Page History
...
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
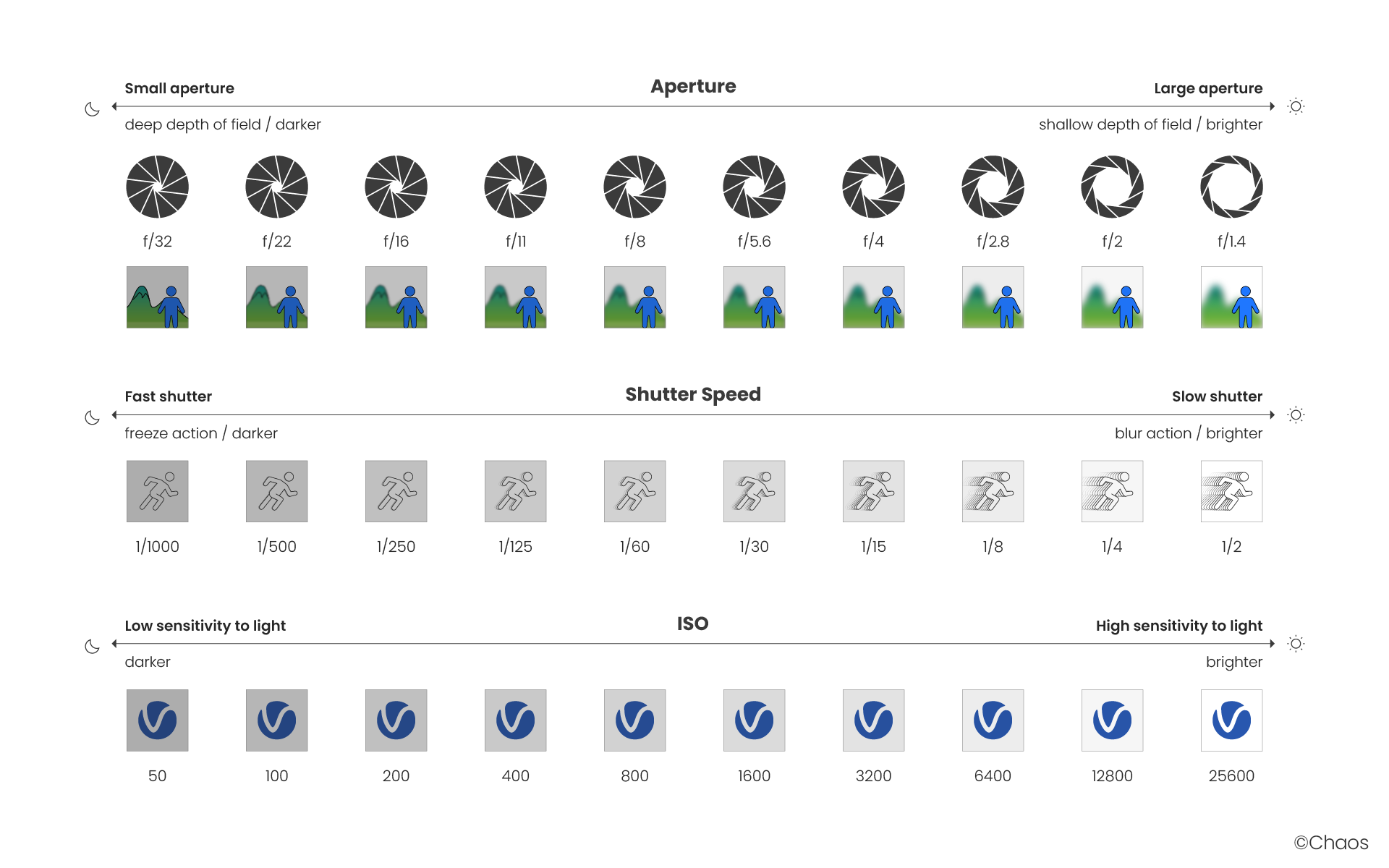
Aperture F-number vs Shutter Speed vs ISO
Cheat Sheet
The main options that control the brightness of a V-Ray Physical camera are Aperture F-number, Shutter Speed and ISO. They affect each other and you need to balance them according to your scene. Keep in mind that these settings do not correspond to those of a real-life camera. They apply only to the V-Ray Physical camera.
| Fancy Bullets | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
|
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Depth of Field
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...