The Dome light is a type of VRayLight that provides somewhat even lighting to a scene.
Overview
A Dome light is a type of VRayLight that shines inward at the scene as if from a spherical or hemispherical light source outside the scene extents. This light is frequently used for Image-Based lighting using panoramic HDR images used as environments.
Sample Use
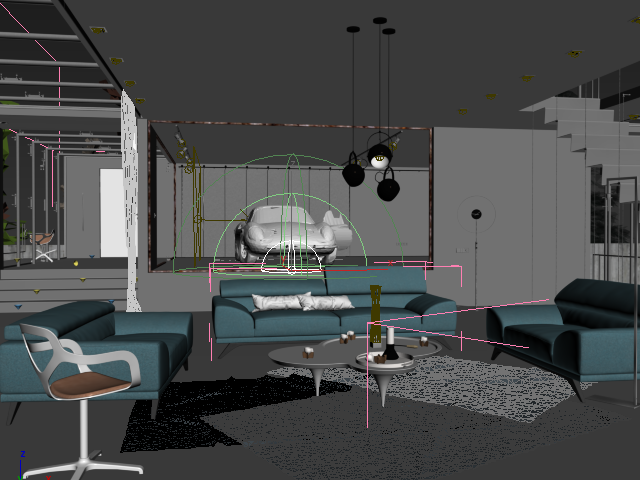
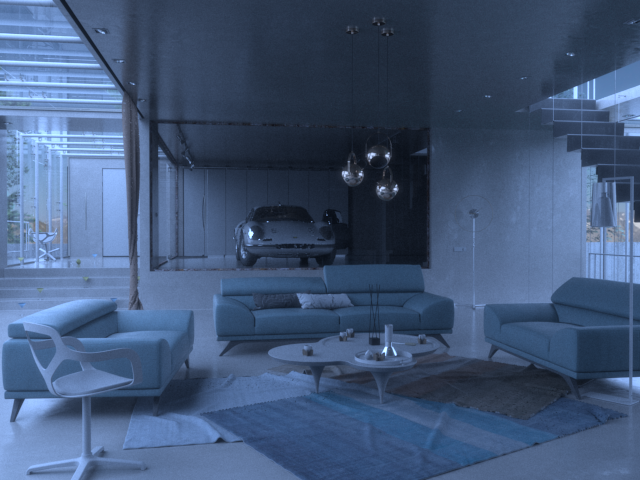
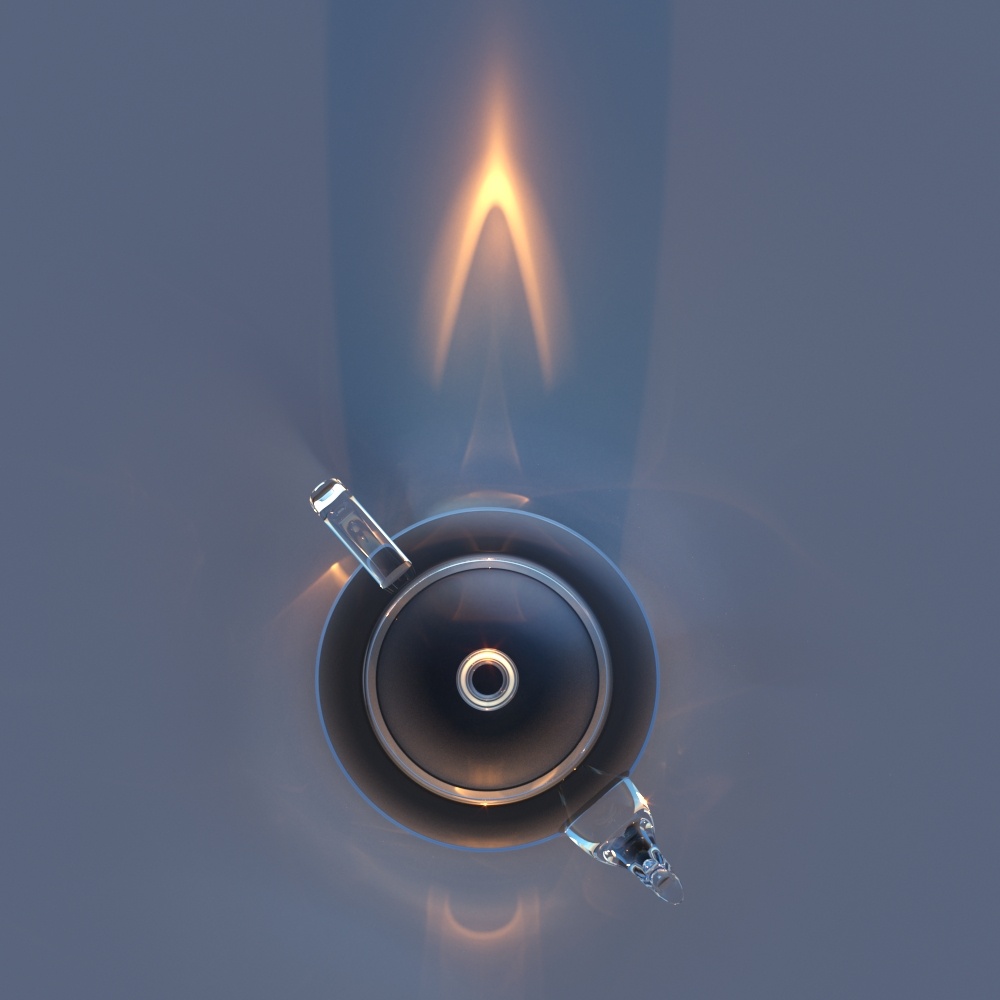
In the images below, a dome light is positioned and is the only source of light in the render.
Dome light in the scene
Rendered image of Dome lighting
General Rollout
On – Turns the VRayLight on and off.
Type – Specifies the shape and function of the light:
Plane – The VRayLight takes the shape of a planar rectangle. See the Plane, Disc, Sphere Light page.
Sphere – The VRayLight has the shape of a sphere. See the Plane, Disc, Sphere Light page.
Dome – The VRayLight emanates from a virtual hemispherical or spherical dome larger than the scene extents regardless of the Dome light icon's size. The light emanates from above the Z-axis of the light, where the light source actually surrounds the entire scene. Additional parameters specifically for this light are under the Dome light rollout. A dome light is commonly used with a texture to produce image-based lighting.
Mesh – Allows the usage of any mesh object as the shape of the light. See the Mesh Light page.
Disc – The VRayLight takes the shape of a planar disc. See the Plane, Disc, Sphere Light page.
Targeted – When enabled, a separate target object is attached to the light source. This target object can be moved separately from the light source, making it easier to point the light within the scene. The value specifies the distance from the light source to the target. While any type of VRayLight can have a target, the target is truly useful only with Plane and Disc lights. This option can be changed only on the Modify tab.
Radius – The radius of the Finite dome light. This option is only available when the Finite dome option is enabled.
Proj height – Offsets the height of the environment map projection. This option is only available when the Finite dome option is enabled.
Ground blend – Controls the transition between the ground plane and the hemispherical upper part of the Finite dome. A value of 0.0 means a sharp transition, whereas a value of 1.0 means that the dome morphs into a sphere. Intermediate values blend between the two. This option is only available when the Finite dome option is enabled.
Units – Specifies the light units. Using correct units is essential when you work with the VRayPhysicalCamera. The light automatically takes the scene's unit scale into consideration to produce the correct result for the scale you are working with. The possible values are:
Default (image) – The color and multiplier directly determine the visible color of the light without any conversion. The light surface appears with the given color in the final image when seen directly by the camera (assuming there is no color mapping involved).
Luminous power (lm) – Total emitted visible light power measured in lumens. When this setting is used, the intensity of the light does not depend on its size. A typical 100W incandescent light bulb emits about 1500 lms of light.
Luminance (lm/m²/sr) – Visible light surface power measured in lumens per square meter per steradian. When this setting is used, the intensity of the light depends on its size.
Radiant power (W) – Total emitted visible light power measured in watts. When using this setting, the intensity of the light does not depend on its size. Keep in mind that this is not the same as the electric power consumed by a light bulb for example. A typical 100W light bulb only emits between 2 and 3 watts as visible light.
Radiance (W/m²/sr) – Visible light surface power measured in watts per square meter per steradian. When this setting is used, the intensity of the light depends on its size.
Multiplier – Multiplier for the light color, and also the light intensity for some Units settings.
Mode – Specifies the mode in which the color of the light is determined:
Color – When selected, the Color swatch specifies the color of the light rays and of the light source itself when visible in renderings. For Units settings other than Default (image), this color is normalized so that only the color hue is used.
Temperature – When selected, the color of both light rays and the light source itself is specified by the Temperature value expressed in Kelvin.
Map – Enables the use of a texture for the light surface. The button selects the map to use. The texture intensity is also affected by the Multiplier value.
Dome Light Rollout
The Dome light supports texture maps that determine the amount of light coming from each direction on the virtual dome hemisphere based on HDR images. For more information, see The IBL example below.
Spherical (full dome) – When enabled, the dome light covers the entire sphere around the scene. When disabled (the default), the light covers a hemisphere only.
Finite dome – When enabled, changes the way the Dome Light is calculated so that it emulates a dome with a physical size in the scene. This is useful when we need to introduce some parallax for the background when moving the camera and also to project the light texture on the ground. The finite dome consists of a ground plane, a hemispherical upper part and a transition area between the two. For more information, see the How to embed an object in place into an HDRI example below.
Affect alpha – When enabled, the virtual sphere on which the dome texture is mapped is visible as a solid object in the rendered image's alpha channel.
Lock texture to icon – When enabled, the texture placement on the Dome light is controlled by the rotation of the Dome light icon in the scene.
Ray Dist – Specifies the method of determining the maximum distance to which shadow rays are going to be traced.
None – Does not specify a maximum distance.
Explicit – The maximum distance is determined by the Distance parameter.
Photon emission
Target radius – Defines a sphere around the light icon where photons are shot when caustics are used. The Dome light gizmo draws the area in the viewport for ease of use.
Emit radius – Defines a sphere around the light icon from which photons are shot towards the target radius area. The Dome light gizmo draws the area in the viewport for ease of use.
Note: Using a far clipping plane on your camera hides the light dome from being visible in the final render.
See the Photon emission example below for more information.
Adaptive dome – Speeds up the rendering by optimizing the sampling algorithm for the dome light.
Example: How to embed an object in place into an HDRI
Example: Finite Dome
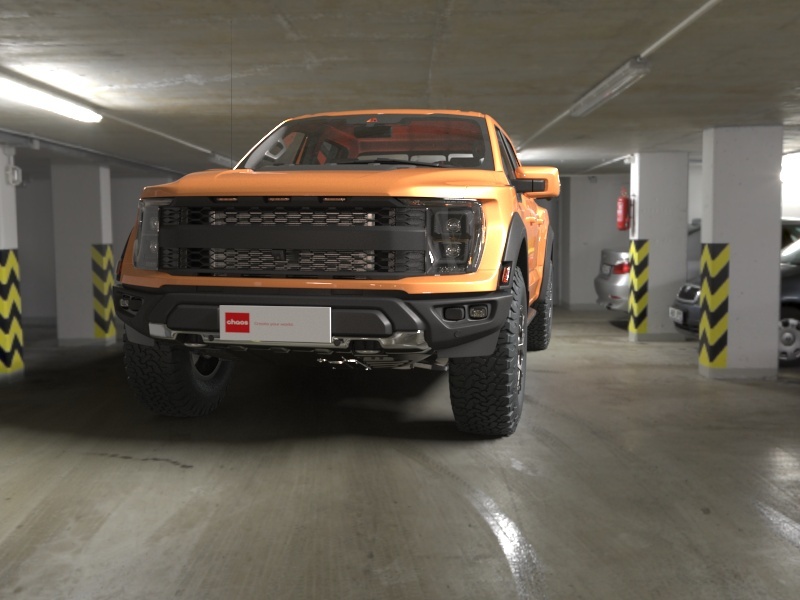
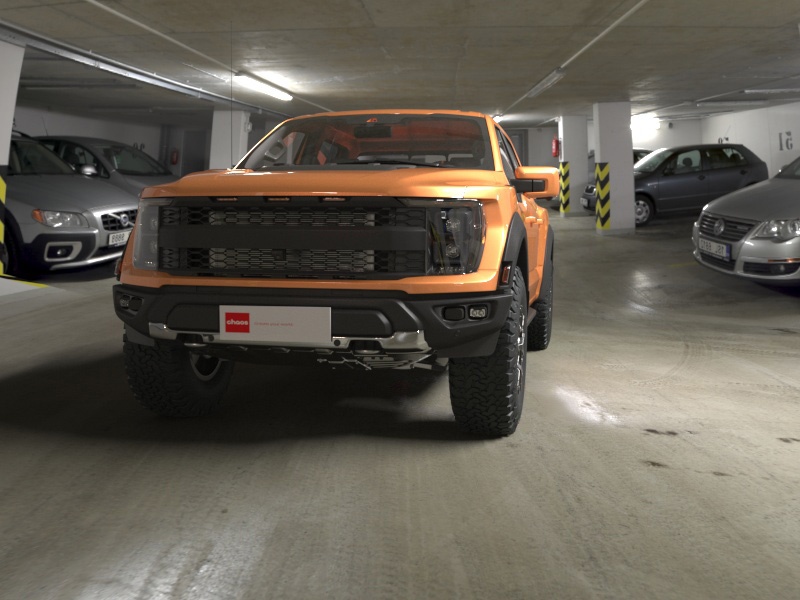
This example shows how enabling the Finite dome option adds depth to a scene's background and augments the lighting. It also adds a ground plane. With the Finite dome enabled, the object looks as if it is actually placed in the background scene.
Example: Photon Emission
The example below shows how increasing the Emit Radius and Target Radius parameters affect the caustics effect. The Dome light gizmo shows the area where the caustics are generated. Higher Emit Radius value makes the effect more spread out and blurry.
Target Radius = 20, Emit Radius = 25
Target Radius = 15, Emit Radius = 20
Target Radius = 40, Emit Radius = 45
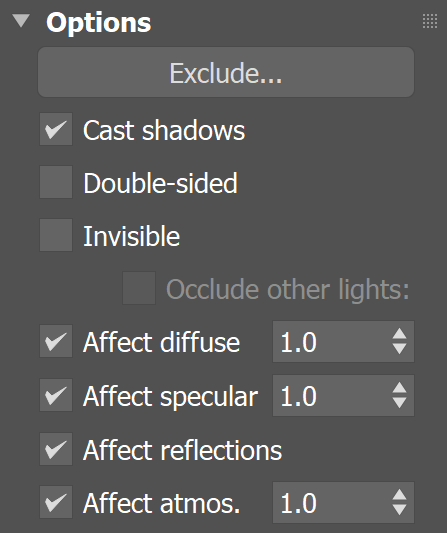
Options Rollout
Exclude – Opens the 3ds Max Exclude/Include window for selection of objects to be excluded or included in illumination and/or shadow-casting for this light.
Cast shadows – When enabled (the default), the light casts shadows. Turn this option off to disable shadow casting for the light.
Double-sided – This option has no effect for Dome light sources.
Invisible – Controls whether the shape of the light source is visible in the rendered image. When disabled, the light source is rendered in the color specified by the Color or Temperature setting in the Intensity rollout. This option only affects the visibility of the light when seen directly by the camera or through refractions. The visibility of the light with respect to reflections is controlled by the Affect reflections option.
Note: Regardless of whether this option is enabled, the light source still is taken into account by Global Illumination calculations, which might cause secondary GI rays to be blocked by or bounced off the light's surface. To make the light completely invisible to GI, place a VRayColor texture map into the light's texture slot and set the alpha value for the VRayColor map to 0.0.
Affect diffuse – Determines whether the light affects the diffuse portion of the materials. The Multiplier value on the Intensity rollout controls the light's contribution to the diffuse portion of the materials.
Affect specular – Determines whether the light affects the specular portion of the materials. The Multiplier value on the Intensity rollout controls the light's contribution to specular reflections.
Affect reflections – Specifies whether the light source appears in reflections.
Affect atmospherics - Specifies whether the light influences the atmospheric effects in the scene. The value determines the amount of involvement.
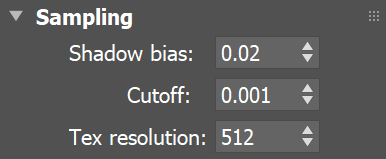
Sampling Rollout
Shadow bias – This value moves the shadow toward or away from the shadow-casting object (or objects). Lower values move the shadow toward the object(s), while higher values move it away. If this value is too low, shadows can "leak" through places they shouldn't, produce moire patterns or make out-of-place dark areas on meshes. If this value is too high, shadows can "detach" from an object. If the value is too extreme in either direction, shadows might not appear in the rendering at all.
Cutoff – Specifies a threshold for the light's intensity, cutting off the light's effect on a surface when it falls below this value. Lights lose intensity due to GI bouncing or decay. When light hits a surface but its intensity falls below the cutoff, the effect of the light on that surface is not computed. This can be useful in scenes with many lights, where you want to limit the effect of the lights to some distance around them or reduce computations (and thus reduce rendering time) where the light's impact is negligible. Larger values limit the light's effect on objects to a smaller area around the light source, while lower values increase the range of the light's effect. If you specify 0.0, there is no cutoff and the light is calculated for all surfaces regardless of intensity loss. The default value is 0.001. This parameter is not available when the renderer is set to GPU.
Tex resolution – Specifies the resolution at which the texture is resampled for importance sampling.
Viewport Rollout
Enable viewport shading – When enabled, the effect of the light is visible in the viewport.
Viewport wire color – When enabled, the light's wireframe is displayed in the specified color in viewports.
Icon text – Enables or disables the preview of the light name in the viewport.
Texmap preview – If a texture is used to drive the light, enabling this shows the texture in the viewport. This option is grayed out if your 3ds Max viewport is configured to use Nitrous viewport driver. To enable, switch to the direct3D viewport.
Notes
- To enable the preview of the Dome Light illumination through the Nitrous preview in the viewport, the following windows variable has to be manually created VRAY_DOME_VIEWPORT=1