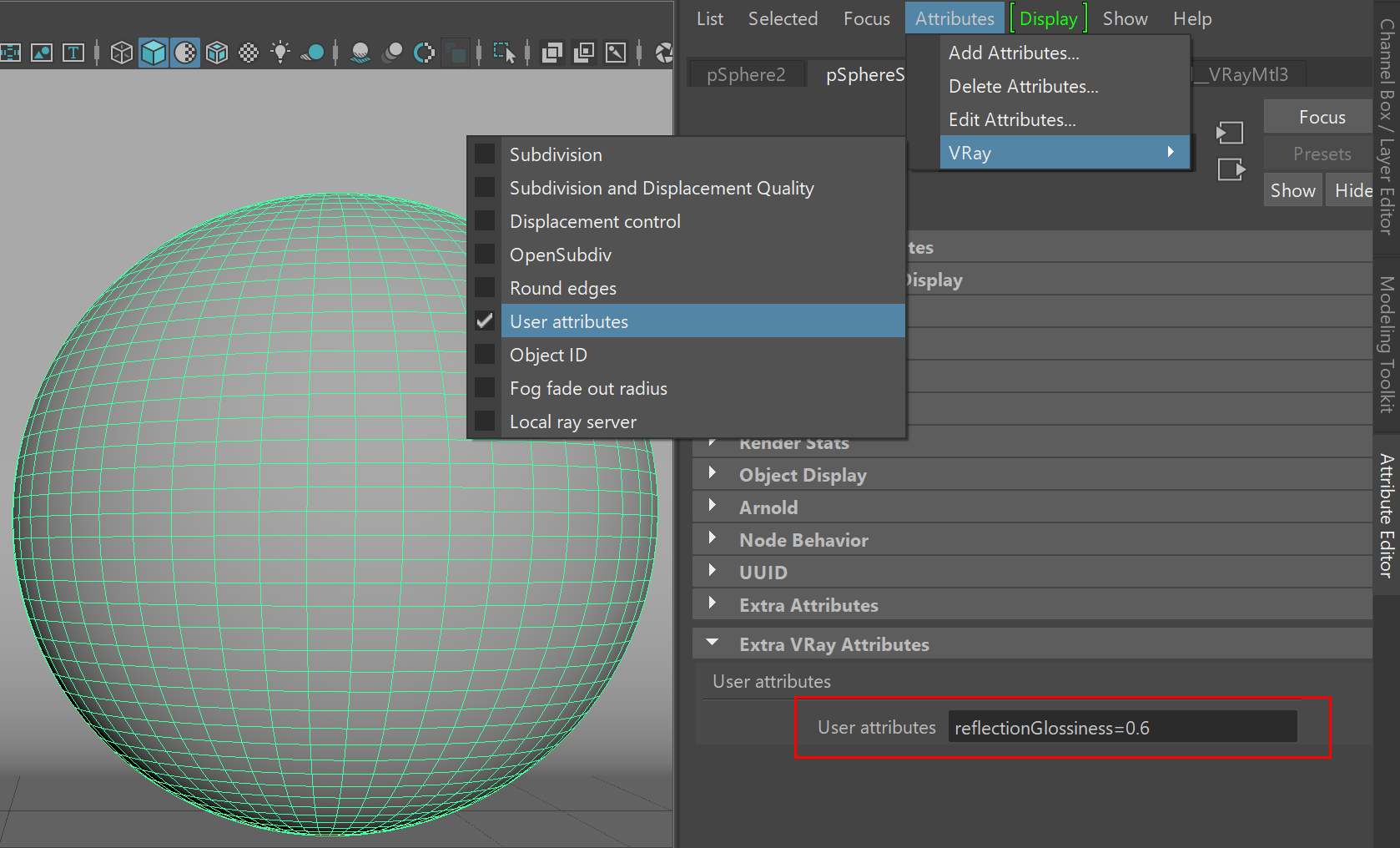
This example shows the format for the value of the user attribute and how it is interpreted. The VRayUserScalar texture is used to control controls the VRayMtl Reflection Glossiness parameter. A user attributed named reflectionGlossiness is used to specify different values for the reflection glossiness of values on two objects.
| Section | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
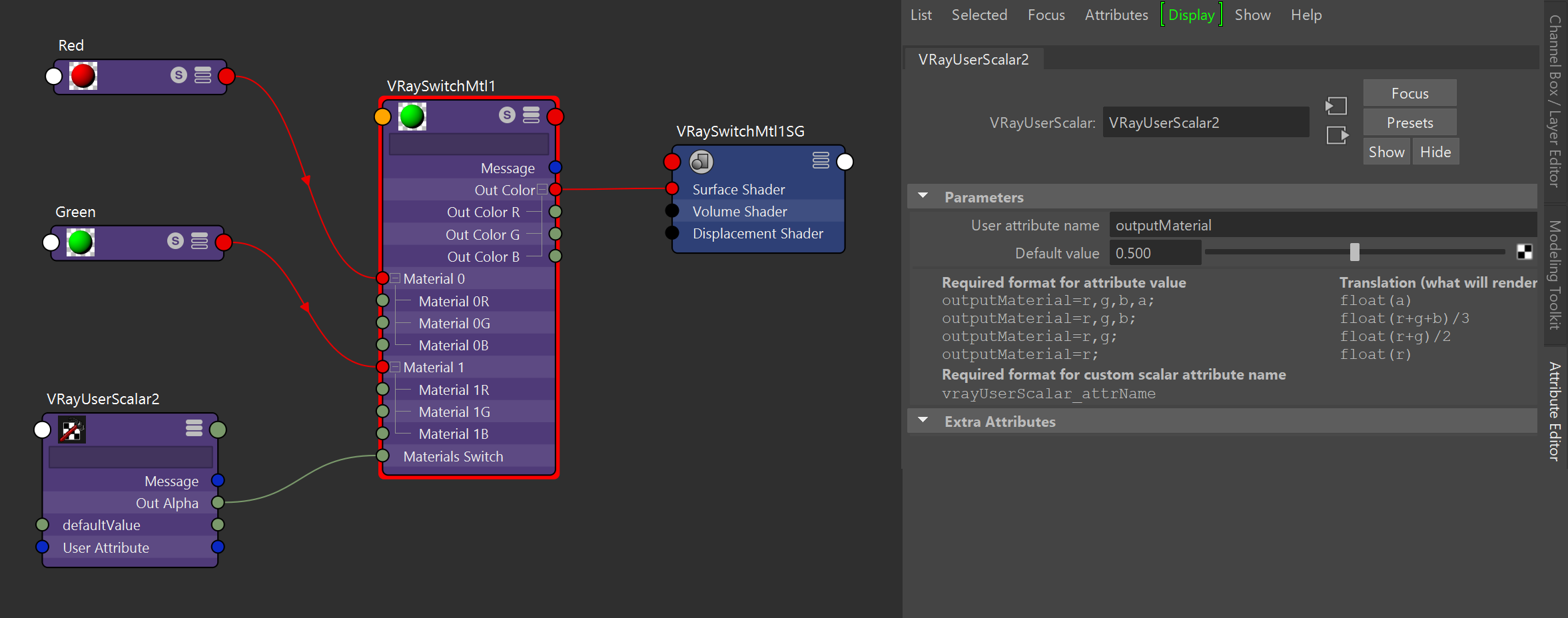
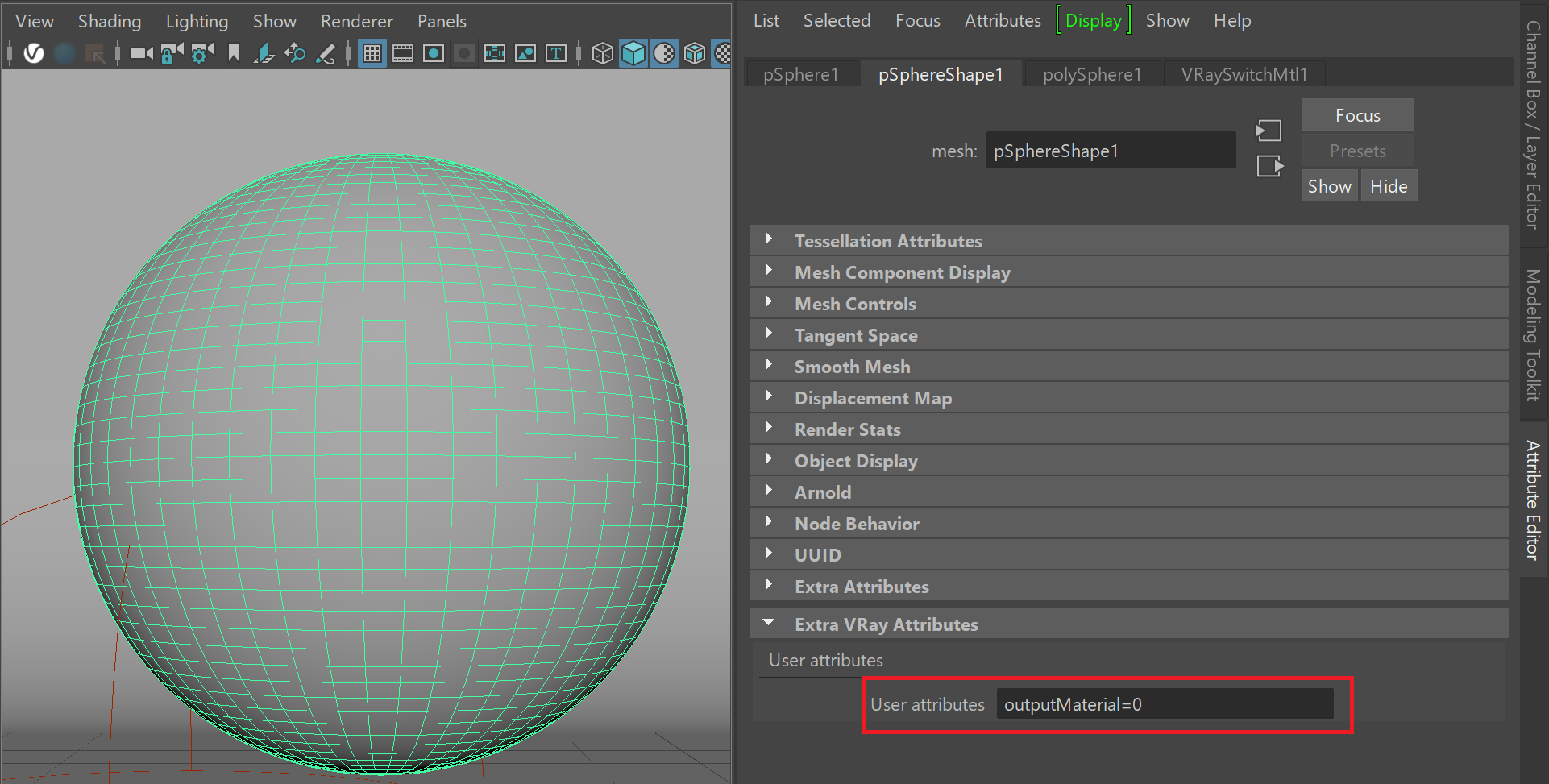
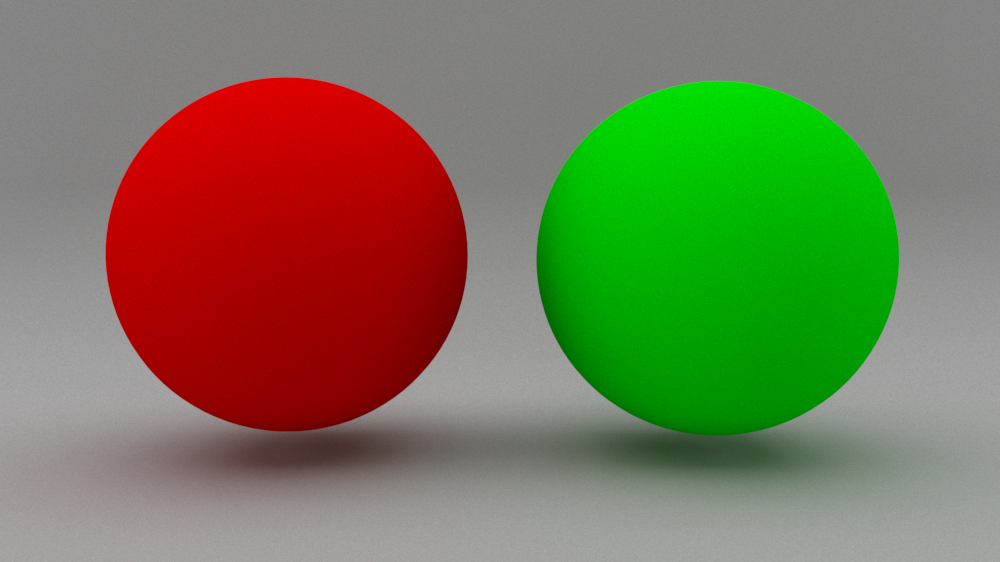
Example: VRayUserScalar with VRaySwitchMtl
This example uses VRayUserScalar to control how materials from a VRaySwtichMtl are distributed to different objects.
shows how VRayUserScalar determines the distribution of two materials linked in a VRaySwtichMtl to two objects. Two different VRayMtls are linked as Material 0 and Material 1 of in a VRaySwtichMaterial. A VrayUserScalar is linked to used as the SwitchMtl's Material Switch slot and a user attribute named outputMaterial is used to drive drives the material distribution.
| Section | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|