This page provides information on the V-Ray Frame Buffer and its features.
Overview
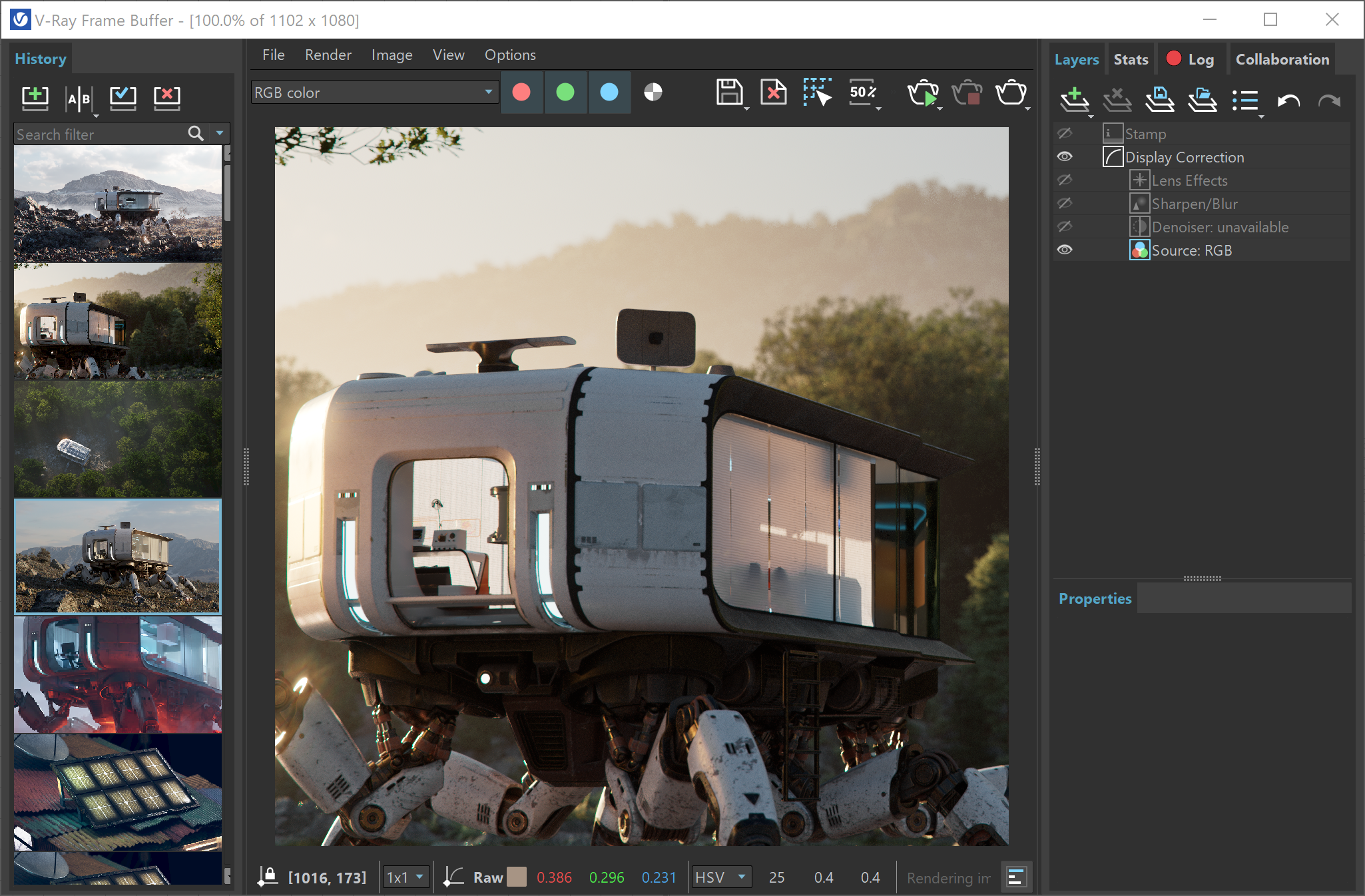
The V-Ray Frame Buffer (VFB 2) is a second generation V-Ray virtual frame buffer.
The VFB is much more than a render image holder window, with Light Mix capabilities for modifying the scene lighting after rendering and Layer Compositing for a higher level of post-processing adjustments.
- Image preview:
Loads render elements channels via a dropdown list;
Works with display corrections;
Loads various 8bit and 32bit file formats, including V-Ray resumable files;
Image comparison between 2 or 4 renders;
- Image management:
Keeps the rendered image in full 32-bit floating point format;
Can store history of rendered images with their post rendering corrections;
Can save corrected output to various image formats;
- Image editing and post processing:
Add Color Corrections to rendered image and its elements;
Layer Compositing for anything from a simple Back to Beauty workflow or advanced compositing;
LightMix adjustment of the scene lighting after rendering the image;
- Scene editing:
Can modify actual lights values by transferring updated intensity and color from LightMix mode;
- Denoiser control;
Region rendering control and test resolution;
Allows you to choose the order in which the buckets are rendered.
Drag-n-dropping a file directly in the VFB opens the file.
V-Ray Update
If a newer version of V-Ray is available, you are notified by a button in the VFB toolbar. For more information, see the V-Ray UI page.
VFB Menu
The V-Ray Frame Buffer menu holds the main frame buffer commands. Some of the options are also available in the VFB toolbar for a quick access.
Menu | Menu Options | |
|---|---|---|
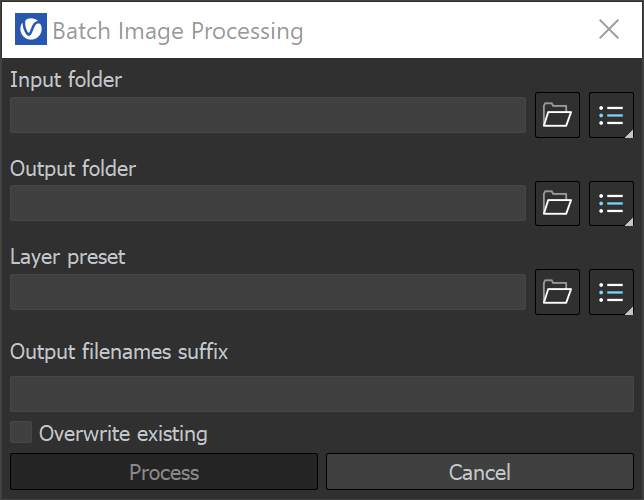
File | Save current channel – Saves the currently loaded channel to an image file format. Save all image channels to separate files – Saves all the render elements to separate files. Press the options () button to open a menu with more options. Save all image channels to single file – Saves the image to a multi-channel EXR or .vrimg file. Load image – Opens an image file from disk to be previewed in the V-Ray Frame Buffer. Drag-n-dropping a file directly in the VFB is also supported. Batch image processing – Allows processing of multiple .vrimg files with the same layer tree changes at the same time. Upload image to Chaos Collaboration – Uploads an image to Chaos Cloud Collaboration for sharing and commenting. Recent Files – Provides quick access to recently used files. | Save all image channels to separate files options Save VFB color corrections to render elements – When enabled, all color corrections are saved to the render channels (as opposed to only the RGB and effectsResult channels). |
Batch Image Processing Input folder – Specifies a path to start images. Output folder – Specifies a path for the output images. Layer preset – Specifies a layer tree corrections preset. Output filenames suffix – Specifies a suffix added to the output image filenames. Overwrite existing – Enables overwrite of existing files with the same name in the output folder. | ||
Render | Start interactive rendering – Starts IPR rendering. Stop rendering – Stops the ongoing rendering at its current state. It takes the render's current state as valid to perform all post-rendering tasks such as post-effects, denoising or image output saving. Abort rendering – Cancels the current render. When the render is cancelled, the output image is not saved. Render – Starts rendering. IPR Debug Shading – Enables the Debug shading/Isolate selected options in IPR. The submenu gives access to the following modes: Isolate Selected – Renders only the selected object(s), while the rest of the scene is rendered black. You can also select material or texture nodes to isolate all objects with the assigned shader; | |
Image | Follow mouse – Renders the closest bucket found to the mouse pointer, when using the bucket image sampler. If the progressive sampler is used, V-Ray samples the closest pixels to the mouse pointer. Follow mouse – Drag the mouse over the VFB while rendering to change what part of the image is sampled first; Copy current channel to clipboard – Copies the current channel to the clipboard. Duplicate to host frame buffer – Creates a Maya virtual frame buffer copy of the current VFB. Clear image – Clears the contents of the frame buffer. This is useful when starting a new render to prevent confusion with the previous image. | |
View | Display color space –Specifies the color space, in which the image is displayed. None – Does not specify a color space; Zoom VFB – Zooms in/out the rendered image in the VFB. Zoom 50% – Zooms out to 50%; Channels – Chooses which channels to display. View red channel – Displays the red channel; Test resolution – Enables test resolution in VFB. The submenu allows choosing a percentage of the render resolution to set as the test resolution. You can choose between 10%, 25%, 50%, 75%, 110%, 125% and 150%. Note: This only affects V-Ray and does not affect the native Maya test resolution setting found under Maya's Render Setup dialog. Color clamping – Opens the color clamping submenu options: Force color clamping – Forces color clamping; Use pixel aspect – Enables visualization of the pixel aspect ratio. Flip – Provides the option to Flip horizontally or to Flip vertically the preview in the VFB. Double-clicking on either option temporarily applies the effect. Clicking anywhere on the toolbar returns the preview to default. The flipped image cannot be exported. Panorama View – Enables a panoramic preview of the scene. Panning in the VFB moves the 360° panorama. Images imported into the VFB can also be viewed in Panorama View. The panoramic preview cannot be exported. Show History – When enabled, displays the history tab in the VFB. When disabled, hides the history tab. Show Layers – When enabled, displays the layers tab in the VFB. When disabled, hides the layers tab. | |
Options | VFB settings – Opens the VFB Settings window where you can adjusts settings for Render View, Render Region, History and Layers. | |
VFB Toolbar
| This dropdown gives access to render elements rendered for the scene. The selected render element is displayed in the VFB. By default, the RGB color and Alpha render elements are available. Any additional render elements that have been added to the scene also appear in the drop-down. | |
| Displays the coordinates of the mouse pointer. | |
| Specifies the sampled area size. Click on the arrow to open a context menu with the available sampled area sizes: 1x1, 3x3, 5x5, and 7x7. | |
| Specifies whether color and display corrections are applied (RGB) or not (Raw) when showing the sampled pixel values at the current mouse pointer position. | |
| Displays the RGB pixel values at the current mouse pointer position before applying any color corrections. | |
Specifies RGB values. Click on the arrow to open a context menu with the available option. None – Does not specify the RGB value. | |
| Displays the Hue, Saturation and Value of the pixel under the current mouse position when HSV is selected. | |
| Displays the HEX of the pixel under the current mouse position when Web is selected. | |
| Displays the 8bit color palette of the pixel under the current mouse position when 8bit is selected. |
| Locks the mouse pointer coordinates and displays information for the selected pixel. | ||
| Shows corrected colors. | ||
| Displays the Red channel. | ||
| Displays the Blue channel. | ||
| Displays the Green channel. | ||
| Displays the Alpha channel. | ||
| Saves the image to disk. Press and hold the icon to bring up the submenu: Save current channel – Saves the current channel to an image file format; | ||
| Clears the contents of the frame buffer. This is useful when starting a new render to prevent confusion with the previous image. | ||
| Renders the closest bucket found to the mouse pointer, when using the bucket image sampler. If the progressive sampler is used, V-Ray samples the closest pixels to the mouse pointer. With this option enabled, you can right-click on the image and select Lock bucket starting point to lock the bucket (or sampling) starting point. | ||
Enables/disables test resolution in the VFB. Press and hold to bring up the submenu to select the percentage of the render resolution to set as the test resolution. Note: This only affects V-Ray and does not affect the native Maya test resolution setting found under Maya Render Setup dialog. | ||
| Allows you to render regions in the VFB. See the Render Region section for more information. | ||
Enables the Debug shading/Isolate selected options in IPR. Press and hold to choose between the different modes: Isolate Selected – Renders only the selected object(s), while the rest of the scene is rendered black. You can also select material or texture nodes to isolate all objects with the assigned shader; | ||
Starts IPR. Left-click and hold to access a list of available cameras from which to render. | ||
Stops the current rendering. Right-click and hold to open the drop-down menu. Abort rendering – Cancels the current render. When the render is cancelled, the output image is not saved. | ||
Starts rendering. Left-click and hold to access a list of available cameras from which to render. | ||
| Pauses interactive rendering. | ||
Render History
The V-Ray VFB keeps a history of previously rendered images, and lists each with a number, frame number, thumbnail, and textual details in the Render history panel. Up to four images can be called from the history to be compared in the VFB (as shown below). History files are stored as .vrimg files in a user-specified folder. Render history settings can be configured in the VFB Settings window. If the Render History is disabled, a link to the VFB Settings History tab is displayed in the panel.
| Enables or disables image A/B vertical comparison. Select images A and B from the render history. | |
| Enables or disables image A/B horizontal comparison. Select images A and B from the render history. | |
| Enables or disables image A/B/C/D comparison. Select images A, B, C and D from the render history. | |
| Saves the current image from the VFB to the render history. The image is placed at the top of the render history list. | |
| Loads the selected image from the render history to the VFB. | |
| Removes the selected image from the render history. |
| A search field where you can filter the images based on the scene paths and notes. |
The keyboard keys from 1 to 9 can be used to quickly load the first 9 images from the history to the VFB.
Edit note – Allows you to add a text comment to the image; the comment appears below the image.
Set A – Sets the render as A image for A/B comparison.
Set B – Sets the render as B image for A/B comparison.
Load to VFB – Loads the selected image in the VFB (same as double-clicking on the image).
Delete – Deletes the selected image from history. The image is moved to the system's Recycle Bin and can be restored from there if needed.
Load layers – Loads the layer tree preset of the selected image.
Load V-Ray settings – Loads the V-Ray settings used for the saved render.
Compare V-Ray settings – Opens the Compare V-Ray settings dialogue, where you can compare the render setups of saved renders.
Image Info – Opens a window containing detailed information about the image, including, but not limited to Camera, Aperture, Target Distance, File Path, V-Ray version, render time. Have in mind that the camera values are saved in system units. Also, the vrayrevison info displayed in the list is not related to the saved .vrimg file but to the current V-Ray build installed for Maya.
Open scene – Opens the rendered scene in the viewport. This option works as long as the initial file path of the scene has not changed after the render.
Copy scene path – Copies the full path to the scene.
Copy project path – Copies the full path to the project.
Show in folder – Opens the folder containing the image and selects the image.
Upload image to Chaos Collaboration – Uploads an image to Chaos Cloud Collaboration for sharing and commenting.
Reload history – Re-reads the history image list. This may be needed if the history folder is updated outside of Maya (e.g. from another Maya session).
Manually saved .vrimg files can also be added to the History folder, but they need to be saved with all image channels in one .vrimg file to keep the complete image info.
VFB Filters
The V-Ray VFB provides a variety of filter presets.
The Filters panel preset previews provide easy check of multiple color corrections scenarios. Preview thumbnails are auto updated on render end. Manual reload from the button or right-click option is needed for image load from History. Applying one of the filters, adds it as a folder on top of the layer tree. On the next filter load the top preset folder in the layer tree is replaced by the new corrections.
To create custom filters in the VFB Layers panel right-click on a folder containing correction layers and save it as a .vlpdir file. Change presets directory from V-Ray Frame Buffer > Options menu > VFB Settings > Filter/Layer presets > Path. Personal custom filters are now shown in the panel and can be loaded quickly.
| Refreshes the preview thumbnails. | |
| Applies the selected thumbnail preset folder to the layer tree. | |
| A text search field which provides fast location of the desired filters. The filter text is selected when pressing Enter from the keyboard. |
If a Filters folder path has not been specified, a link to the Filter/Layer presets tab is displayed in the panel.
Double-click on any preview thumbnail applies its preset folder to the layer tree.
If you want current corrections to be taken into account for the Filter thumbnail previews, disable the Ignore existing correction for the Filter thumbnails from V-Ray Frame Buffer > Options menu > VFB Settings > Filter/Layer presets.
VFB Shortcuts
These shortcuts navigate through the VFB image. Please note that the VFB window must have the current focus for the shortcuts to have effect:
| Mouse | Description |
| Mouse wheel | Zoom in/Zoom out |
| Double-click left button | Zoom to 100% |
| Page Up/Page Down | Switch between render elements |
| Middle button dragging | Pan (hand tool) |
| Keyboard | Description |
| + / = | Zoom in |
| -/_ | Zoom out |
| * | Zoom to 100% |
| Arrow keys | Pan left, up, right, down |
| F | Fit region or whole image. Available only if render region option is used. |
| Esc | Abort render |
| Q | Enable history A/B vertical compare mode. |
| W | Enable history A/B horizontal compare mode. |
| E | Enable history A/B/C/D compare mode. |
| 1-9 | Load the respective image from the VFB2 history |
| H | Show/hide history |
| L | Show/hide whole right panel |
| P | Show/hide only layers tree |
| S | Show/hide settings |
| F11 | Toggle fullscreen |
| Ctrl+C | Copy the VFB image to the Windows clipboard; the image is copied exactly as it appears on the screen (meaning sRGB/LUT/OCIO etc corrections are applied). The full resolution image is copied to the clipboard, even if the VFB view is zoomed in/out. |
VFB IPR Options
Select object – Directly select scene objects by clicking on them in the VFB2 rendering area.
Select material – Pick a scene material from an object that is being rendered. You only need to click on that object in the VFB2 rendering area and the material editor will open with it.
Set focus point – When enabled, allows the user to set the camera focus distance by left clicking in the VFB. This requires rendering with a V-Ray Physical Camera with Depth of Field enabled or a regular camera with the Depth of Field Camera Overrides enabled.
Lock bucket starting point – Forces V-Ray to render the closest bucket found to the mouse pointer, when using the bucket sampler. If the progressive sampler is used, V-Ray samples the closest pixels next to the mouse pointer. Drag the mouse over the V-Ray frame buffer while rendering to change what part of the image is done first. You can turn this on and of on-the-fly while rendering.
Note that the keyboard shortcuts work only within the VFB window.
The Undo shortcut (Ctrl+Z) for these actions does not work within the VFB window though. It only works when the focus is on the Maya windows.
Layers
The V-Ray Frame Buffer includes a suite of color corrections and tools for adjusting the image. The tools are added as layers and displayed in a layer tree. You can enable or disable a particular tool using the visibility icon () to the left of its name.
For more information on using the Layers, see the Layers page and the VFB Composite page.
Creates a layer. Multiple layers of the same type can be added. Folder - Allows grouping multiple layers in folders. This is only available when the Source layer is set to Composite; For more information, see the Layers page. | |
| Deletes the selected layer(s). | |
| Saves a layer tree preset. | |
| Loads a layer tree preset. | |
| Quick access to custom layer presets. You must set the path to it in the VFB Settings. | |
| Undo create layer. | |
| Redo create layer. |
Render Stats
The V-Ray Frame Buffer allows monitoring of different statistics and information about your scene in the Stats panel. The exact contents of the Stats changes depending on the scene, the rendering mode (interactive vs production, bucket vs progressive) and others.
Right-click to display a context menu, allowing you to copy the Stats values.
Log
The Log panel provides messages about the render process. Verbosity control is available and you can filter the type of messages shown in the Log: All, Error Only, Error & Warnings, or Error, Warnings & info. Additional options are available when you click the Open options button:
Show progress – Shows a completion percent of each task (e.g. building Light Cache).
Wrap – Wraps longer lines in order to avoid horizontal scroll.
Undock – Docks/undocks the Log tab.
Note that the V-Ray Log is also accessible via the Show log button.
The Log tab can be detached and used as a separate window or docked elsewhere.
Ctr+F opens a search field at the bottom of the Log tab.
These parameters control the V-Ray messages displayed in both the Maya Output Window and V-Ray Frame Buffer Log panel.
Collaboration
The Collaboration tab provides a collaboration tool for sharing your work with other users. You can upload images from the VFB to the Chaos Cloud Collaboration where other users can add comments and annotations.
Signing in Chaos Cloud Collaboration using your Chaos credentials is required once. After that you are automatically signed in every time you open the Collaboration tab.
When first opening the Collaboration tab, click anywhere in the tab to upload the current image in the VFB to Chaos Cloud Collaboration. Following that, you can upload other images via the Upload image to Chaos Collaboration button or some of the other options provided by the VFB.
Automatically, there is a default project folder where the images are uploaded to Chaos Cloud Collaboration. You can create multiple projects and folders from the browser.
The Collaboration tab has several sections: Upload files containing a list of images for upload, Recent containing recent projects, and Browse with locations where the images are uploaded.
– Deletes the current image from the upload list.
– In the Upload files, uploads the current image in the VFB to Chaos Cloud Collaboration. In Browse, creates a new project or folder.
– Renames the Upload file.
Upload to selection – Uploads the image(s) to Chaos Cloud Collaboration in the selected project or folder.
New upload – Clears the Collaboration tab and prepares it for new upload of images.
Open in browser – Opens the uploaded images in Chaos Cloud Collaboration.
It is also possible to directly drag the images from the Explorer to the Collaboration tab.
Chaos Collaboration is not supported on V-Ray for Maya 2024 running on macOS, and V-Ray for Maya versions 2022 and 2023 on Linux.
Render Region
Region rendering can be used in both IPR and Production modes to isolate only part of the frame for rendering. Usually, when a render region is used, you would like to save the whole frame instead of the region only.
| Region render | Renders rectangular regions in the VFB. | |
| Polygon region render | Allows creation and use of multiple polygonal regions in the VFB at once. Press ESC to cancel the vertex creation. |
Polygon Region Context Menu
The context menu is only available when the Polygon region render is selected. Right-click inside the region in the VFB viewport to open.
Freeform – Selects the Polygon region render mode.
Rectangular – Selects the Region render mode.
Add/Delete vertex – Adds/deletes vertices of a selected polygon.
Delete polygon – Deletes the selected region.
Delete all – Deletes all regions.
Undo/Redo – Undoes/redoes various actions related to the region render shapes.
Saving Files with Render Region
Saving single channel .exr files ignores the render region and always saves the full frame. This applies when saving the .exr through VFB.
Saving multi-channel .exr files writes just the render region data in the file by default but it can be set to save full frame instead. In order to save the render region with the rest of the frame, set its exr data window option to Whole Image. Saving multi-channel .exr files from VFB > Save all channels to single file saves the render region when it is enabled from the VFB. This happens even if you have selected a render region on top of the already rendered frame, without an actual region used in the rendering process. To save the full frame from VFB, disable the render region.
How to Post-Process Renders in the VFB
Watch this video to learn how to make the most out of V-Ray for Maya’s post-processing capabilities. It shows you how to enhance your renders right from the V-Ray Frame Buffer. Learn how you can explore different lighting scenarios without re-rendering, using LightMix, how to make use of the different color correction options in the VFB, how to easily composite your image and have greater flexibility when it comes to post-processing in the VFB.
Notes
- VFB does not display the G-Buffer layers (like Coverage etc.) .
- VFB does not work with strip rendering.
- VFB does not work with rendering to fields.
- The OpenEXR file format is an open file format for high dynamic range images originally developed by Industrial Light and Magic. The official site of the OpenEXR file format is http://www.openexr.com/
- When using the IPR right-click options, the primary Maya window needs the cursor focus to use Ctrl+Z to Undo.
- If an 8-bit file is saved through the VFB or the Render Output / Save image settings, the color space (for example sRGB) is embedded and the image appears as in the frame buffer when loaded in an external image viewer. If a 32-bit (exr, hdr, tif) image is saved, it remains linear and relies on the external image viewer to handle the display color space.
- The VFB test resolution is ignored for command-line rendering and Backburner jobs. The Test Resolution button is inactive in IPR if Fit resolution to VFB is enabled.
- Motion blur is not rendered in IPR.