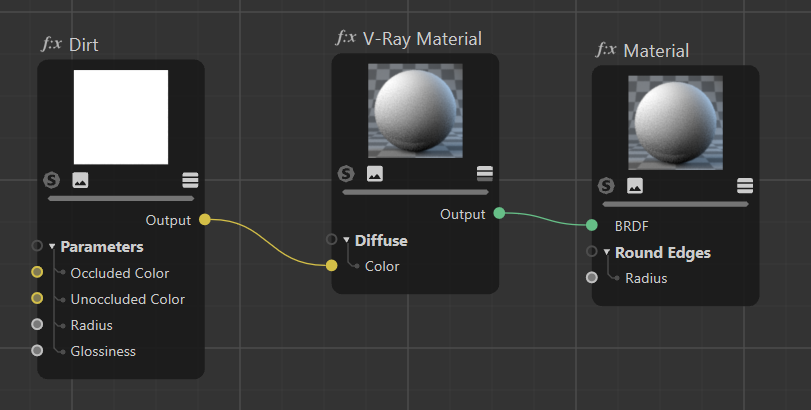
This page provides information about the Dirt node in V-Ray for Cinema 4D.
Overview
Parameters
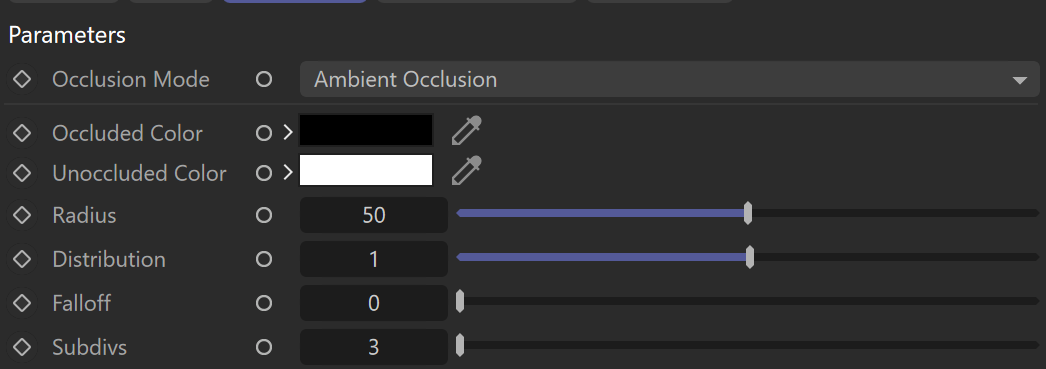
Occlusion Mode – Specifies the mode in which the dirt map is going to be calculated.
Ambient Occlusion – Normal ambient occlusion is calculated.
Reflection Occlusion (Phong, Blinn, Ward) – Reflection occlusion is used. The difference between Ambient and Reflection occlusion is basically in the direction in which rays are traced. With Ambient Occlusion, rays are traced in all directions uniformly, while with Reflection Occlusion the direction depends on the viewing direction (just as when calculating reflections) and the spread of the rays depends on the Reflection glossiness and BRDF type used.
Inner Occlusion – Allows the user to invert the effect with respect to surface normals - e.g. instead of crevices, open corners are shaded with the occluded color. This mode changes the direction of tracing the rays. When this mode is selected, the rays are traced inside the surface, otherwise, they are traced outside the surface.
Ambient + inner Occlusion – A combination of Ambient Occlusion and Inner Occlusion modes used for enhanced weathering effect.
Occluded Color – Specifies the color that is returned by the texture for occluded areas. You can also use a texture map for this parameter.
Unoccluded Color – Specifies the color that is returned by the texture for unoccluded areas. You can also use a texture map for this parameter.
Radius – Determines the amount of area (in scene units) where the Dirt effect is produced. You can also use a texture to control the radius. The texture intensity is multiplied by the radius to calculate the final radius at a given surface point. If the texture is white at a given surface point, the full radius value is used. If the texture is black, a radius of 0.0 is used.
Distribution – Forces the rays to gather closer to the surface normal. The effect is that the dirt area is being narrowed closer to the contact edges. For Ambient Occlusion, set this parameter to 1.0 to get distribution similar to the ambient lighting on a diffuse surface.
Falloff – Controls the speed of the transition between occluded and unoccluded areas.
Subdivs – Controls the number of samples that V-Ray takes to calculate the dirt effect. Lower values render faster but produce a more noisy result. Low Noise Threshold values in the Image Sampler clean the result further.
Bias
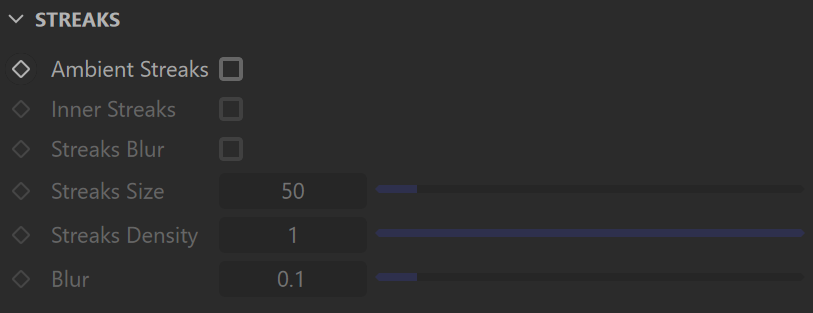
Streaks
Inner Streaks – Draws streaks across the Dirt effect respective to Inner Occlusion.
Streaks Blur – When enabled, blurs the dirt streaks.
Streaks Size – Controls the thickness of all streaks.
Streaks Density – Controls the density of the dirt streaks.
Blur – Controls the amount of blur applied to the dirt streaks.
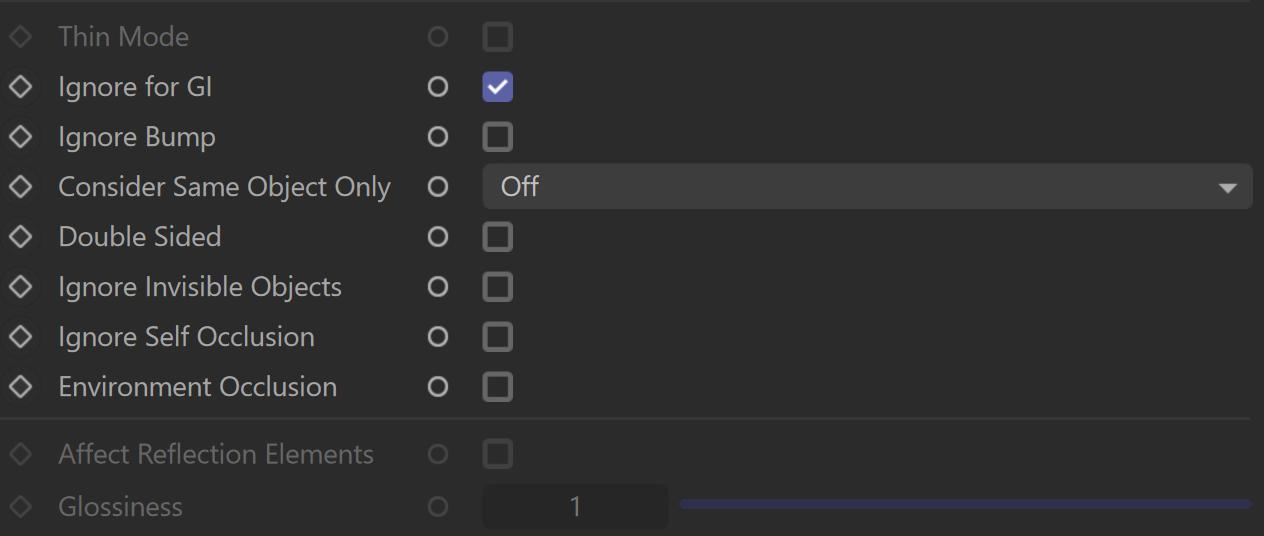
Thin Mode – When enabled, V-Ray Dirt enhances the look of thin surfaces by casting less dirt on them.
Ignore for GI – When enabled, the Dirt effect is ignored in GI calculations.
Ignore Bump – When enabled, bump maps are excluded from V-Ray Dirt computations.
Consider Same Object Only – When enabled, the Dirt affects only the objects themselves, without including contact surfaces and edges. If off, the entire scene geometry is participating for the final result.
Double Sided – When enabled, rays are traced both in the direction of the normal and in the opposite direction. This creates an effect where both crevices and edges are occluded.
Ignore Invisible Objects – When enabled, Dirt takes into account the opacity of the occluding objects. This can be used, for example, if you want to calculate ambient occlusion from opacity-mapped trees, etc. When disabled (the default), occluding objects are always assumed to be opaque. Note that working with correct opacity is slower since, in that case, Dirt must examine and evaluate the material on the occluding objects.
Ignore Self Occlusion – When enabled, the object does not occlude itself. It is occluded only by other objects in the scene.
Environment Occlusion – When enabled, Dirt includes environment contribution to the shading of unoccluded areas.
Affect Reflection Elements – When enabled, the ambient reflection affects the Reflection render elements. This can be used to create a reflection mask.
Glossiness – Controls the spread of the rays traced for Reflection Occlusion. A value of 1 means that just a single ray is traced (just like when tracing clear reflections); smaller values cause multiple rays to be traced in the approximate reflection direction.
Include/Exclude
Mode Include/Exclude – Allows you to disable/enable the calculation of the Dirt node for specific objects. Excluded object are be shaded by the Dirt node.
Add/Remove Object Link – Adds or removes a link from an object.
Object – Specifies the linked object.
Include Children – Enable this option to include all object's children in the dirt effect.
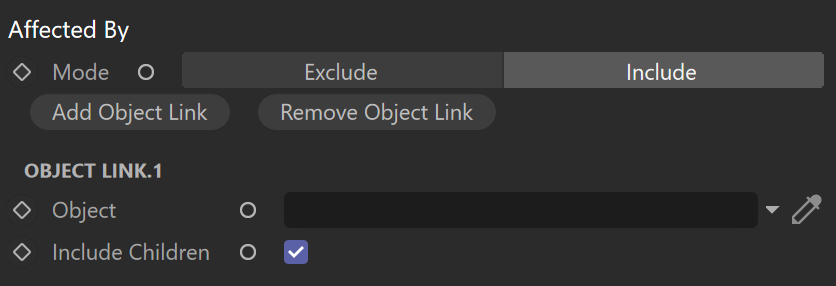
Affected By
Affected By – Specifies a list of objects which affect the calculation of the Dirt node. Excluded objects are considered "invisible" for the calculations of the Dirt effect - they don't produce the effect over other objects.
Add/Remove Object Link – Adds or removes a link from an object.
Object – Specifies the linked object.
Include Children – Enable this option to include all object's children in the dirt effect.