This page provides information about the Gaussian splats geometry in V-Ray for Cinema 4D.
Overview
3D Gaussian Splatting is a method for creating a 3D scene from images or videos. It requires several pictures of an object, each taken from a different angle. With Gaussian Splatting, the images are blended to produce a detailed, three-dimensional representation of the object. Instead of depicting the scene as a collection of meshes, a Gaussian splat represents the scene as a type of point cloud, where each point is a 3D Gaussian.
Gaussian splats help you create a realistic environment for your scenes.
This feature is not yet available in V-Ray GPU.
UI Path: ||V-Ray menu|| > Geometry > V-Ray Gaussians
Gaussian Splats Usage
Used as Extended Environment
One use of Gaussian splats is to represent an environment, typically generated from photos or videos of the scene.
There are advantages over the traditional environment maps, including proper parallax and view-dependent effects and the ability for Gaussian splats to occlude other objects in the scene.
For Gaussian splats to work as environments in V-Ray, the Affect Matte Surfaces option should be enabled, and the Affect Shadows option should usually be disabled.
See the example for more information.
On Other Matte Surfaces
To make the Gaussian splats rendered as part of the background, i.e., visible on other matte objects even if they are behind them. This is achieved by enabling the Affect Matte Surfaces option from the parameters.
See the example for more information.
Used as Individual Objects
Gaussian splats can also be used to represent smaller individual objects in the scene. In that case, the Affect Matte Surfaces option typically is turned off, and the Affect Shadows option is enabled. The latter is needed so that the Gaussian splats can cast proper shadows on other objects in the scene.
Note that the lighting and reflections are baked into the Gaussian splats objects, and therefore these objects are not affected by the scene lighting.
See the example for more information.
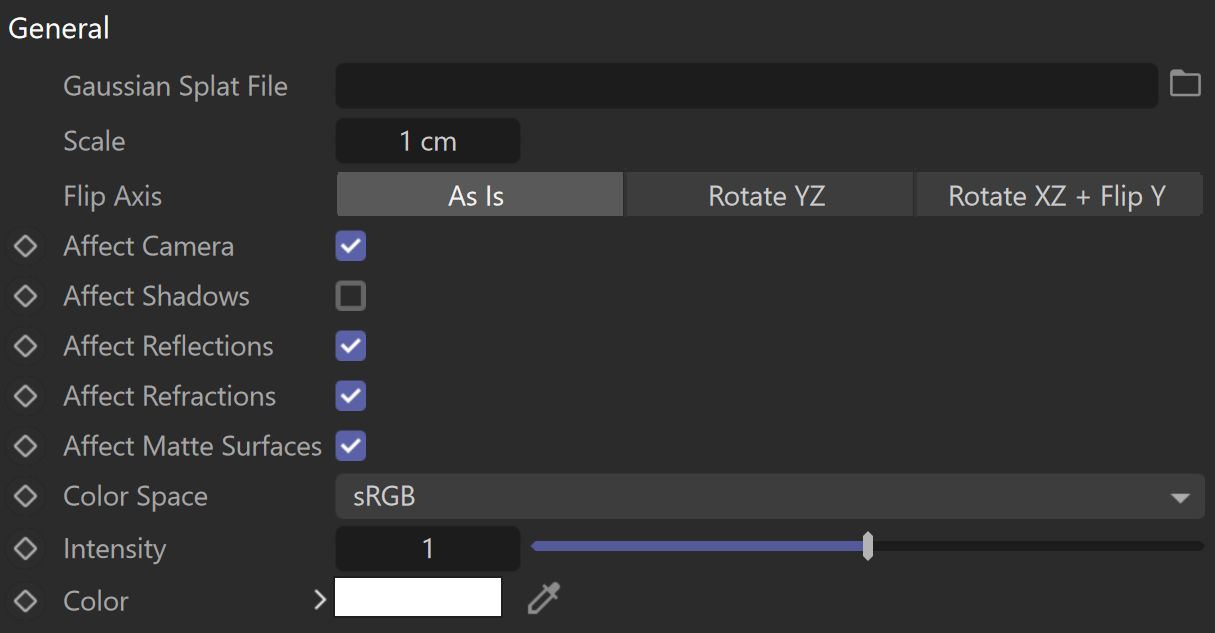
General
Gaussian Splat File – Loads the Gaussian splats file. Currently, only .ply files are accepted.
Scale – Scales the Gaussian splats up and down.
Flip Axis – Controls which axis is used as a vertical - the Y or Z axes for the loaded file. You can choose between:
As Is – No changes in the axes are applied.
Rotate YZ– Switches the Y and Z axes.
Rotate XZ + Flip Y – Switches the X and Z axes and flips the Y axis.
Affect Camera – Specifies whether the Gaussian splats should be visible to the camera. See the example.
Affect Shadows – When enabled, Gaussian splats block shadows from lights. When disabled, the Gaussian splats become transparent to shadow and GI rays. It is recommended that this option be turned off when using the Gaussian splats as environment or individual objects. See the example.
Affect Reflections – Specifies whether the Gaussian splats should be visible in reflections. See the example.
Affect Refractions – Specifies whether the Gaussian splats should be visible in refractions. See the example.
Affect Matte Surfaces – When enabled, Gaussian splats appear as part of the background on matte surfaces. It is recommended to enable this for Gaussian splats used as an environment and disable it for Gaussian splats used as individual objects. See the example.
Color Space – Specifies the color space of the data in the Gaussian splats file.
Default – Takes the current color correction that is set in Maya. That means it does not change the colors.
To read the Gaussian splats file as it was written, select the respective input color space - sRGB, ACEScg, or Raw.
Intensity – Increases or decreases the Color multiplier for the Gaussian splat.
Color – Specifies a filter color for the splat. By default, the Color is white, which does not affect the splat. See the example.
Preview
Type – Specifies how the Gaussian splats are rendered in the viewport.
Disabled – The Gaussian splats are not visible in the viewport and cannot be selected from there. You can select them from the Object Manager only.
Bounding Box – The Gaussian splats are represented by a bounding box.
Limited Point Cloud – This is the default mode. The Gaussian splats are represented by cloud points in a bounding box. The bounding box is restricted by the Point Radius and the Point Count.
Unlimited Point Cloud – The Gaussian splats are represented by cloud points in a bounding box. The bounding box is restricted only by the Point Radius.
Point Radius – Determines the radius around the Gaussian geometry, where the cloud points are visible in the viewport. This option works when the Type is set to Limited/Unlimited Point Cloud.
Point Count – Determines the exact number of points to be visible in the viewport. This option works when the Type is set to Limited/Unlimited Point Cloud.
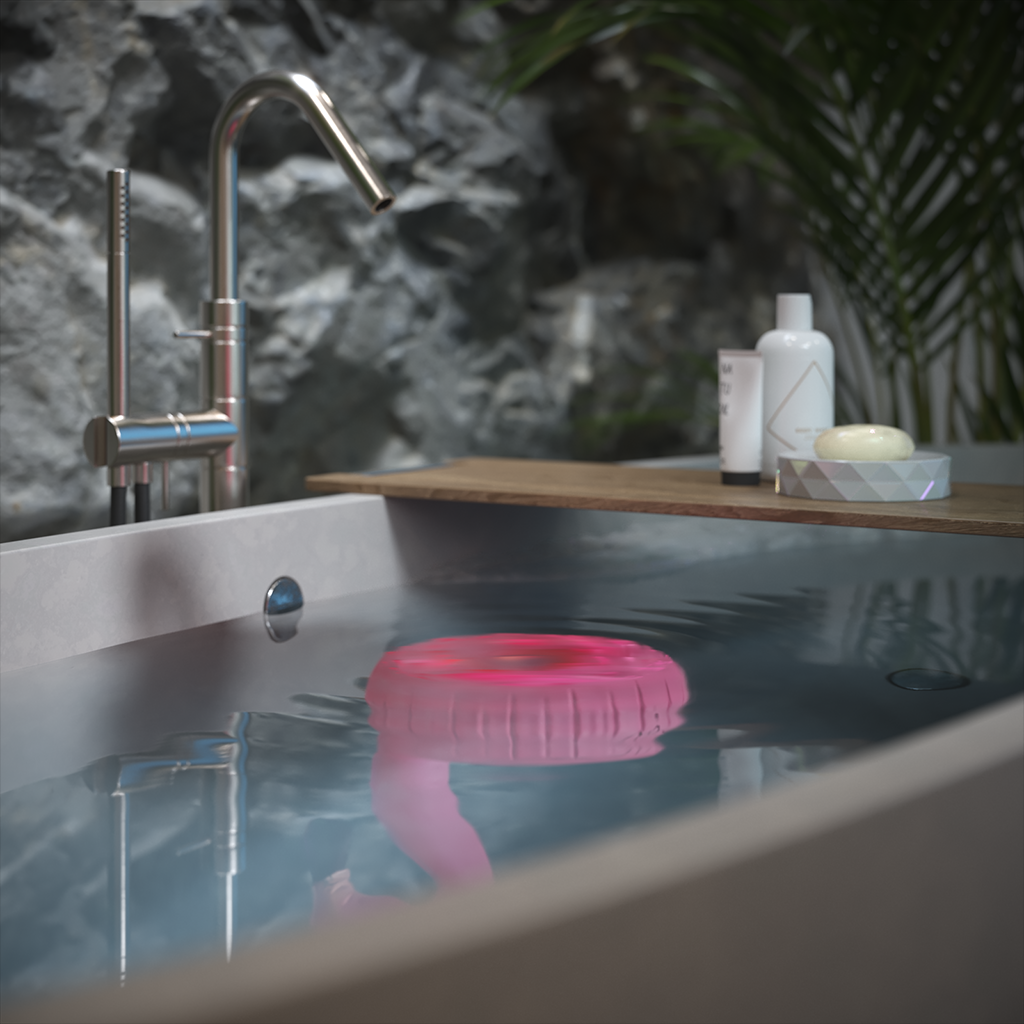
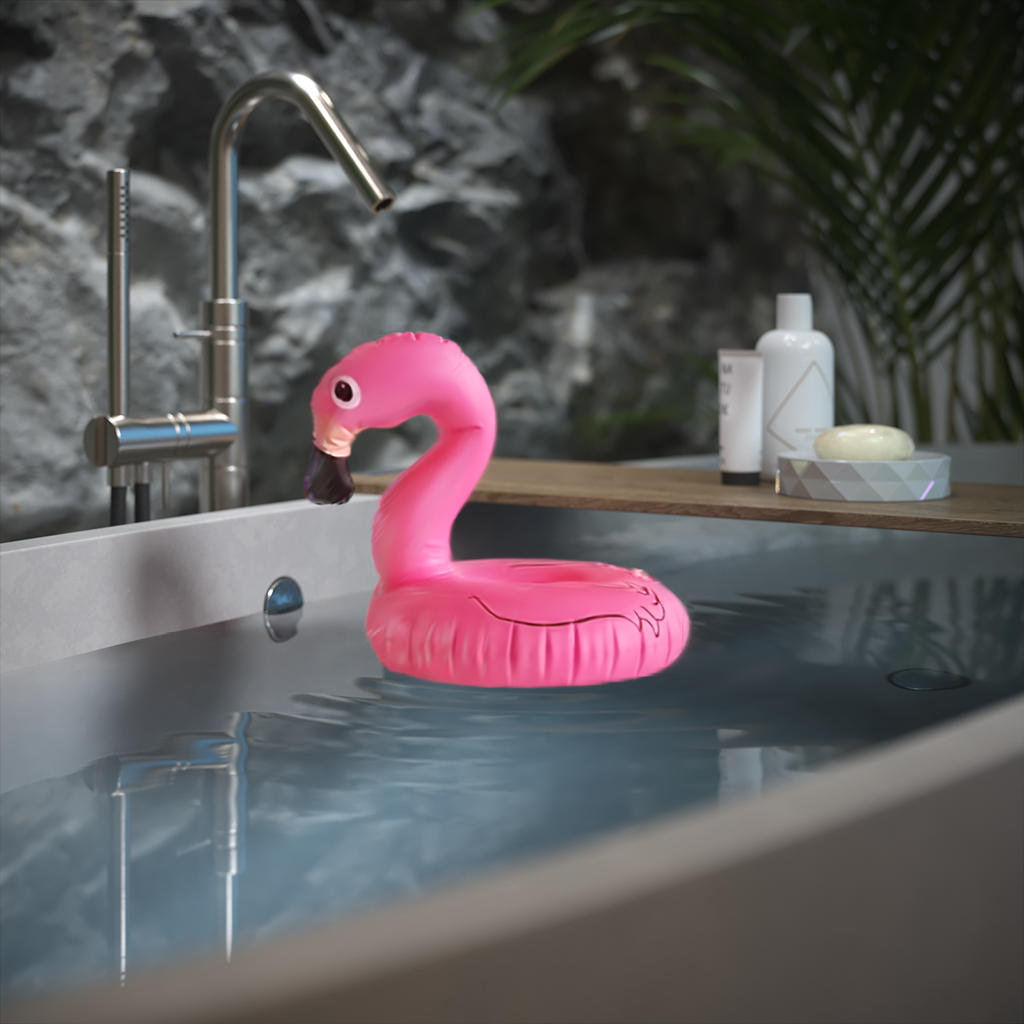
Example: Affect Camera
The Gaussian Splats object can be hidden from the camera, like any other geometry object in the scene, by using the Affect Camera option.
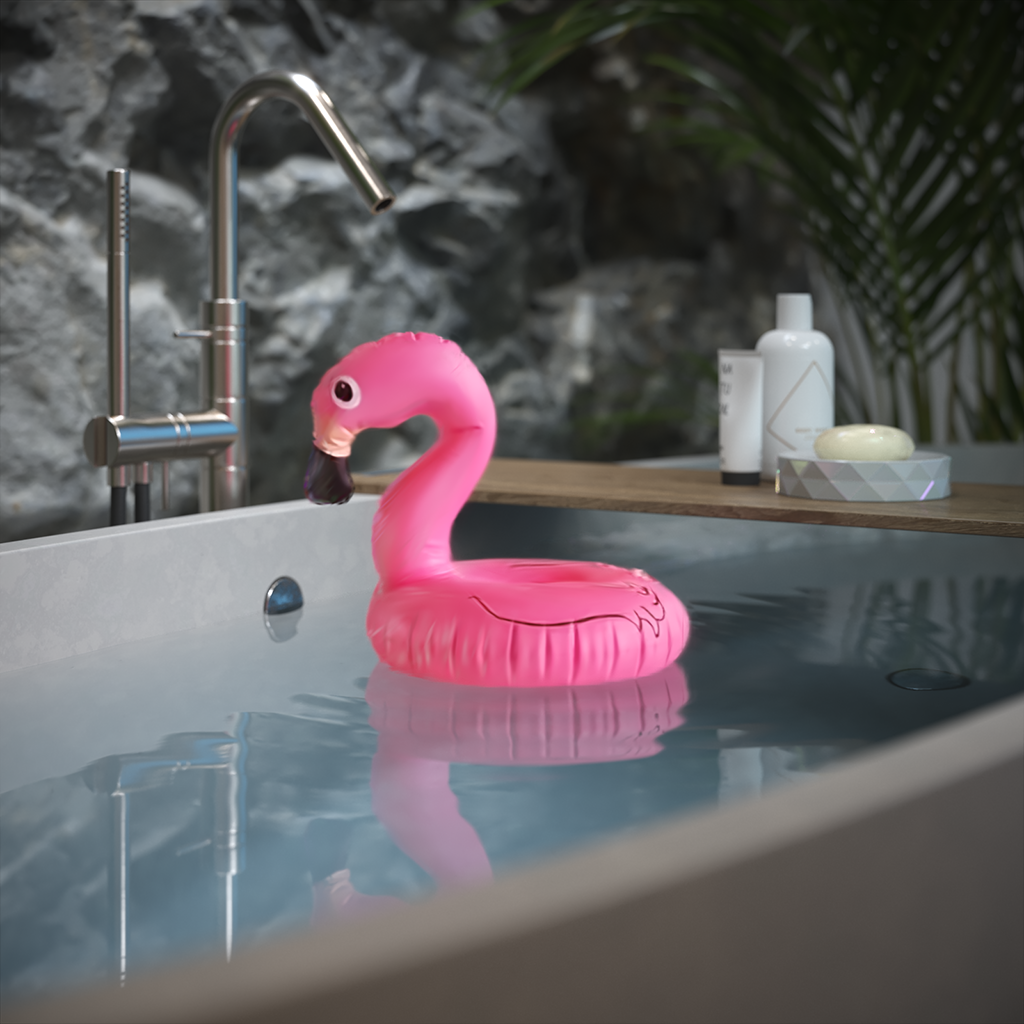
Example: Affect Reflections
The Affect Reflections option controls if the Gaussian splats object is reflected in other objects in the scene.
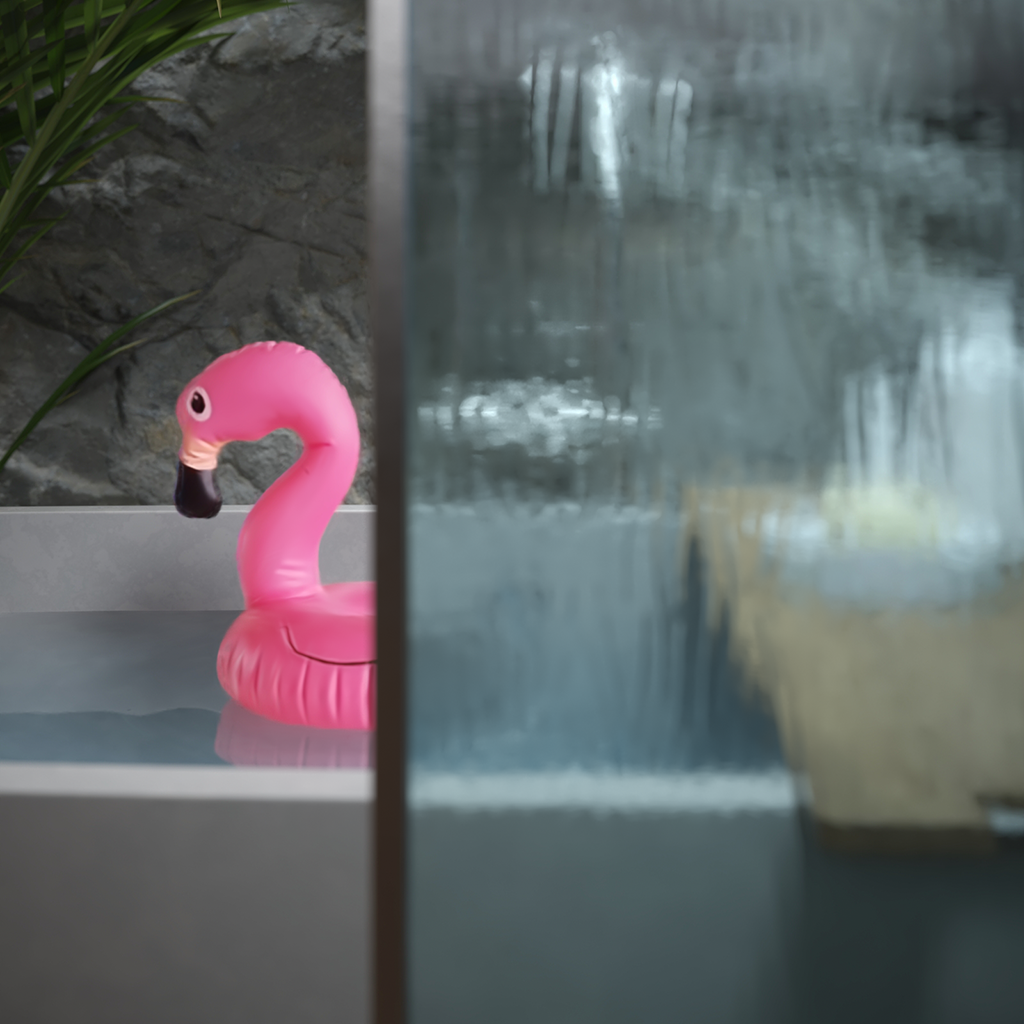
Example: Affect Refractions
The Affect Refractions option makes the Gaussian splats object seen by other objects in the scene that exhibit refractive properties.
Example: Affect Shadows
This example shows how the pink flamingo can produce shadows when the Affect Shadows option is enabled, and doesn't block light when it's not.
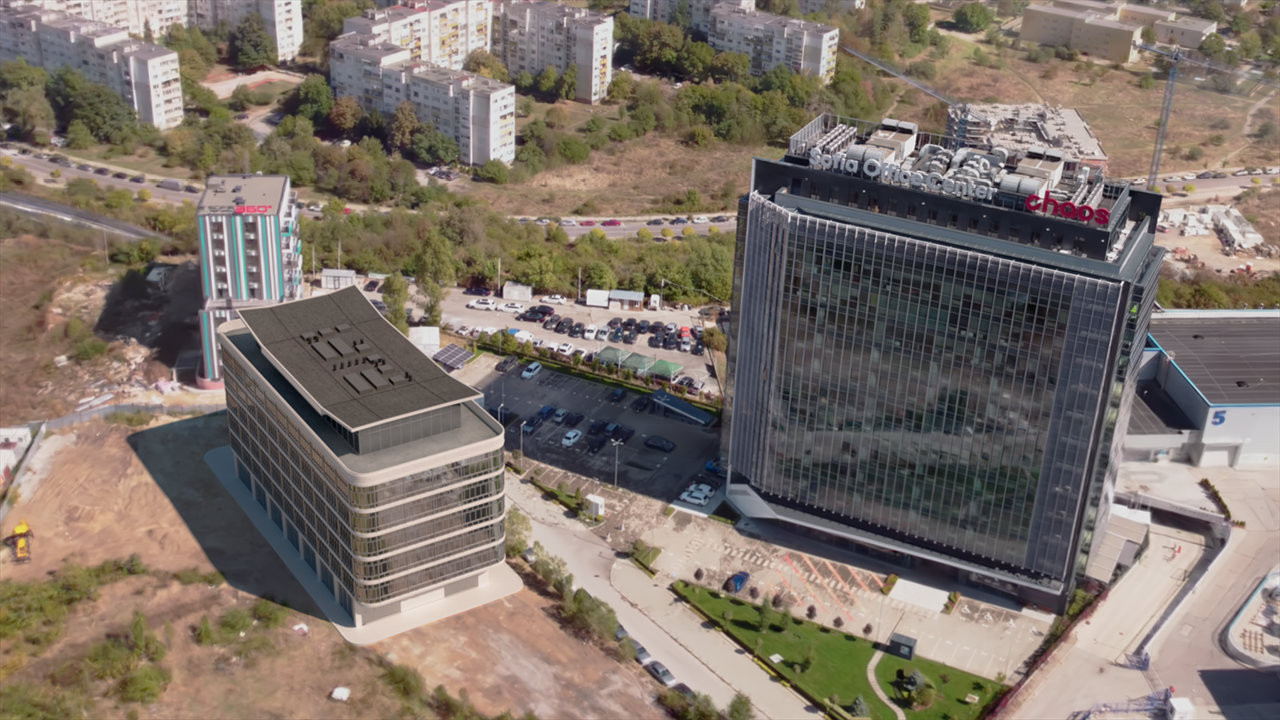
Example: Affect Matte Surfaces
In this example, the Gaussian splat is used as an environment. The left building in the rendering that casts shadows over the plane, is a Cosmos asset (mesh).
When the Affect Matte Surfaces option is enabled, the Gaussian splat is considered as background and receives shadows from the casting object.
Example: Color
The Color shown on each render as a box is used as a filter for the original Gaussian splat diffuse color.