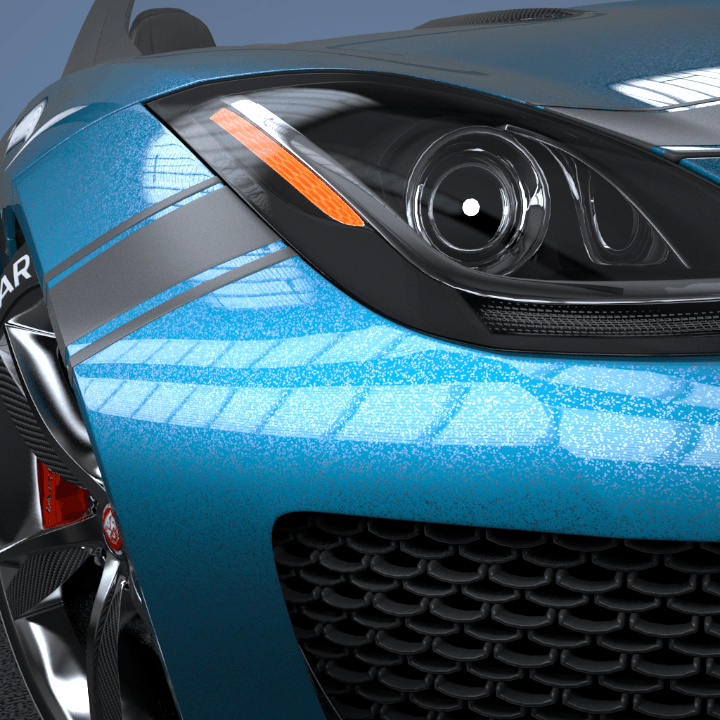
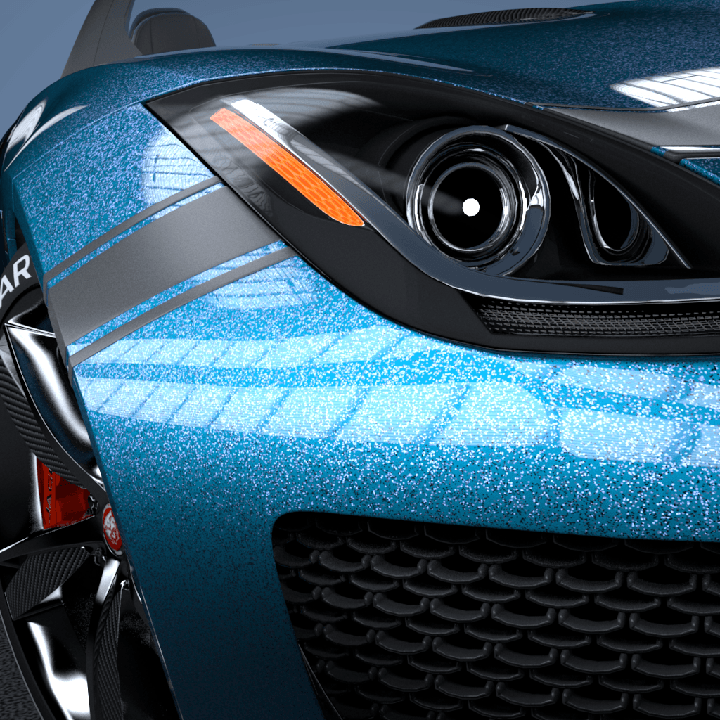
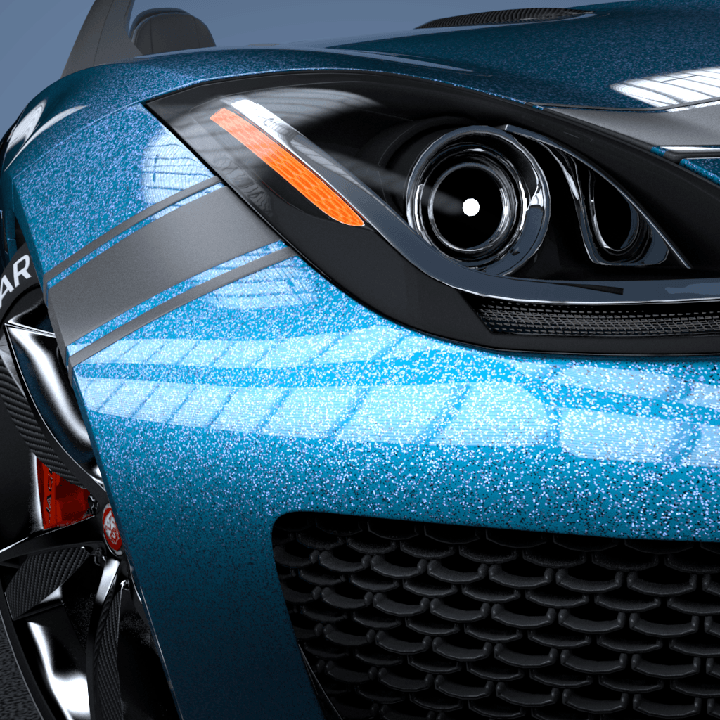
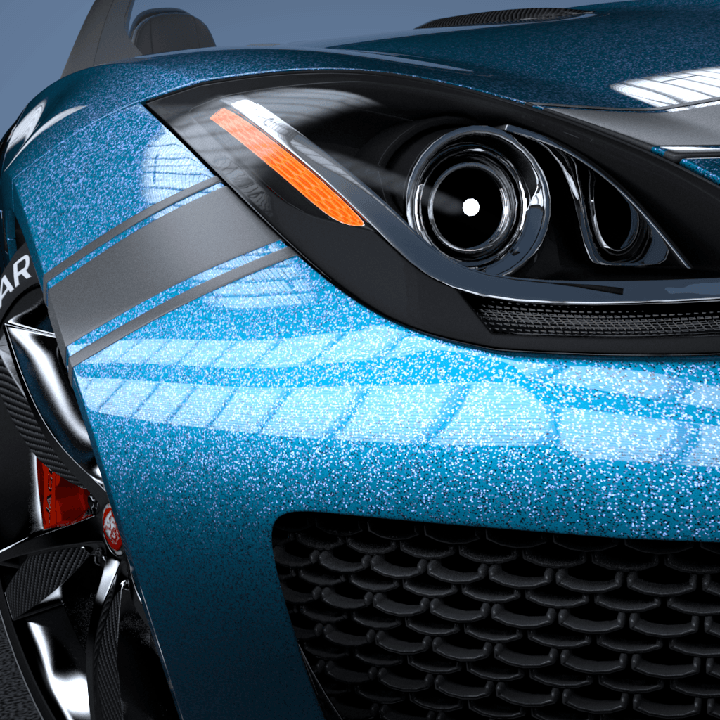
This page provides some details on the settings available for the Car Paint Material in V-Ray.
Overview
The VRayCarPaintMtl material is a material that simulates a metallic car paint. It is a complex material with four layers: a base diffuse layer, a base glossy layer, metallic flakes layer, and clear coat layer. The material allows the adjustment of each of these layers separately.
© Saddington Baynes
Base Parameters
Base Color – The diffuse color for the base layer.
Base Reflection – The reflectivity of the base layer. The reflection color itself is the same as the Base color.
Base Glossiness – Reflection glossiness for the base layer.
Map Type – Specify whether a bump map or a normal map effect will be added to the base material.
Bump map
Normal map in tangent space
Normal map in objectspace
Normal map in screen space
Normal map in worldspace
Map – Specifies the bump/normal map to be used.
Base Bump Mult – A multiplier for the bump/normal effect.
Base Trace Reflection – Toggle reflections for base layer. This parameter is inactive with V-Ray GPU engine.
Flakes Parameters
Flake Color – The color of the metal flakes.
Flake Glossiness – The glossiness of the metal flakes. It is not recommended to set this above 0.9 as it may produce artifacts.
Flake Orientation – Controls the orientation of the flakes relative to the surface normal. When this is 0.0, all flakes are perfectly aligned with the surface. When it is 1.0, the flakes are rotated completely randomly with respect to the normal. Values above 0.5 are not recommended as they can produce artifacts. For more information, see The Flake Orientation Parameter example below. This parameter is inactive with V-Ray GPU engine.
Flake Density – The density (number of flakes) for a certain area. Lower values produce less flakes and higher values produce more flakes. Set this to 0.0 to produce a material without flakes. For more information, see The Flake Density Parameter example below.
Flake Scale – Scales the entire flake structure. For more information, see The Flake Scale Parameter example below.
Flake Size – The size of the flakes relative to the distance between them. Higher values produce bigger flakes and lower values produce smaller flakes. For more information, see The Flake Size Parameter example below.
Flake Map size – Internally the material creates several bitmaps to store the generated flakes. This parameter determines the size of the bitmaps. Lower values reduce RAM usage, but may produce noticeable tiling in the flake structure. Higher values require more RAM, but tiling is reduced. Be careful when using the Directional filtering method, as it may quickly take up gigabytes of RAM for larger map sizes. For more information, see the Antialiasing Filters example below.
Flake Filtering Mode – Determines the way the flakes are filtered. Filtering is extremely important to reduce the work required to produce a clean image. See the Examples for a demonstration of this parameter. This parameter is inactive with V-Ray GPU engine.
Simple – This method is faster and uses less RAM but is less accurate. It averages the orientation of the flakes together, which may alter the appearance of the material when viewed from a distance.
Directional – This method is slightly slower and uses more RAM but is more accurate. It groups the flakes based on their orientation before performing the filtering, so that the material appearance is preserved.
Flake Seed – The random seed for the flakes. Changing this produces different flake patterns.
Mapping Type – Specifies the method for mapping the flakes. The possible values are:
Explicit mapping channel – The flakes are mapped using the specified channel.
Triplanar projection in object space – The material automatically computes mapping coordinates in object space based on the surface normals.
Mapping Channel – The mapping channel for the flakes when the Flake mapping type is set to Explicit mapping channel. This parameter is inactive with V-Ray GPU engine.
Flake UV Coords – Allows connecting a texture placement node. This parameter is inactive with V-Ray GPU engine.
Flake Trace Reflections – Toggles reflections for flake layer. This parameter is inactive with V-Ray GPU engine.
Example: The Flake Orientation Parameter
This set of images demonstrates the effect of the Flake orientation parameter. Note how lower values produce flakes more aligned with the surface normal, so that light is reflected more uniformly. Higher values produce more random flakes leading to more variation in the flake illumination.
Flake Orientation: 0.0
Flake Orientation: 0.3
Flake Orientation: 0.5
Example: The Flake Density Parameter
This set of images shows the effect of the Flake density parameter. Note how larger values produce more flakes, but do not change the flake size.
Flake Density: 0.5
Flake Density: 1.0
Flake Density: 2.0
Example: The Flake Scale Parameter
This set of images demonstrates the effect of the Flake scale parameter. Note how lower values scale the entire flake structure.
Flake Scale: 0.01
Flake Scale: 0.04
Flake Scale: 0.08
Example: The Flake Size Parameter
This set of images shows the effect of the Flake size parameter. Note how larger values make the individual flakes larger, but do not change their count.
Flake Size: 0.5
Flake Size: 1.0
Flake Size: 2.0
Example: The Flake Filtering Parameter
This example shows the effect of the Flake filtering parameter.
Flake Filtering: Simple
no anti-aliasing
Flake Filtering: Directional
no anti-aliasing
The flake orientation gets averaged, altering the appearance. The material transitions more abruptly from dark to light with the flakes appearing brighter and nosier.
The material appearance is correctly preserved due to the higher filtering accuracy.
Example: Anti-aliasing Filters
Here is an example briefly demonstrating the effect of different anti-aliasing filters on the final result.
Note that rendering with a particular filter is not the same as rendering without a filter and then blurring the image in a post-processing program like Adobe Photoshop. Filters are applied on a sub-pixel level, over the individual sub-pixel samples. Therefore, applying the filter at render time produces a much more accurate and subtle result than applying it as a post effect.
Flake Filtering: Simple
Flake Map Size: 256
Flake maps take less than 1 MB
Flake Filtering: Simple
Flake Map Size: 512
Flake maps take between 1 and 2 MB
Flake Filtering: Simple
Flake Map Size:1024
Flake maps take 5 MB
Flake Filtering: Simple
Flake Map Size: 2048
Flake maps take 21 MB
Flake Filtering: Directional
Flake Map Size:256
Flake maps take 10 MB
Flake Filtering: Directional
Flake Map Size:512
Flake maps take 40 MB
Flake Filtering: Directional
Flake Map Size:1024
Flake maps take 161 MB
Flake Filtering: Directional
Flake Map Size: 2048
Flake maps take 645 MB
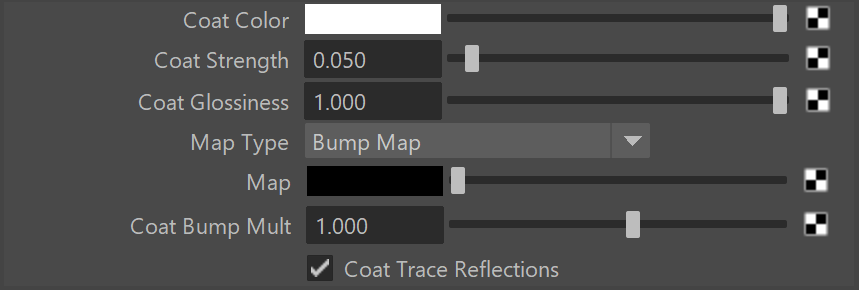
Coat Parameters
Coat Color – The color of the coat layer.
Coat Strength – The strength of the coat reflections when the surface is viewed directly from the front.
Coat Glossiness – Glossiness of the coat reflections.
Map Type – Choose between several types of Normal Maps and Bump map.
Map – A slot for the bump or normal map. This parameter is inactive with V-Ray GPU engine.
Coat Bump Mult – A multiplier for the bump or normal map. This parameter is inactive with V-Ray GPU engine.
Coat Trace Reflections – Toggles reflections for coat layer. This parameter is inactive with V-Ray GPU engine.
Options
Cutoff Threshold – Cutoff threshold for the reflections of the different layers.
Double Sided – When enabled, the material is double-sided.
Trace Reflections – Global switch to toggle reflections for all layers.
Max Depth – The number of times a ray can be reflected.
Notes
- The VRayCarPaintMtl material needs to precalculate several textures related to the flakes. Depending on the Flake map size parameter, this may take a few seconds. When using the swatch preview, this may lead to slight delays between changing a parameter and the update of the material swatch.