This page provides information about the V-Ray Override Material in Cinema 4D.
Overview
The Override Material is a utility material provided with the V-Ray renderer. It allows a surface to look different depending on whether it is seen through reflections, refractions, or GI.
With this material you get fine controls over the color bleeding, reflections, refractions, and shadows of the objects.
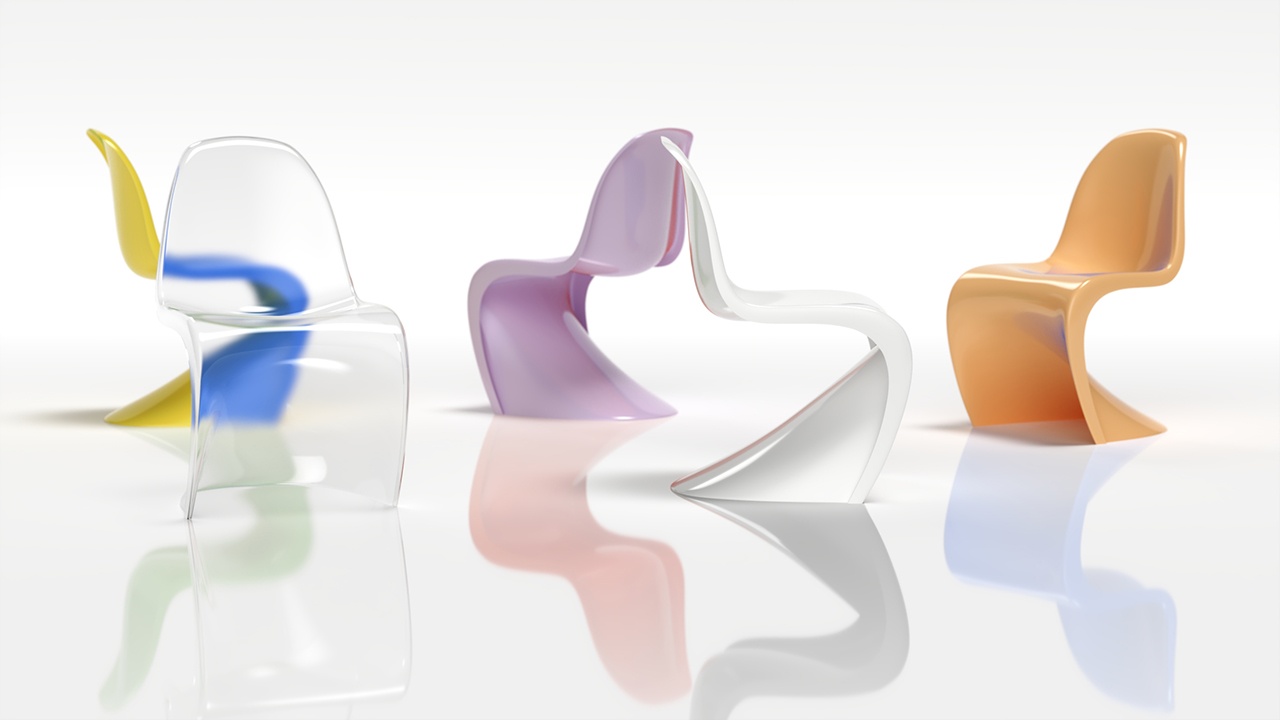
The example render here shows the use of the Override Material to create some interesting reflections and refractions of the chairs. Notice how the yellow chair changes its color when seen through a refractive material. The reflections of the colored chairs, seen in the floor, display variation of the colors as well.

UI Paths
||V-Ray|| > Override Material
||Create|| > V-Ray > Override Material (disabled Separate menu for V-Ray materials)
Parameters
Base Material – Specifies the material V-Ray uses while rendering the object.
Enable GI Material – When enabled, the specified GI Material overrides the Global Illumination in the scene.
GI Material – Specifies the material V-Ray uses while calculating the GI solution. See the Gi Material override example below for more information.
Enable Reflection Material – When enabled, V-Ray uses the specified material, when the object is seen in reflections.
Reflection Material – Specifies the material V-Ray uses, when the object is seen in reflections.
Enable Refraction Material – When enabled, V-Ray uses the specified material, when the object is seen in refractions.
Refraction Material – Specifies the material V-Ray uses, when the object is seen in refractions.
Enable Shadow Material – When enabled, V-Ray uses the specified material for the object's shadows.
Shadow Material – Specifies the material that is used to render shadows cast from the object.
Example: Using GI Material Option
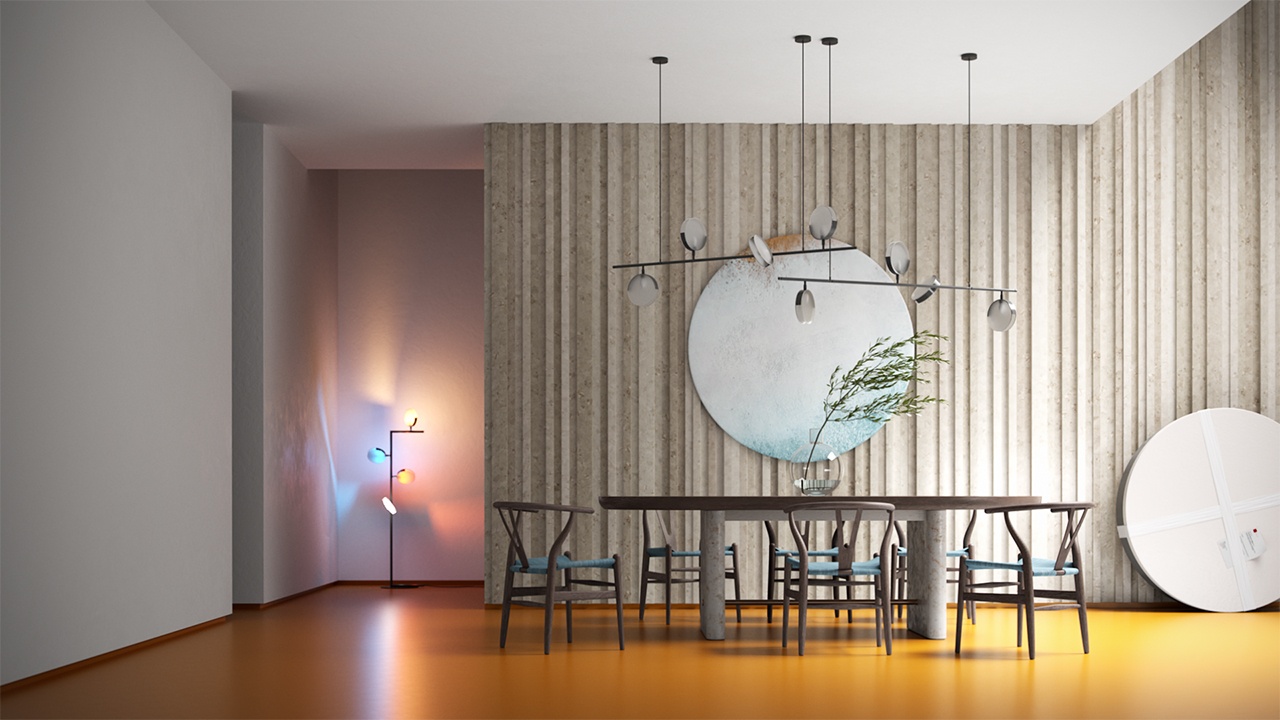
This example explores how the orange color coming from the vivid orange colored floor leaks through and colors the rest of the objects in the scene (walls, skirtings, etc.).
In the first image, it is visible that all walls, objects, and the ceiling are rendered in some light orange color. This is due to the color bleeding, generated by the GI calculations.
In the second image, the scene is rendered with a VRayOverride GI material assigned to the floor. The VRayOverrideMtl is set with a concrete gray V-Ray material for the GI Material and with the default orange material for Base Material.
So now V-Ray knows that while calculating the GI it has to use the GI material, and during rendering it uses the Base material. The result of that is quite different from the previous render as the color bleeding is gone.
For a much more complex scene, with lots of different geometry, shaders, textures, etc., using the VRayOverride material can be very helpful.

Enable Outlines – When enabled, adds outlines to the object the material is applied to. This option is disabled by default. Line Color – Determines the color of the outlines. A Texture can be applied. Line Width – Determines the width of the outlines in pixels. The soft limit is 100. Click on the arrow to expand. A Texture can be applied. Opacity – Determines how opaque the lines are. Click on the arrow to expand. You can attach a Texture for the opacity. The Mix Strength option determines the percentage of blending between the Opacity value and the texture. Outer Overlap Threshold – Determines when outlines are created for overlapping parts of the object. Lower values reduce the outer overlapping lines, while higher values produce more overlapping outer lines. Normal Threshold – Determines at what point lines are created for parts of the object with varying surface normals (for example, at the inside edges of a box). Lower values mean that only sharper normals generate an edge, while a value of 0.5 means that 90 degrees or larger angles generate internal lines. Higher values mean that smoother normals can also generate an edge. Don't set this value to pure 1.0, as this fills curved objects completely. Overlap Threshold – Determines when outlines are created for overlapping parts of the object. Lower values reduce the internal overlapping lines, while higher values produce more overlapping lines. Don't set this value to pure 1.0, as this fills the objects completely. Inner Line Control – When enabled, allows the inner line to be edited further. This option is disabled by default. Inner Line Color – Determines the color of the inner lines. A Texture can be attached Inner Line Width – Determines the width of the inner lines in pixels. Click on the arrow to expand for the Texture option, where you can attach a texture to serve as the inner line width.Outlines
Inner Line Control
Options
Material Id Enabled – Enables the use of Material ID.
Material ID – The color used by the Material ID render element. You can also use a shader here.
Multimatte ID – The integer ID of the material to be used by the Multi Matte render element.
Round Edges Enabled – Enables the Round Edges effect, which uses bump mapping to smooth out the edges of the geometry during render time.
Radius – Specify a radius (in world units) for the Round Edges effect. Since the actual geometry is not being changed and only the normals of the faces are affected, large values may produce undesirable effects.
Consider Same Object Only – When enabled, the rounded corners are produced only along edges that belong to the object, which has the attribute applied. When disabled, rounded corners are also produced along edges formed when the object with the attribute intersects other objects in the scene.
Corners – Choose which edges are considered in the calculation. Possible options are:
Convex and Concave – Considers all edges.
Convex Only – Only applies Round Edges effect to edges with convex angles.
Concave Only – Only applies Round Edges effect to edges with concave angles.
Preview Settings
Override Preferences – When enabled, the parameters in this tab override the global preferences of the scene for the selected material.
Enable Preview – When disabled, the previews of the material in the Viewport and the Material Editor are disabled. The material is displayed in all black. This saves on processing power.
Enable Global Illumination – When disabled, global illumination is not calculated for the current material preview.
Quality – Determines the quality of the material previews. Higher values give more detail but slow down processing.
Editor Map Size – Determines the resolution of the material preview. If you have extra-detailed textures applied to the material, this option allows you to preview those textures in higher resolution at the preview step, without needing to render.
Default
64×64 (16 KB)
128x128 (64 KB)
256x256 (256 KB)
512x512 (1 MB)
1024x1024 (4 MB)
2048x2048 (16 MB)
4096x4096 (64 MB)