This page provides information on the V-Ray Aerial Perspective Atmospheric Effect.
Overview
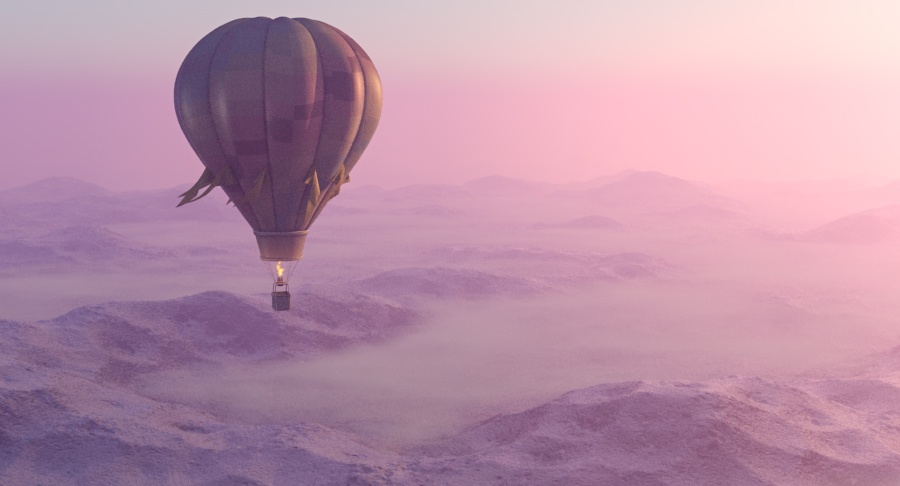
The VRayAerialPerspective atmospheric effect simulates the aerial perspective effect, the result of viewing objects from a distance through the Earth's atmosphere. The effect is similar to fog or haze. This atmospheric effect works together with VRaySun and the VRaySky to calculate an approximation to the aerial perspective effect.
While this effect renders faster than VRayEnvironmentFog and produces a similar result, it is only an approximation. For example, it does not produce volumetric shadows.
Parameters
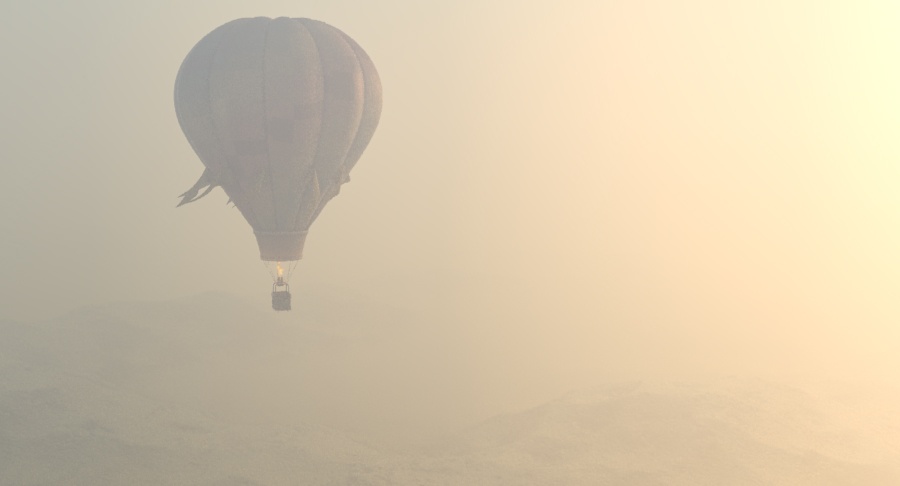
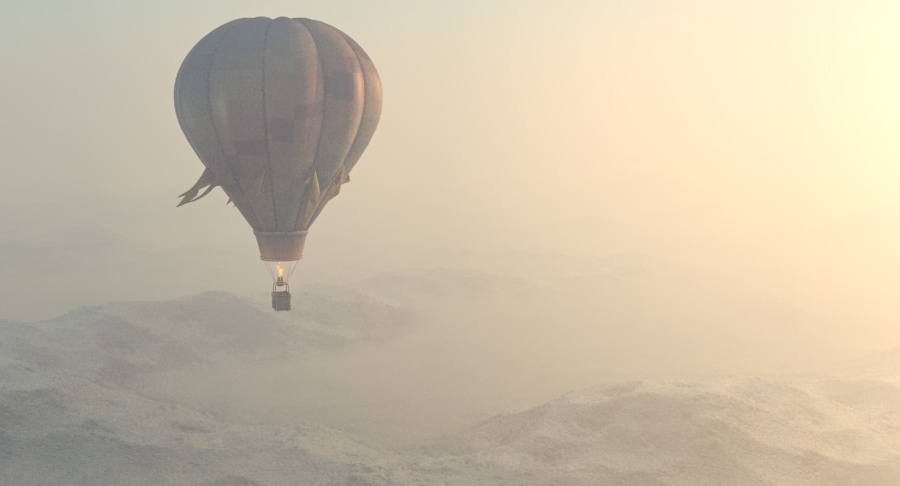
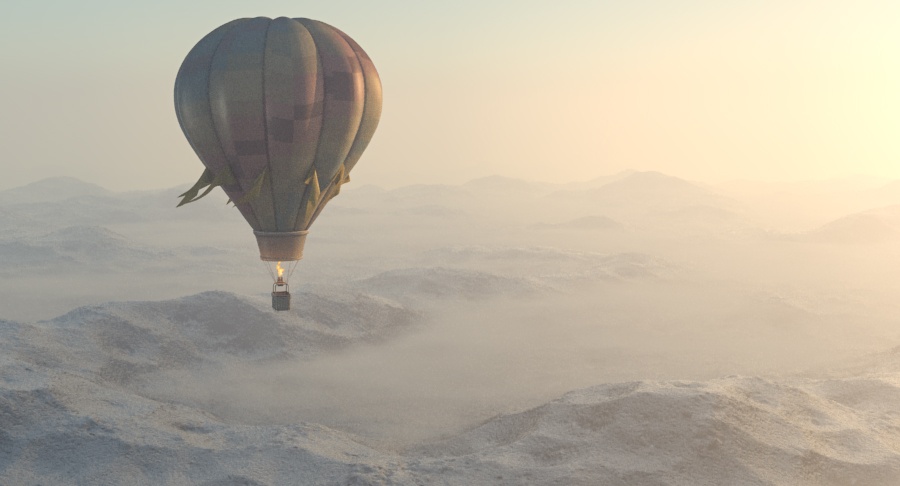
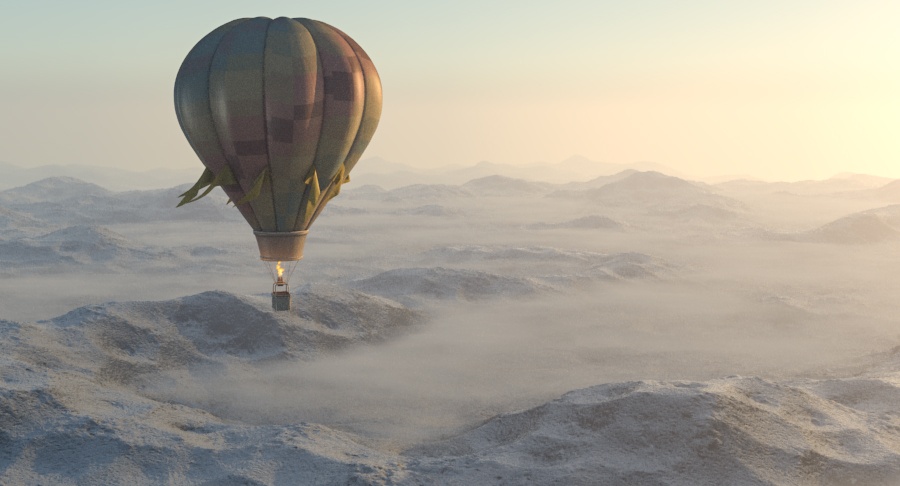
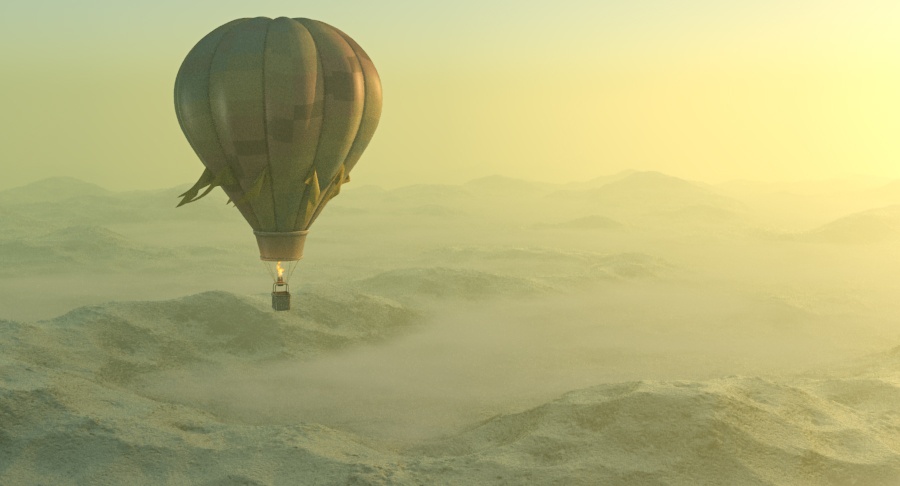
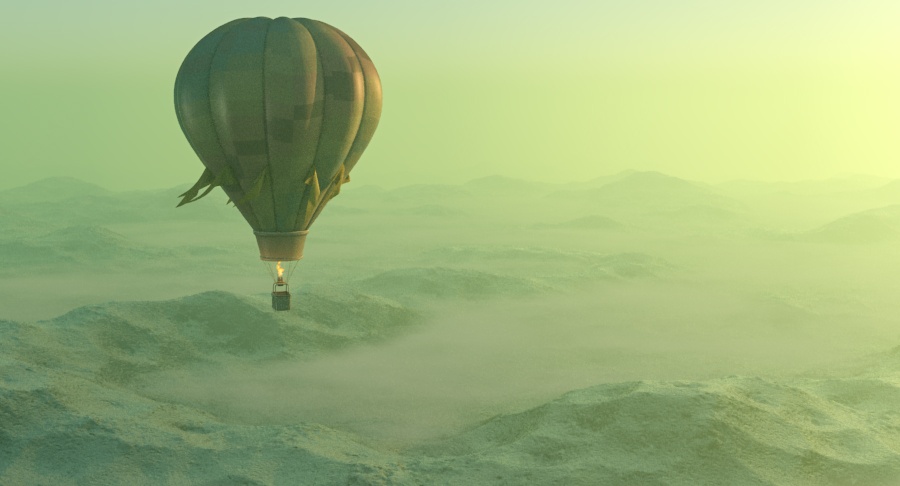
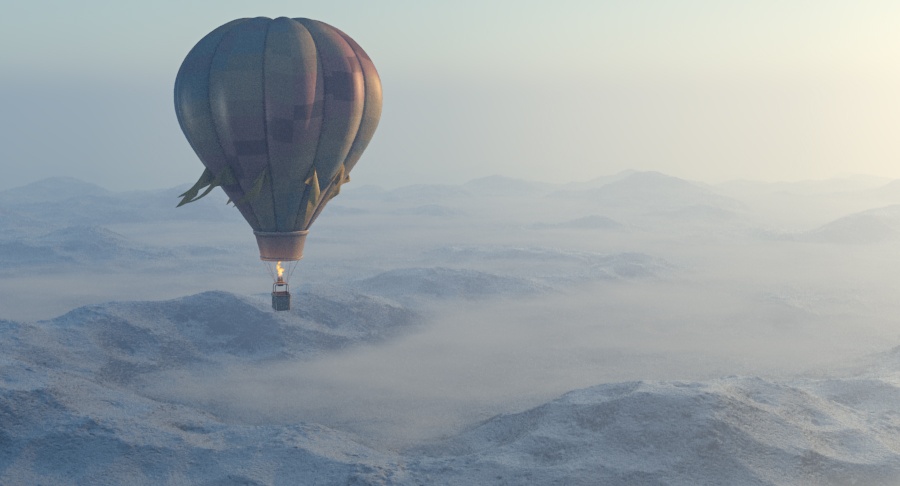
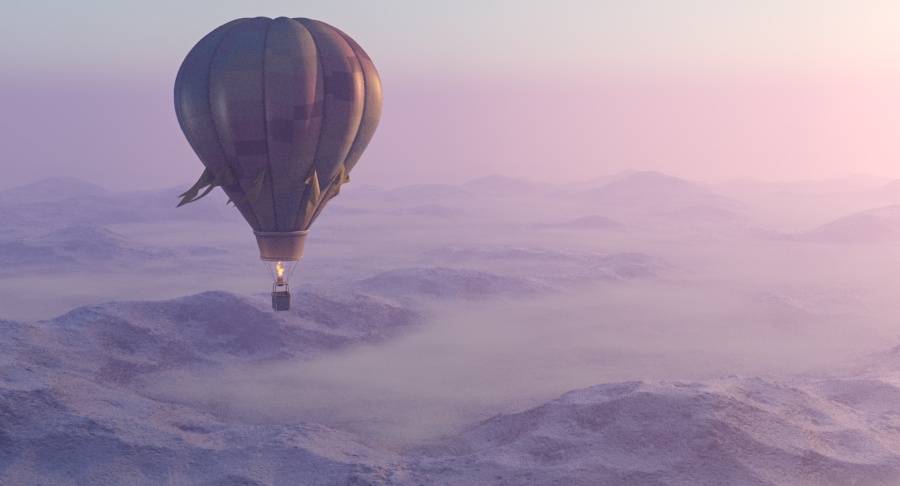
Visibility range (in meters) – Specifies the distance at which the fog has absorbed 90% of the light coming from objects behind it. Lower values make the fog appear denser, while larger values reduce the effect of the aerial perspective. The value is in meters and is converted internally based on the currently selected 3ds Max units. For more information, see the Visibility Range example below.
Atmosphere height (in meters) – Specifies the height of the atmosphere layer in meters. Lower values can be used for artistic effects. The value is in meters and is converted internally based on the current 3ds Max units. For more information, see the Atmosphere Height example below.
Inscattered light intensity – Controls the amount of sunlight scattered from the atmospheric effect. The default value 1.0 is physically accurate; lower or higher values could be used for artistic purposes.
Affect environment rays – When disabled, the atmospheric effect is applied only to camera rays that hit actual objects, but not to rays that hit the VRaySky. This option is disabled by default because the VRaySky texture already takes into account the amount of scattered sunlight. However, it is possible to enable this option for artistic effects, especially with low visibility ranges. For more information, see the Affect Environment Rays example below.
Affect background – Specifies whether the effect is applied to camera rays that hit the background (if a background other than VRaySky is used). This option is enabled by default, but some interesting effects are possible when disabled.
Filter color – Affects the color of the inscattered light. For more information, please see the Filter Color example below.
Primary visibility – When disabled, the aerial perspective effect is only seen by secondary rays (e.g. refractions, reflections, etc.).
Affect alpha – Specifies whether the aerial perspective affects the Alpha channel.
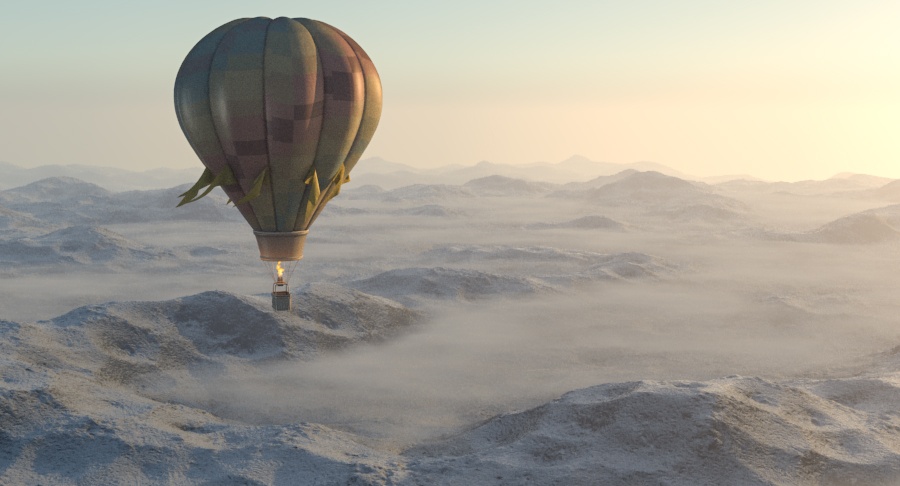
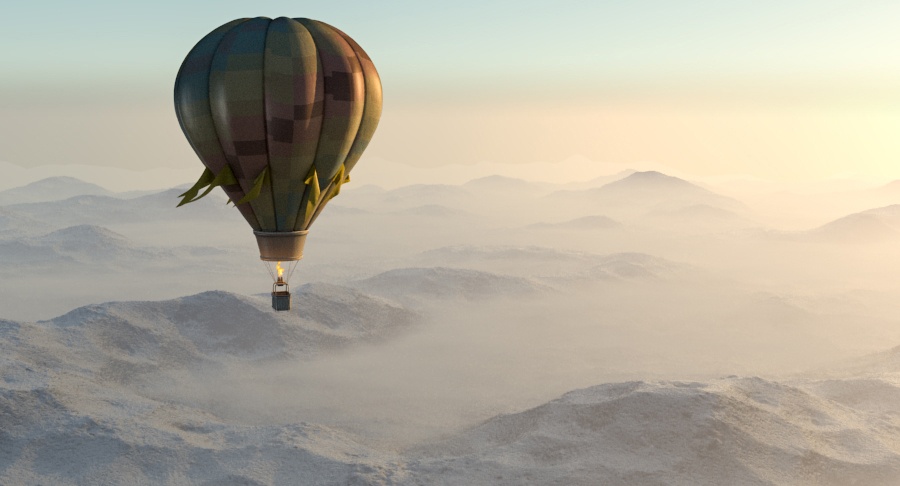
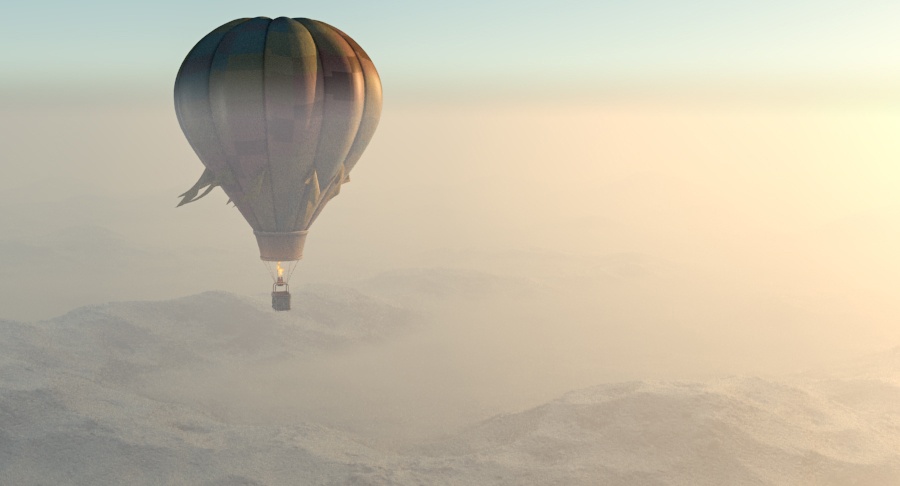
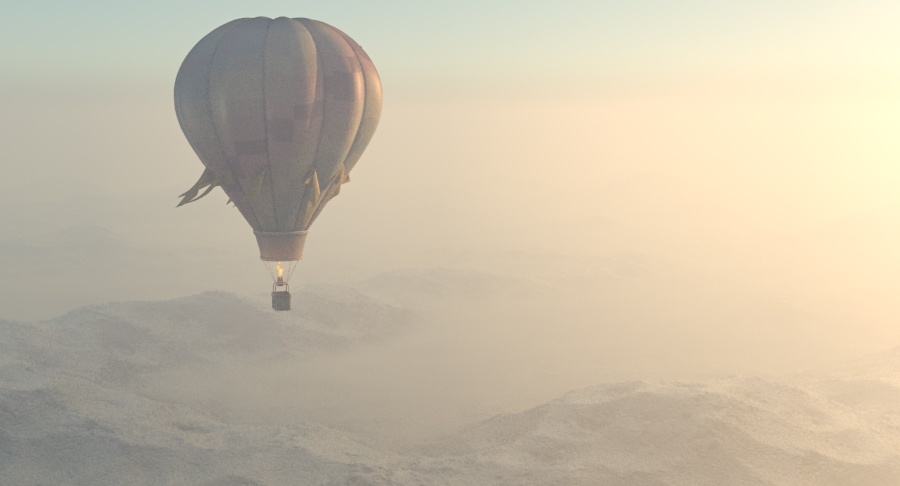
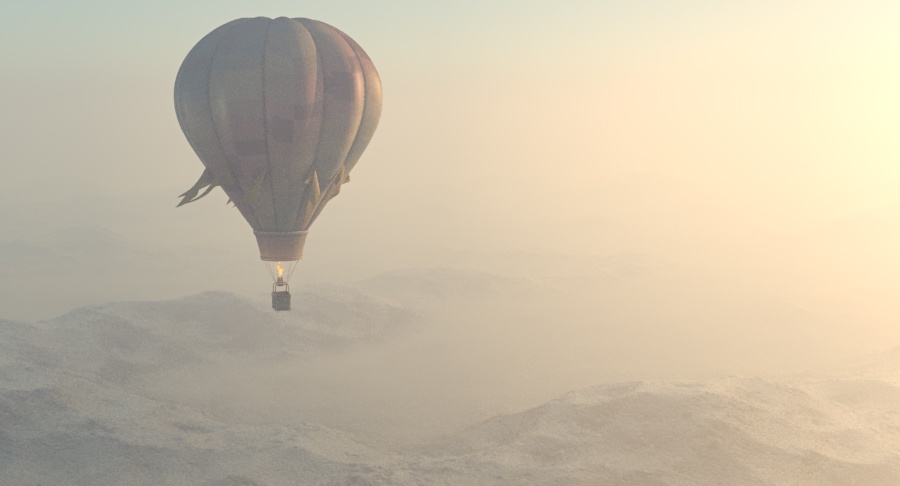
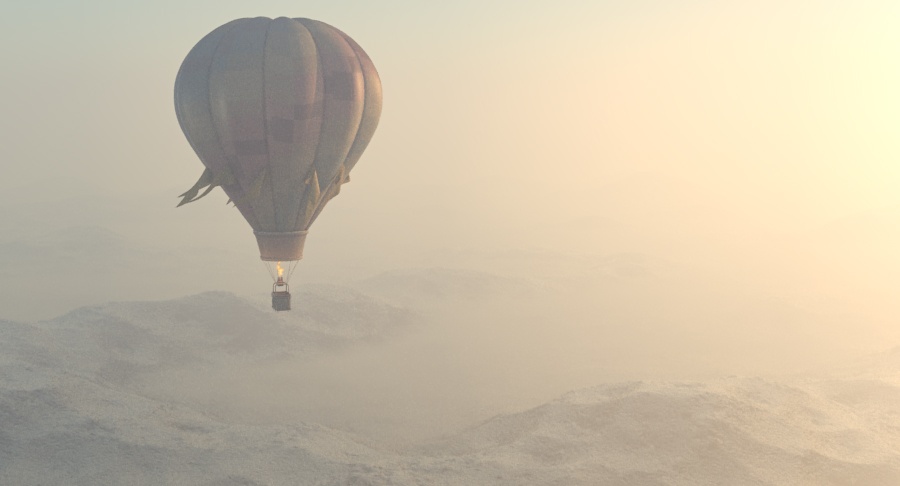
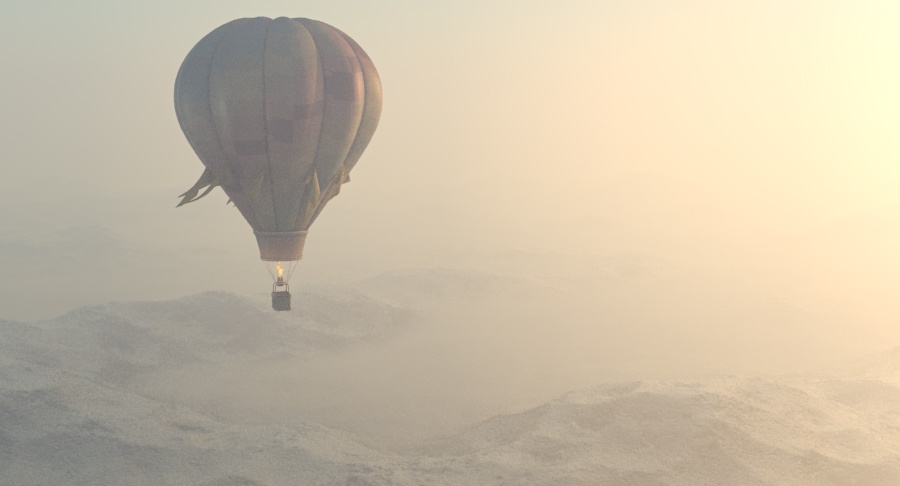
Example: Visibility Range
This example demonstrates the effect of the Visibility range parameter. Lower values make the fog appear denser, while larger values reduce the effect of the aerial perspective. The value is in meters and is converted internally based on the currently selected 3ds Max units.
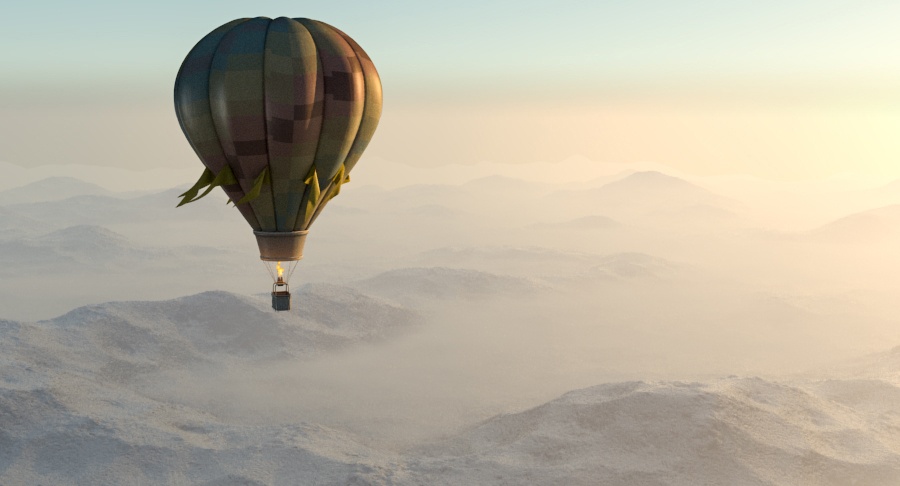
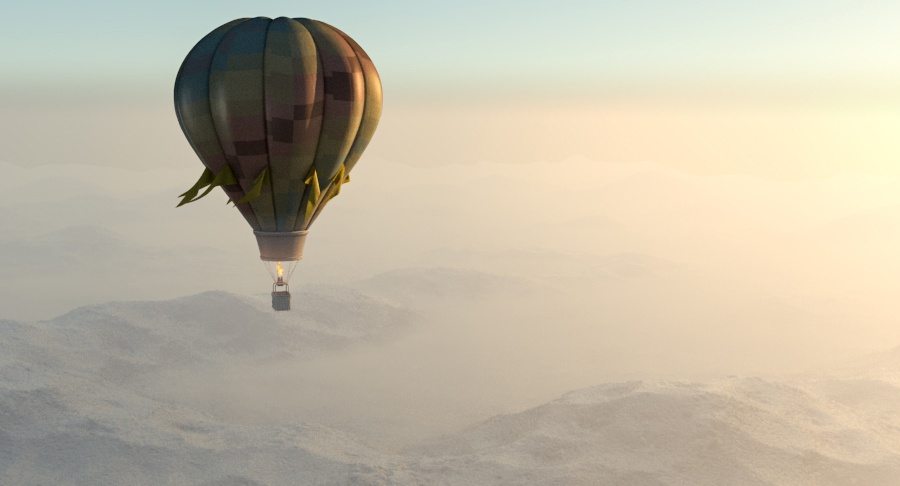
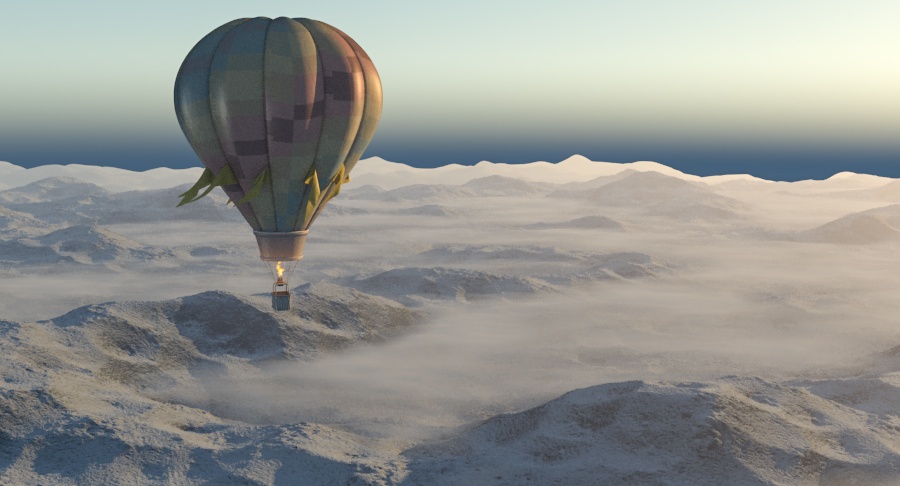
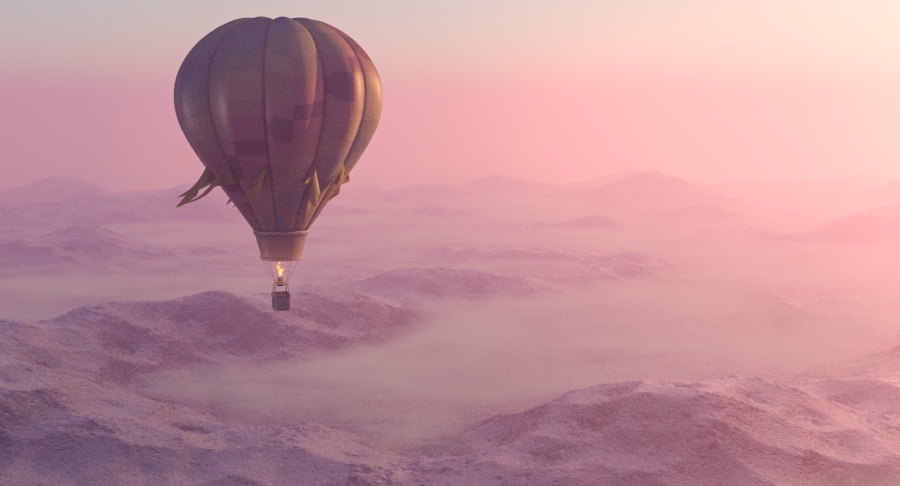
Example: Atmosphere Height
This example demonstrates the effect of the Atmosphere height parameter. Lower values can be used for artistic effects. The value is in meters and is converted internally based on the current 3ds Max units. Note that this is dependent on the scene scale, and in our example relatively low values were sufficient due to the small scene scale.
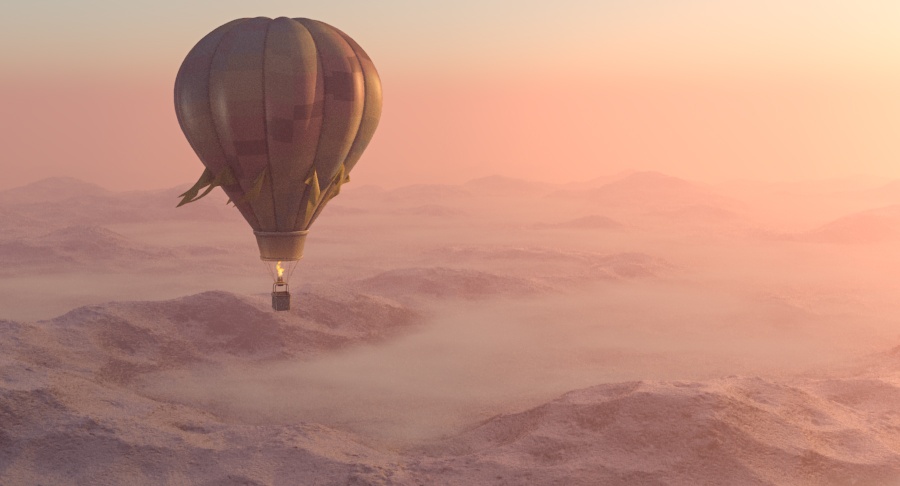
Example: Affect Environment Rays
When disabled, the atmospheric effect is applied only to camera rays that hit actual objects, but not to rays that hit the VRaySky.
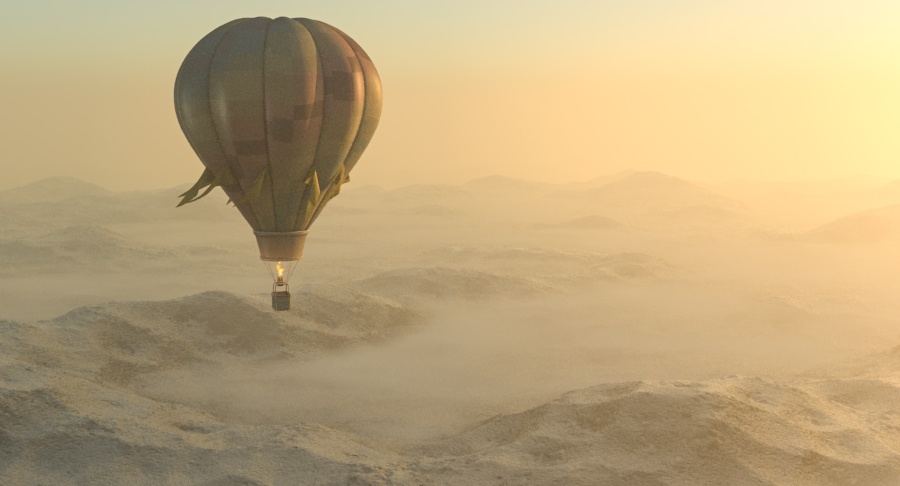
Example: Filter Color
Affects the color of the inscattered light. In the example below the filter color is set to red (H=0,S=108,V=255) and we are adjusting the Hue value.