This page provides information about the Irradiance Map GI engine.
This is a legacy option that will be removed in the future. Use the other Global Illumination options instead.
Overview
The Irradiance Map engine can be used to calculate global illumination. It works by creating a map with a collection of points in 3d space along with the computed indirect illumination at those points. This rollout allows the user to control and fine-tune various aspects of the irradiance map.
This rollout is available only if Irradiance Map has been chosen as the Primary Rays GI engine in the Global Illumination Settings.
Irradiance Map GI engine is not supported by V-Ray GPU.
V-Ray includes an Irradiance Map Viewer for viewing and editing irradiance map files.
UI Path
||V-Ray Asset Editor|| > Settings > Global Illumination > Irradiance Map
(When Irradiance Map is set as the Primary Rays engine.)
Parameters
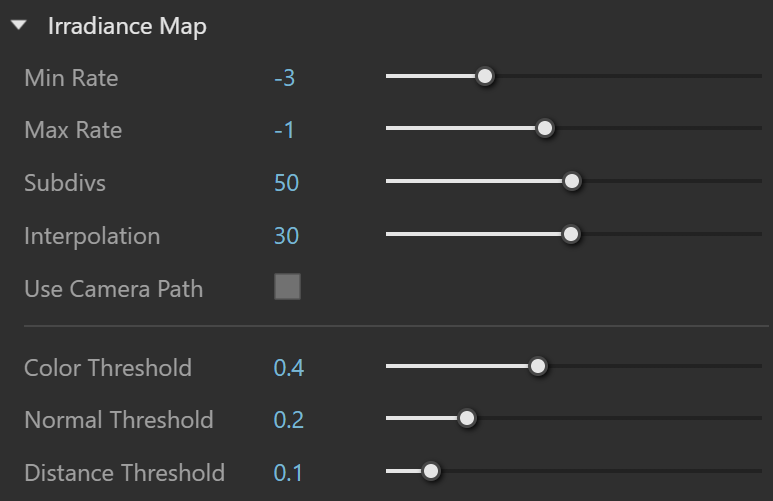
Min Rate – Determines the resolution for the first GI pass. A value of 0 means the resolution is the same as the resolution of the final rendered image, which makes the irradiance map similar to the direct computation method. A value of -1 means the resolution is half that of the final image and so on. You would usually want to keep this negative, so that GI is quickly computed for large and flat regions in the image. This parameter is similar to (although not the same as) the Min rate parameter of the Adaptive subdivision image sampler.
Max Rate – Determines the resolution of the last GI pass. This is similar to (although not the same as) the Max rate parameter of the Adaptive subdivision image sampler.
Subdivs – Controls the quality of individual GI samples. Smaller values make things faster, but may produce blotchy result. Higher values produce smoother images. This is similar to the Subdivs parameter for direct computation. Note that this is not the actual number of rays that are traced. The actual number of rays is proportional to the square of this value.
Interpolation – Specifies the number of GI samples that are used to interpolate the indirect illumination at a given point. Larger values tend to blur the detail in GI although the result is smoother. Smaller values produce results with more detail, but may produce blotchiness if low Hemispheric Subdivs are used. Note that if you use interpolated irradiance maps (i.e. the Mode is set to Animation (rendering)), V-Ray actually multiplies this value by the number of irradiance maps used. For example, if you have the Interpolative Samples set to 20, and the Interpolation frames to 2, V-Ray uses 100 samples to interpolate. This is done in order to preserve the blurring of the GI solution compared to a single frame irradiance map, however it also slows down the rendering. To speed up the rendering in that case, this value can be decreased to 10 or 5.
Use Camera Path – When enabled, V-Ray calculates the GI samples for the entire camera path instead of just the current view. This option is available only if there is an animation set up in the project.
Use Camera Path can be enabled to save the cached map by only rendering the first frame of an animation. The map can then be loaded and used for each frame, saving a considerable amount of time.
Color Threshold – Controls how sensitive the irradiance map algorithm is to changes in indirect lighting. Larger values mean less sensitivity; smaller values make the irradiance map more sensitive to light changes (thus producing higher quality images).
Normal Threshold – Controls how sensitive the irradiance map is to changes in surface normals and small surface details. Larger values mean less sensitivity; smaller values make the irradiance map more sensitive to surface curvature and small details.
Distance Threshold – Controls how sensitive the irradiance map is to distance between surfaces. A value of 0.0 means the irradiance map does not depend on object proximity at all; higher values place more samples in places where objects are close to each other.
Disk Caching
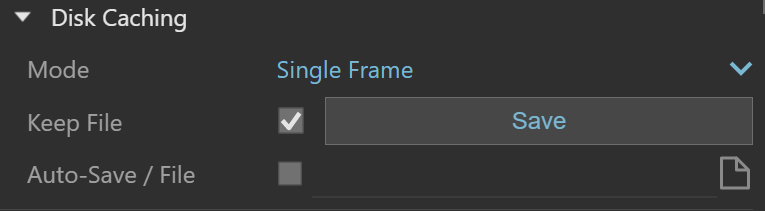
Mode – This option allows the user to select the way in which the irradiance map is (re)used:
Single Frame – Default mode. Computes a new irradiance map for each frame of an animation.
From File – The irradiance map is loaded from a file. No new irradiance map is computed.
Incremental Add to Map – V-Ray uses the irradiance map that is already in memory and only refines it in places that do not have enough detail. This mode is useful when compiling an irradiance map to render multiple views of a static scene or a fly-through animation.
Keep File – When enabled, the last irradiance map map calculated stays in memory after the rendering has finished. Disable this option to automatically delete the map (and thus save memory).
Save – Saves the irradiance map currently in memory for later re-use.
Auto-Save / File – When enabled, V-Ray automatically saves the irradiance map to the specified file at the end of rendering. This option is particularly useful if the irradiance map is sent for rendering on a different machine through network rendering.