Page History
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Anchor layers.maya layers.maya
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| UI Text Box | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
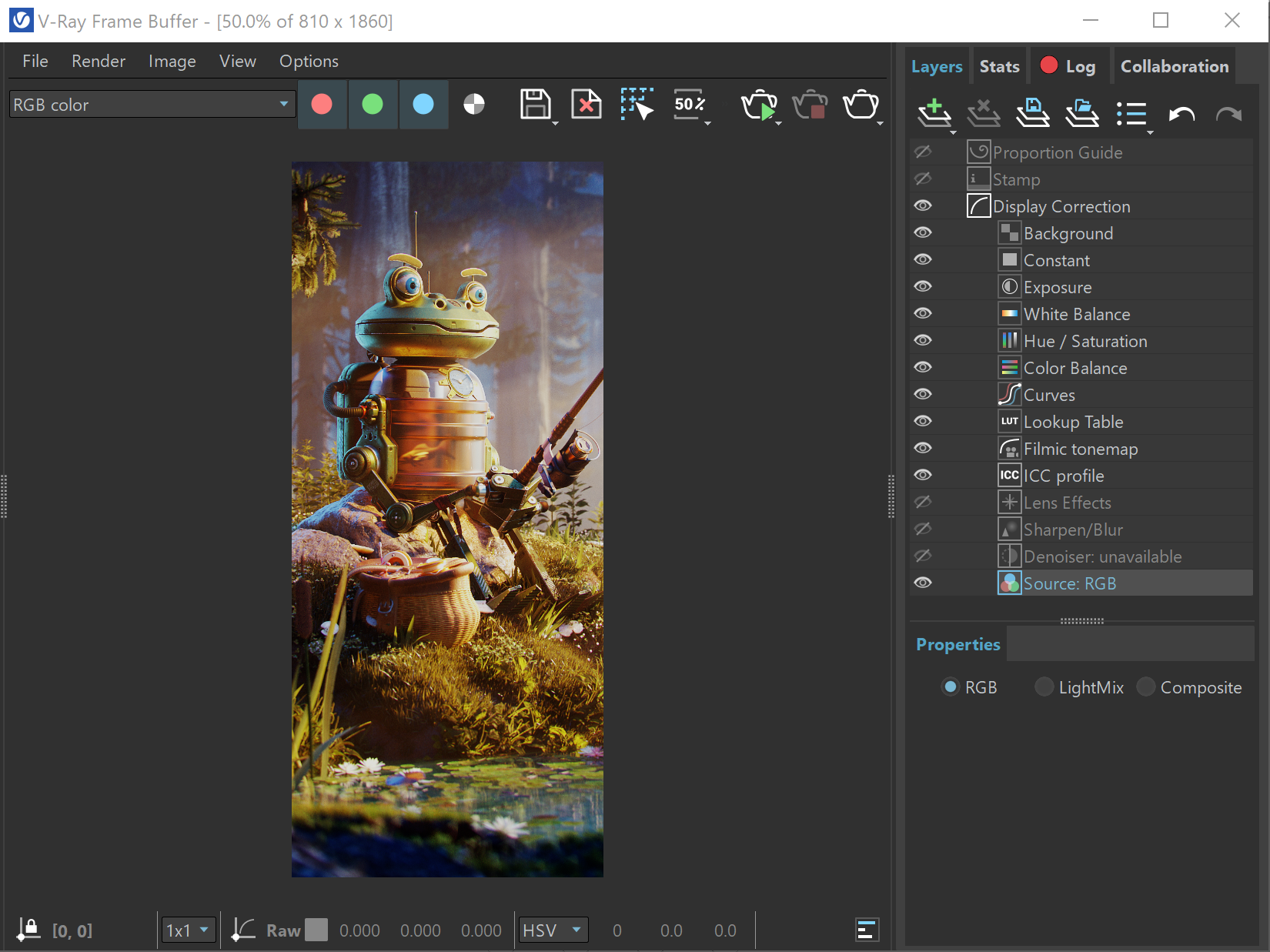
When adding a new layer, it is placed on top of the stack and it is considered the foreground (FG). The result of all layers below it is considered the background (BG). Layers are applied from the bottom to the top. Where darker and lighter pixels are mentioned below, it is in relation to mid-grey. |
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Anchor | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Display Correction
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| UI Text Box | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
Normally you would specify the ICC file for your calibrated monitor here. Programs like PhotoShop display images using your (primary) monitor's ICC profile automatically. However (at least for the moment), Maya is not a color-managed application and you must manually load the monitor ICC profile into the V-Ray frame buffer in order to match the appearance of your images in PhotoShop. |
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ICC
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
LightMix Mode
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Lens Effects
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
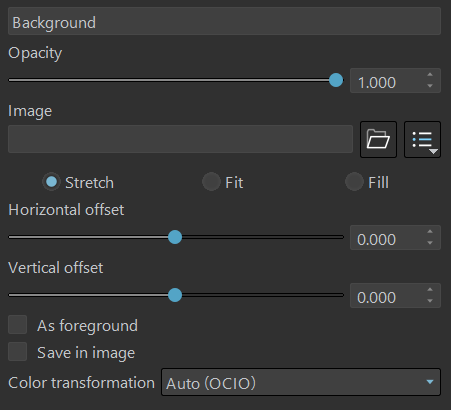
Background
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Constant
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
|
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Constant
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
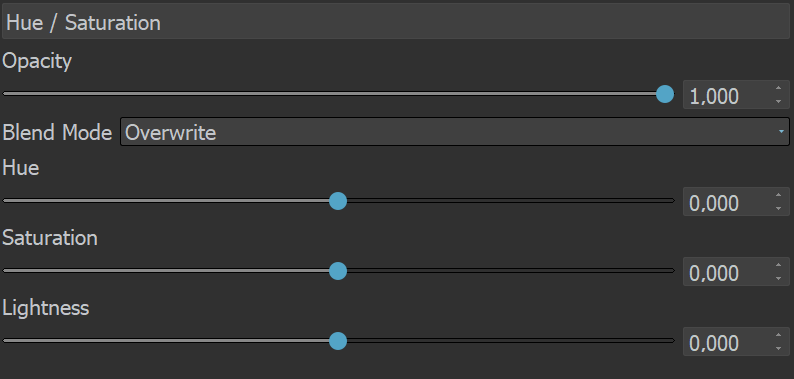
Hue/Saturation
|
Exposure
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
White Balance
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |||||||||||||||
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|
...
Hue/Saturation
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Color Balance
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Curves
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
| UI Text Box | ||
|---|---|---|
| ||
When working with .acv files, some approximations are performed because the curves in the .acv files are described by a different mathematical formulas. |
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Filmic Tonemap
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Example: Filmic Tonemap Layer
For the second image in the example below default values of the Filmic Tonemap layer are used. The type is the default Hable.
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Example: Filmic Tonemap Types
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
...
Example: Filmic Tonemap Layer
For the second image in the example below default values of the Filmic Tonemap layer are used. The type is the default Hable.
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Example: Filmic Tonemap Types
| Section | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
ICC Profile
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Sharpen/Blur
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...
Denoiser
...
| Section | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
...