Page History
This page provides information on the System rollout in the Render Settings.
Overview
...
| Section | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
One of the basic operations that V-Ray must perform is raycasting, the process of determining if a given ray intersects any geometry in the scene and, and if so , - identifying that geometry. From a technical perspective, the simplest way to implement raycasting would be to test the ray against every single renderable triangular face in the scene. Obviously, in scenes with thousands or millions of triangles, this would be very slow. To speed this process, V-Ray organizes the scene geometry into a special data structure called a binary space partitioning (BSP) tree.
The BSP tree is a hierarchical data structure built by subdividing the scene into two parts, then subdividing those two parts, then subdividing the four resulting parts, and so on. Those "parts" are called the nodes of the tree. At the top of the hierarchy is the root node, which represents the bounding box of the whole scene; at the bottom of the hierarchy are the leaf nodes, which contain references to actual triangles from the scene.
The settings in this area of the System rollout control various parameters of V-Ray's Binary Space Partitioning ( BSP ) treeBy default, V-Ray uses the Intel Embree raycaster.
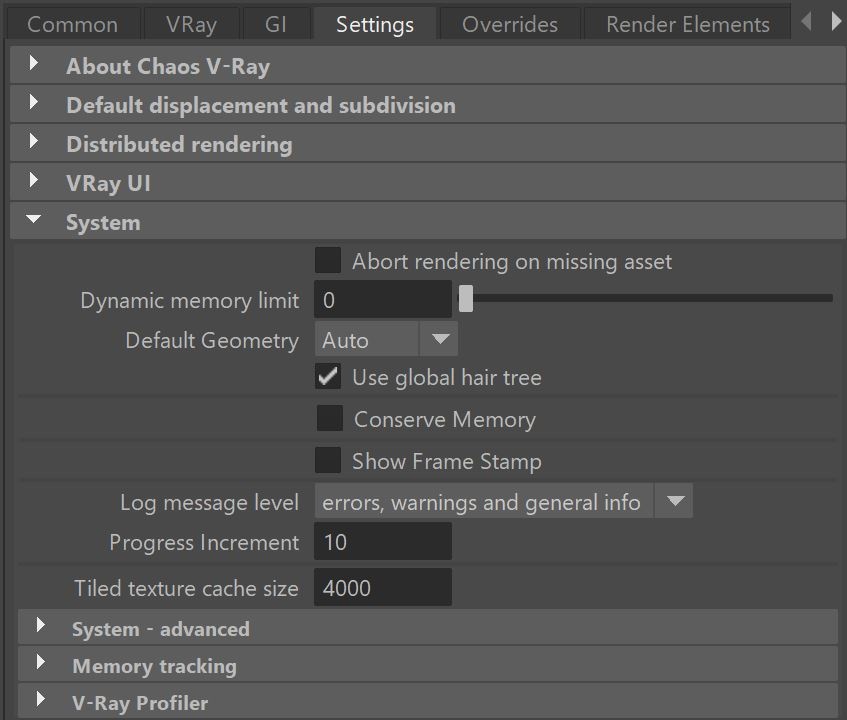
Abort rendering on missing asset – When enabled, the scene will not render if an asset fails to load. When DR is used, the DR server(s) that didn't successfully receive an asset will be excluded from rendering.
...
Dynamic memory limit – The total RAM limit for the dynamic raycastersraycaster, which store stores dynamic geometry, such as displacement and VRayProxy objects. Set this to 0 to 0 to remove any limit (V-Ray takes as much memory as needed). The memory pool is shared between the different rendering threads. Therefore, if geometry needs to be unloaded and loaded too often, the threads must wait for each other, and the rendering performance suffers.
Default Geometry – – Internally, V-Ray maintains four raycasting engines. All of them are built around the idea of a BSP tree, but each has different uses. The engines can be grouped into raycasters for non-motion blurred and for motion blurred geometry, as well as for two raycasting engines: for static and dynamic geometry. This parameter determines the type of geometry for standard Maya mesh objects. Note that some objects (displacement-mapped objects and VRayProxy File Formats for , for example) always generate dynamic geometry, regardless of this setting.
Auto – Some objects are compiled as static geometry, while others as dynamic. V-Ray makes the decision on which type to use based on the face count for an object and the number of its instances in the scene.
Static – All geometry is precompiled into an acceleration structure at the beginning of the rendering and remains there until the end of the frame. The static raycasters are raycaster is not limited in any way and will consume consumes as much memory as necessary.
Dynamic – Geometry is loaded and unloaded on the fly depending on which part of the scene is being rendered. The total memory taken up by the dynamic raycasters raycaster can be controlled by the the Dynamic memory limit parameter.
Auto – Some objects are compiled as static geometry, while others as dynamic. V-Ray decides on which type to use based on the face count for an object and the number of its instances in the scene.
Use global hair tree – When – When enabled, V-Ray will store the hair strands from all hair systems in the scene into a single raytrace acceleration structure at the start of each frame. This speeds up rendering, especially when multiple hair systems are applied to the same object; however, however the entire acceleration structure is kept in RAM for the entire frame. Turning this option off will cause V-Ray to store each hair system into a separate acceleration structure, which can be built on demand and destroyed when the dynamic memory limit is reached.
| UI Text Box | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
| To render an infinite number of hair strands with GPU, the the Use global hair tree option have option has to be disabled. If the Use global hair tree is enabled, the maximum number of hair strands that can be rendered with GPU is 128. |
Conserve Memory – – Slightly slowers Embree method for storing triangles , but reduces memory usage. When using V-Ray GPU renderer, this option is not available.
...
Frame Stamp – The keywords used to render the stamp tokens or keyboards (see table below). These keywords are replaced by V-Ray with the corresponding value:
...
These parameters control the V-Ray messages displayed in the Maya Output Window and V-Ray Frame Buffer Log panel. During rendering, V-Ray writes various information in the file vray4maya_log.txt located in the respective temporary folder. The Output Window (and VFB) shows some of that information so that you can view it without the need to manually open that file.
...
Each message falls into one of four categories: Errors, Warnings, Informative messages, and Debug messages.
Log message level – Determines which messages, if any, are going to be displayed in the Output Window.
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Advanced System Parameters
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Memory Tracking
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
V-Ray Profiler
...
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|