This page provides information on VRscans.
Overview
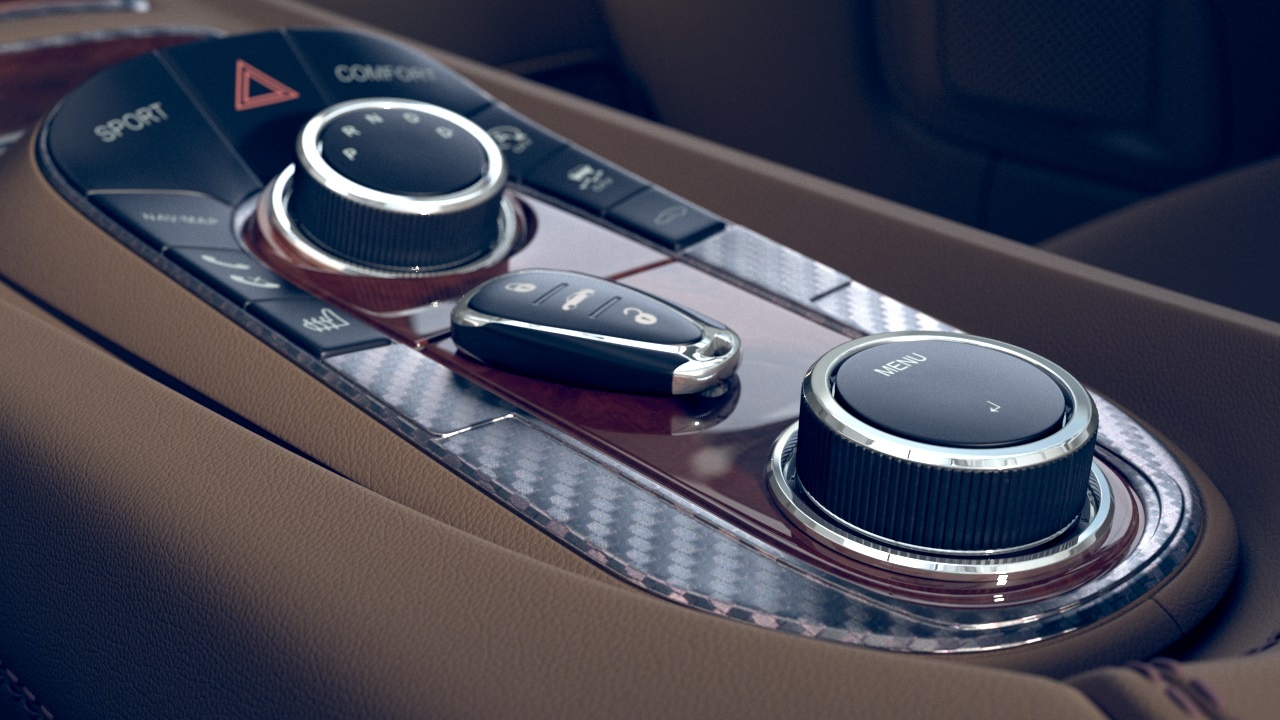
The VRayScannedMtl material applies material information gathered by the Chaos Scans system to an object. The VRscans system captures the appearance of an actual physical material sample, going beyond single-point BRDF capture to faithfully represent the textured appearance of a real-world surface using bidirectional texture function (BTF) approximation. The information is saved in a .vrscan file, which the VRayScannedMtl material then reads to reproduce the material in the rendering.
In V-Ray 6 and later, the Scanned Material doesn't require an additional render license.
In V-Ray versions earlier than V-Ray 6, rendering Scanned Materials requires a separate license, otherwise images render with a watermark.
For full UI access to the VRayScannedMtl in V-Ray 7, update 1, you require a V-Ray Premium license or an additional Material Scanner license.
The VRscans system and VRayScannedMtl material are intended as a solution for users who need to exactly match a given real-world sample.
The scanned material simply stores information about the way a physical material responds to light at individual points on the surface; it has no notion of components that extend across the surface such as diffuse or reflection qualities, or normal or bump maps. The scanned material is simply a faithful representation of how each point on the object responds to light. The .vrscan files tend to be quite large.
For more details on Chaos Scans, please see the Chaos Scans documentation.
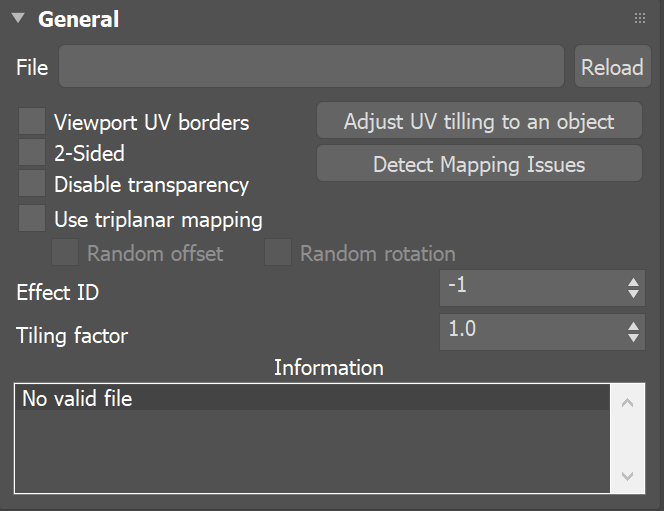
Parameters
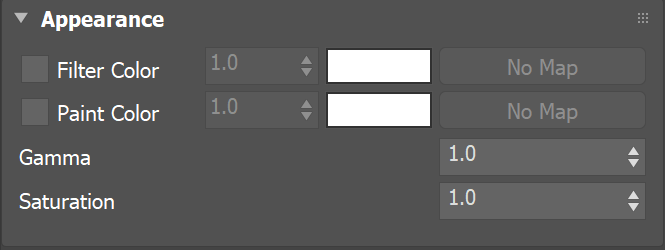
Appearance
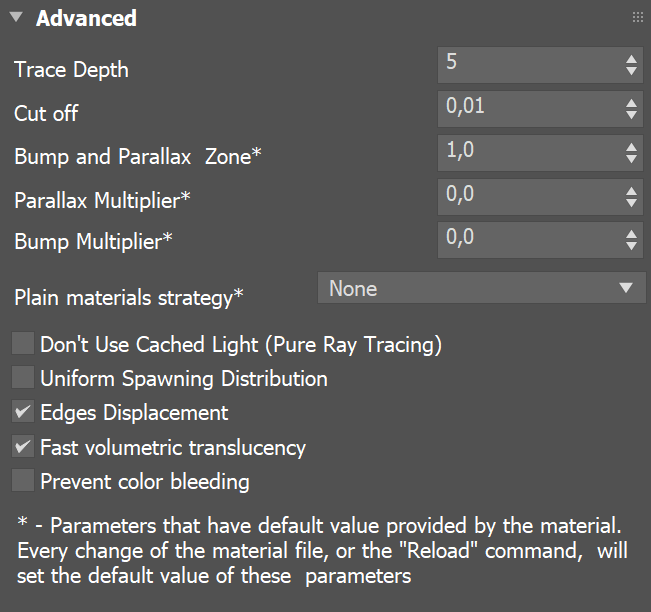
Advanced
Clearcoat
Coordinates
Noise
Example: Tiling Factor
This example shows the effect of the Tiling Factor parameter. The .vrscan material used for the example is Leather.
Example: Saturation
This example shows the effect of the Saturation parameter. The .vrscan material used for the example is Leather.
Example: Filter Color
This example demonstrates the effect of the Filter Color parameter. In the second image, Filter Color is set to 0.5 and rgb (45, 10, 0).
Notes
V-Ray GPU render engine supports VRayScannedMtl under few limitations. In general, if your renderer is set to V-Ray GPU the unsupported features will be grayed out.
- Paint and Filter don't support texture maps;
- Fast Volumetric Transparency is not supported;
- Cut Off parameter is not supported.
VRayScannedMtl can make use of some of the Render Elements. Here is a list of those elements:
- Clear coat reflections stored in VRayReflection Render Element;
- Direct Light Contribution stored in VRayLighting Render Element;
- Indirect lighting by spawned rays stored in VRayGlobalIllumination Render Element;
- Material Opacity stored in VRayAlpha Render Element;
- Received caustics stored in VRayCaustics Render Element.