This page provides information on the .vrmesh format in V-Ray for Unreal.
Overview
VRayProxy imports geometry from an external file at render time only. The .vrmesh contains all geometric information for a mesh – vertices and face topology as well as texture channels, face material IDs, smoothing groups, normals – in short, everything that is needed to render the mesh. In addition, the mesh is preprocessed and subdivided into chunks for easier access. The file also contains a simplified version of the mesh used for preview purposes in the viewports.
Unreal breaks the .vrmesh to its Face IDs, making the different elements of the mesh available for material assignment.
.vrmesh
The .vrmesh can be imported from the Content Browser > Import button.
Animated meshes cannot be represented in Unreal, but if included in an animation, the mesh is animated as well.
The elements of the .vrmesh can be assigned a V-Ray supported material through the Static Mesh Editor, or per instance via the Material category of the Details tab of the selected Actor.
Unreal does not support animated meshes, but if the imported .vrmesh is animated, rendering an animation with it exports it properly.
You can use the .vrmesh in Unreal's Foliage Scatter system.
A directly imported proxy is always represented as a high-poly mesh in the viewport.
Usage Example
Foliage Use
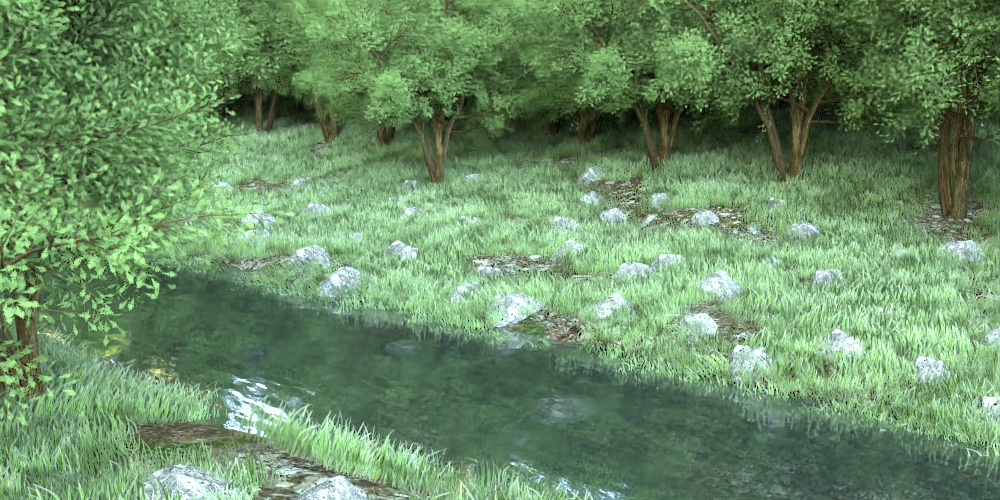
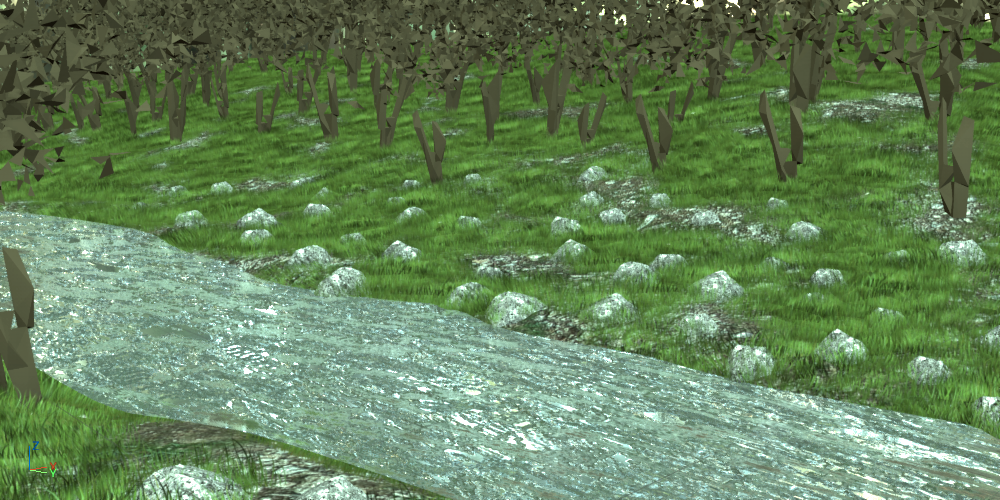
In this short example, a .vrscene file, containing a number of .vrmesh trees, is loaded.
You can preview each proxy in the StaticMesh Editor, but it is only a representation and the full geometry is revealed only when you render.
Using the Paint method, you can select a .vrmesh to scatter with around the scene.
Render to see the final result.
Bake Use
Normally, a proxy is not baked during a bake light process.
However, it is possible to import a proxy and bake it with a light map, provided the mesh has correct UV mapping.
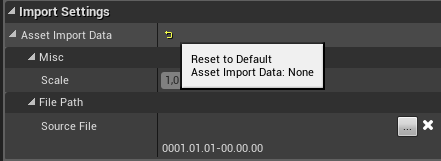
Select the proxy and go to Static Mesh > Import Settings rollout. Press the Reset to Default button, which converts the proxy to a static mesh. The static mesh can now be baked.