This page provides details on the settings for the GLSL Material in V-Ray.
Overview
The VRayMtlGLSL and VRayTexGLSL nodes can be used to load GLSL shaders (.frag, .glsl files) or V-Ray precompiled fragment shaders (.pfrag files) and render them directly with V-Ray. If the shader file describes a material (rather than a texture), it can be rendered with a VRay GLSL Material or by assigning a VRayTexGLSL map to the color slot of a VRayLightMtl material.
Note that both VRayGLSLMtl and VRayTexGLSL share the same user interface.
This material and the VRayTexGLSL map are part of the first stage of V-Ray implementation of GLSL support. In this version of V-Ray, the shaders are compiled to byte code for a software virtual machine, which is then interpreted. Due to this run-time interpretation, GLSL shaders can be somewhat slower to render than V-Ray shaders written in C++. In future builds of V-Ray, shaders will be directly compiled to machine code for faster rendering.
Basic Parameters
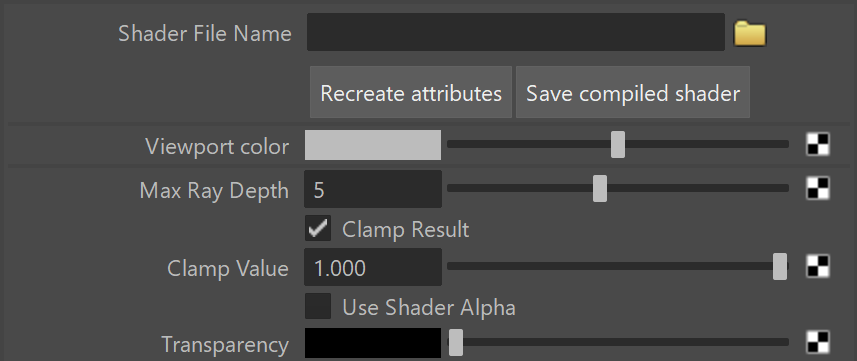
Shader File Name – Specifies the .glsl, .frag, or .pfrag file which contains the shader code.
Recreate attributes – Reloads the shader and recreate its parameters.
Save compiled shader – Saves the shader file as a binary precompiled fragment shader file (.pfrag ).
Viewport color – Specifies the diffuse component of the material used in the viewport shading.
Max Ray Depth – Specifies the maximum reflection/refraction depth for the shader.
Clamp Result – Determines whether to force the result in the [0, Clamp Value] range or not.
Clamp Value – Specifies the upper clamp limit if Clamp Result is enabled.
Use Shader Alpha – Uses the alpha calculated in the shader.
Transparency – Overrides the alpha if Use Shader Alpha off.
Shader Attributes
This section holds all parameters found in the shader itself and can be edited from here.
GPU Support
The GLSL shader is supported by V-Ray GPU within limitations. Below you can find detailed information about the GPU support.
| Feature | GPU Support |
|---|---|
| Built-in variables | |
| gl_NormalMatrix | Always identity matrix. |
| gl_ModelViewMatrixTranspose | Always identity matrix. |
| gl_TextureMatrix | Always identity matrix. |
| gl_TextureMatrixInverse | Always identity matrix. |
| gl_TextureMatrixInverseTranspose | Always identity matrix. |
| gl_TextureMatrixTranspose | Always identity matrix. |
| gl_ModelViewMatrixInverseTranspose | Always identity matrix. |
| gl_FogFragCoord | Always is a zero. |
| gl_TexCoord[] | All gl_TexCoord[] elements are identical, i.e. multiple UVW channels are not supported. 1 |
| Built-in functions | |
| dFdx(); dFdy() | Always return zero. |
| fwidth() | Always returns zero. |
V-Ray extensions to GLSL | |
| vr_Velocity | Always is a zero. |
| vr_NumSuperSamples | Always is 1. |
| vr_SuperSampleIndex | Always is 1. |
| vr_TextureDu[] | Not supported. |
| vr_TextureDv[] | Not supported. |
| vr_VertexData[] | Not supported. |
| vr_FrameData | Only the following are supported: vr_FrameData.focalLength |
| vr_trace() | Not supported. |
| vr_evalLight() | Not supported. If attempted to call it will assign the following constants to the output light iterator: light.dot_nl = -1.0 |
| vr_intersect() | Not supported. |
| BRDF | Only the following BRDF calls are supported 2: vr_brdf_diffuse() |
| Keywords | The following keywords are ignored: __channel __persistent __native |
References
- Randi J. Rost et al, OpenGL Shading Language, second edition, Addison-Wesley, 2006
- Lighthouse3D.com (link no longer active) - a useful site that describes the basics of GLSL and has many shader examples
Footnotes
1 – This is still work in progress.
2 – Experimental feature.