Page History
This page provides information on the Post Translate tab of the V-Ray Renderer settings.
Overview
...
The Post Translate tab exposes options for Python Post Translate of .vrscenes. You can import a script file or write a script directly in Houdini to control plugin parameters.
The V-Ray for Houdini's Post Translate support is based on AppSDK Python binding.
UI Paths:
||out Network|| > V-Ray > V-Ray Renderer > Post Translate tab
...
V-Ray menu > Render Settings > Post Translate tab
...
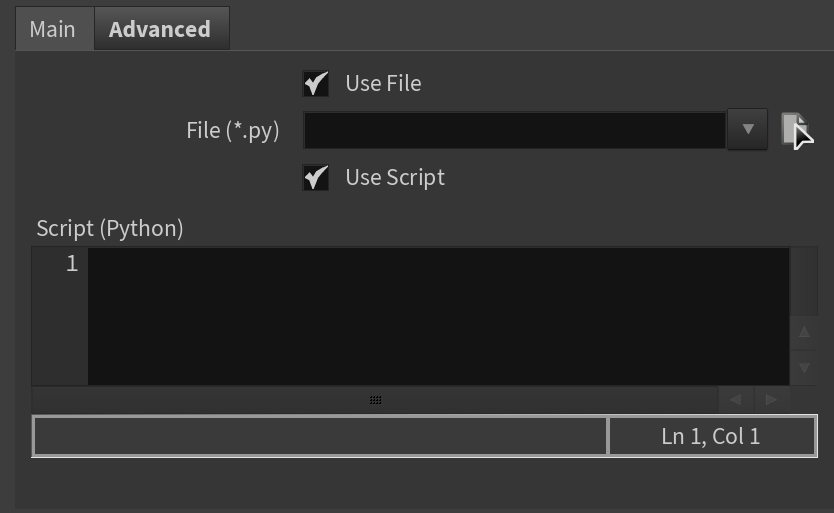
Main Parameters
...
| Section | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Advanced Parameters
...
| Section | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
...
Example: List Scene Plugins
| Code Block |
|---|
import os
import vray
from vfh import vfh_utils
with vray.VRayRenderer() as renderer:
for plugin in renderer.plugins:
vfh_utils.logInfo('plugin ' + plugin.getName() + ' (class ' + plugin.getType() + '):\n') |
...
...
Example: Change Color
...
| Code Block |
|---|
import vray r = vray.VRayRenderer() p = r.plugins["|mat|vrayMaterialBuilder|vrayMtl"] p.diffuse = vray.AColor(0, 1, 1, 1) |
...
Example: Automatically Switch off Displacement for Phantom objects
| Code Block |
|---|
import vray
from vfh import vfh_utils
renderer = vray.VRayRenderer()
for node in renderer.plugins:
if node.getType() != 'Node':
continue
if not node.object_properties:
continue
objProps = node.object_properties
needFix = objProps.camera_visibility == 0 or objProps.matte_surface == 1
if not needFix:
continue
instancer = node.geometry
if not instancer.instances:
continue
for instance in instancer.instances[1:]: # First item is time
instancedNode = instance[-1] # Node is last
if type(instancedNode) is not vray.Plugin:
continue
if instancedNode.getType() != 'Node':
continue
if instancedNode.geometry.getType() in {'GeomDisplacedMesh', 'GeomStaticSmoothedMesh' }:
instancedNode.geometry = instancedNode.geometry.mesh
vfh_utils.syslog("Disabling displacement for \'%s\"" % instancedNode) |
Here, you can check how the script changes the render.
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
...
Example: Convert textures to TX format before rendering
...
| Code Block |
|---|
import os
import vray
import subprocess
from vfh import vfh_utils
def convertToTX(f):
make_tx = os.path.join(os.environ['VRAY_APPSDK'], 'bin', 'maketx.exe')
cmdArgs = [
make_tx,
f
]
call = ' '.join(cmdArgs)
proc = subprocess.Popen(call, universal_newlines=True)
proc.communicate()
return os.path.splitext(f)[0] + '.tx'
with vray.VRayRenderer() as renderer:
for plugin in renderer.plugins:
if (plugin.getType() == 'BitmapBuffer'):
if(os.path.splitext(plugin.file)[1] != '.tx'):
if( not os.path.exists(os.path.splitext(plugin.file)[0] + '.tx')):
plugin.file = convertToTX(plugin.file)
else:
plugin.file = os.path.splitext(plugin.file)[0] + '.tx'
|