The Translucency tab is part of the V-Ray Material parameters.
Parameters
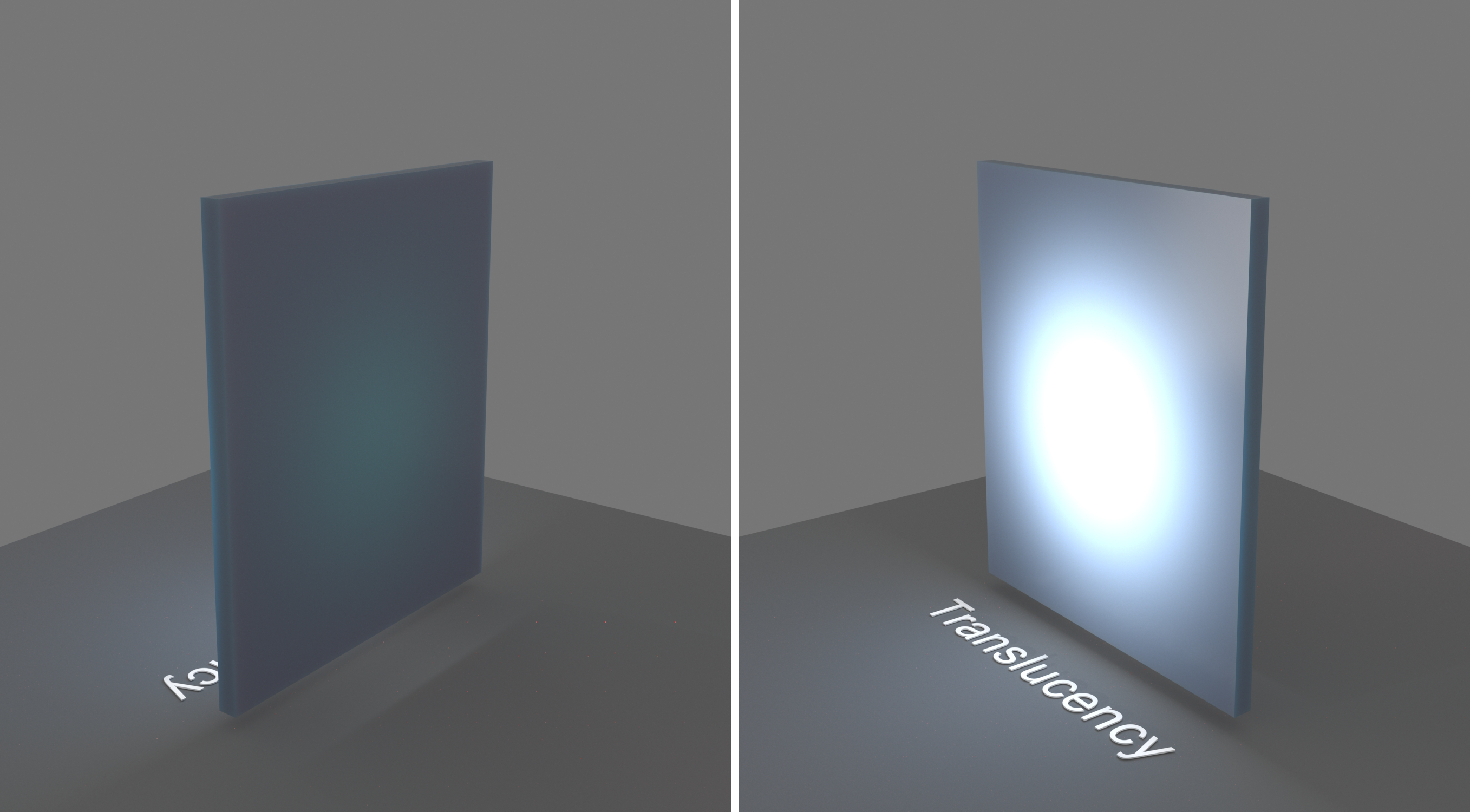
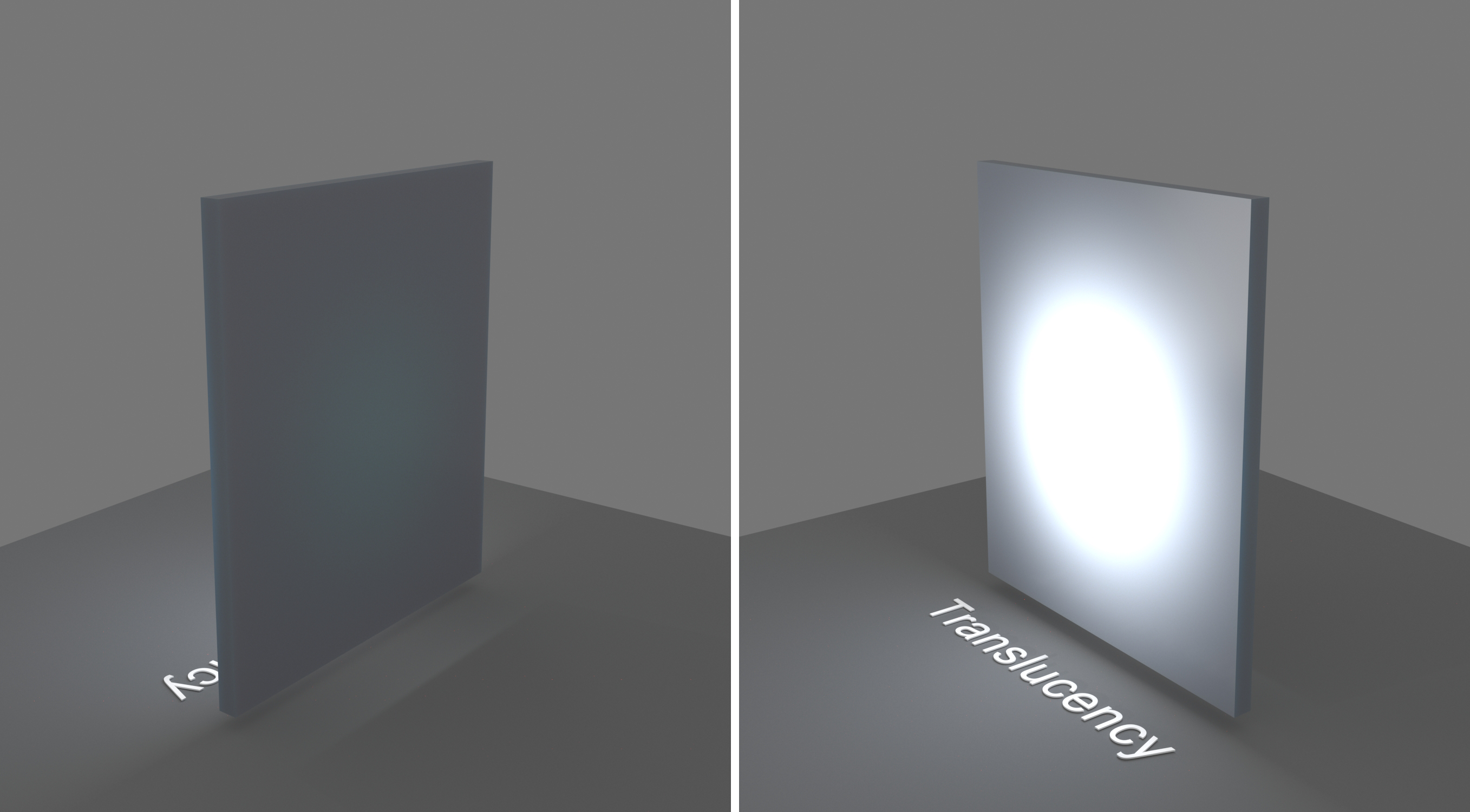
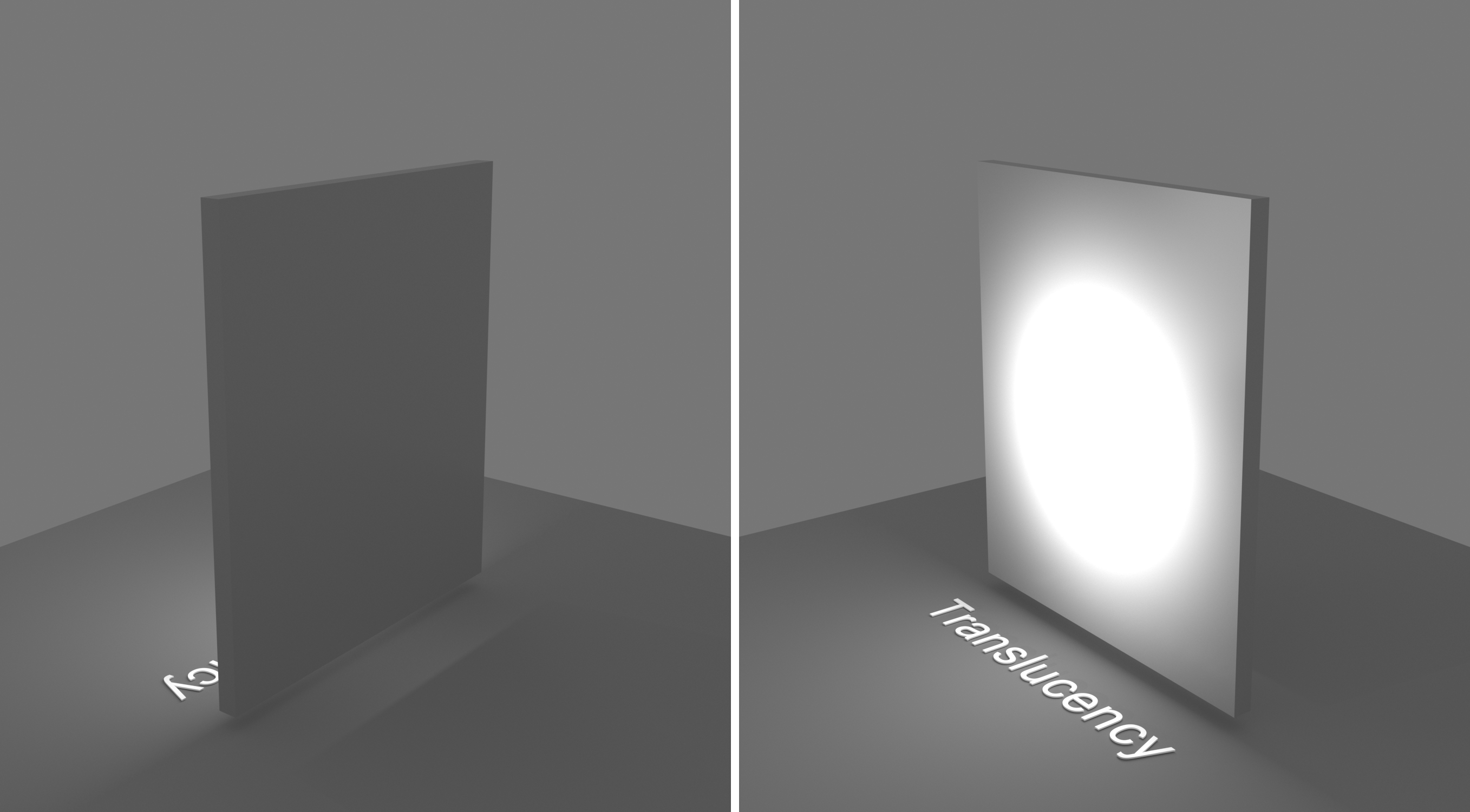
Type – Selects the algorithm for calculating translucency (also called sub-surface scattering). Note that refraction must be enabled for this effect to be visible.
None – When selected, the only available parameters are the Fog Color and Fog Depth. Together with the Refraction Color, they determine the attenuation of light as it passes through the material. In this mode, there is no subsurface scattering.
Volumetric – Works together with the Refraction Color of the material to scatter light inside the object. It is useful for liquids and other highly transparent materials. The Refraction Color and Refraction Glossiness determine respectively how much of the interior of the object is visible and how rays interact with the object’s surface.
SSS – Works independently of the Refraction Color/Glossiness and is useful for skin, wax, marble and other relatively opaque materials.
As the new translucency modes perform multibounce volumetric light scattering, they require closed objects.
None
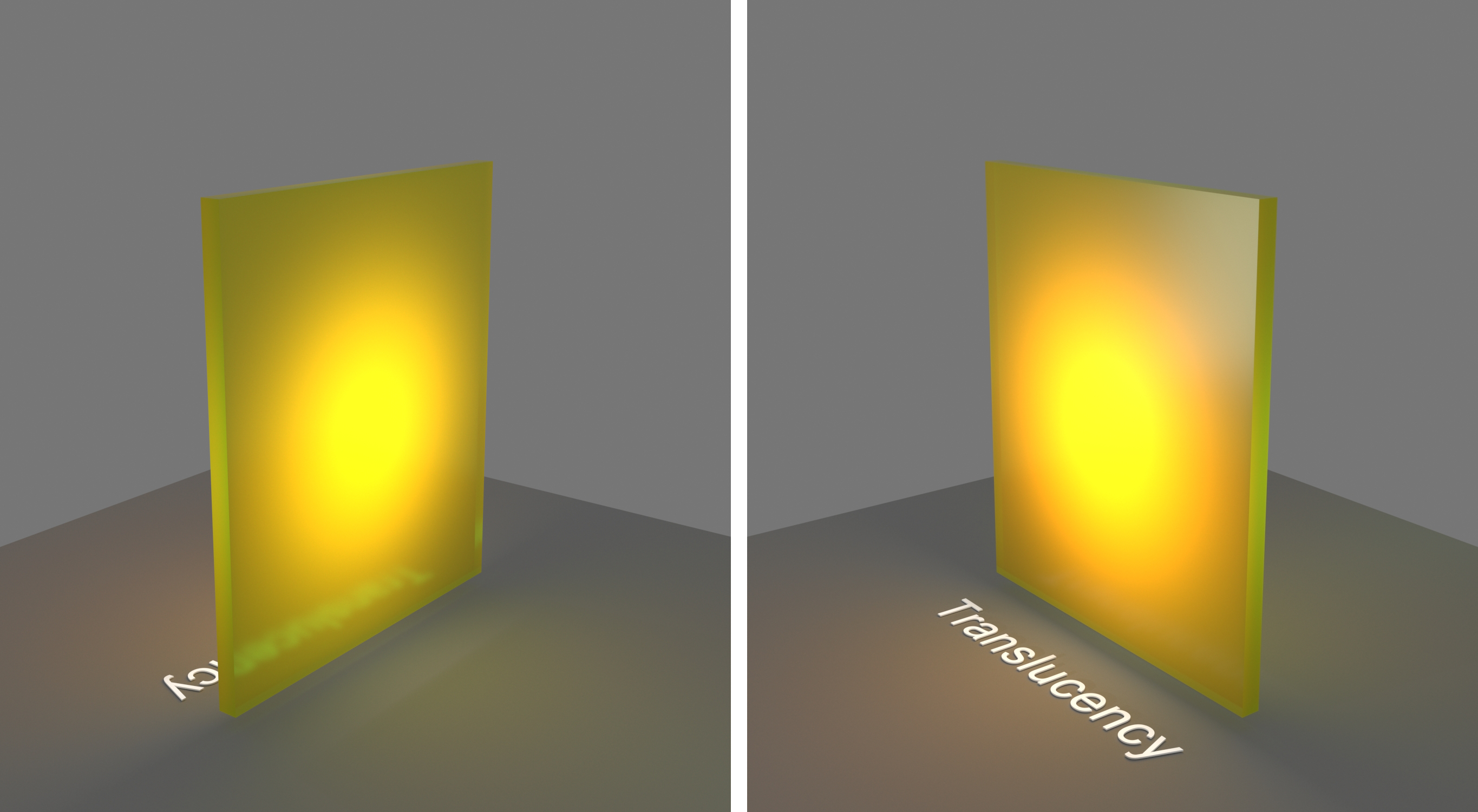
Fog color – Specifies the attenuation of light as it passes through the material. This option allows you to simulate the fact that thick objects look less transparent than thin objects. Note that the effect of the fog color depends on the absolute size of the objects and is therefore scene-dependent unless the Treat Scale as Meters is enabled. This parameter also determines the look of the object when using translucency. This parameter can be mapped with a texture. It is recommended that you use a 3D texture for the purpose. See the Fog color example below.
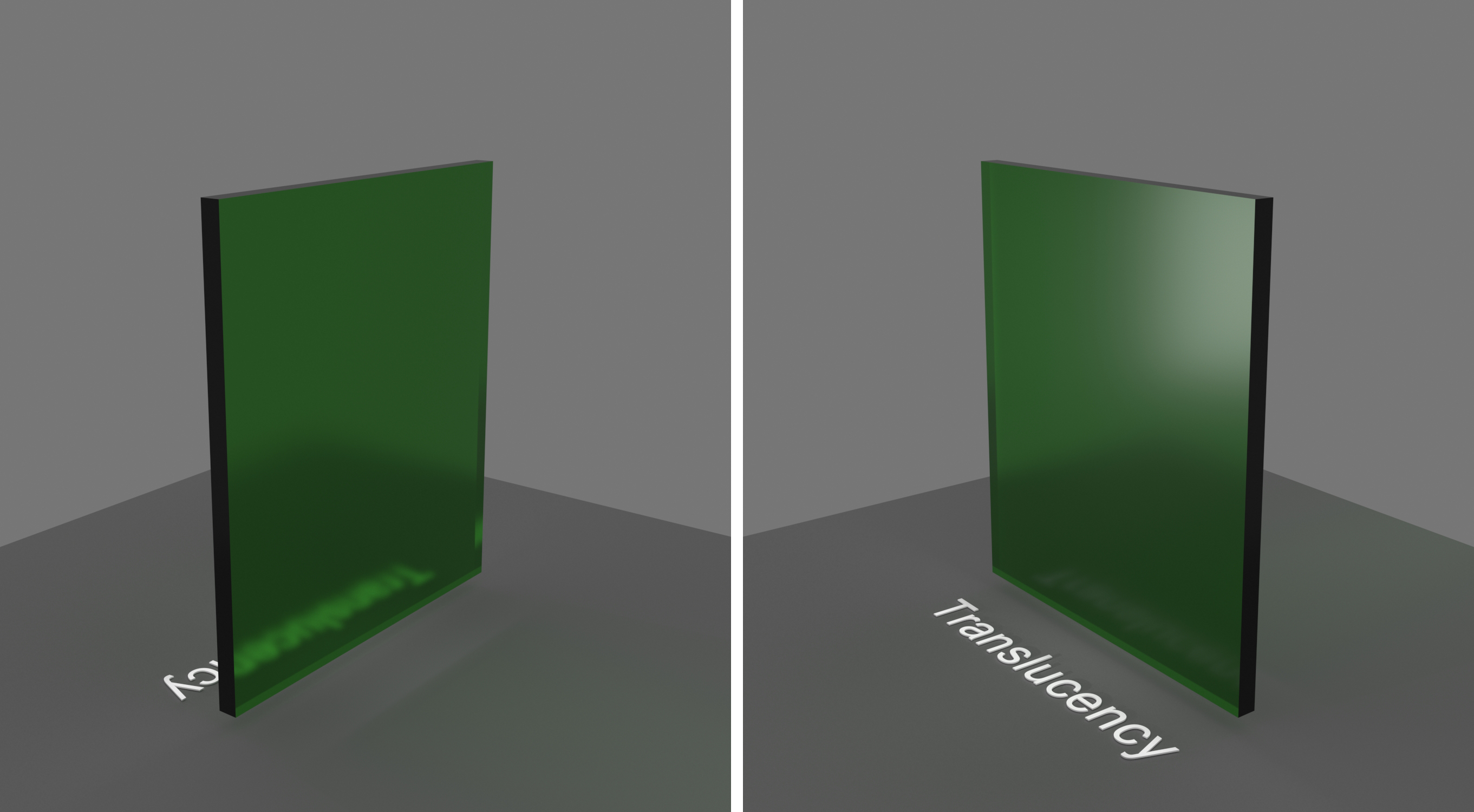
Depth (m) – Controls the strength of the fog effect. Higher values reduce the effect of the fog, making the material more transparent. Smaller values increase the fog effect, making the material more opaque. See the None Depth example below.
Volumetric
Method – Determines how illumination is computed for sub-surface scattering. This option is not supported on V-Ray GPU.
Directional – Scatters more light in the direction from which a light source illuminates the surface. This method requires the Affect Shadows option to be enabled so that shadows extend below the surface. Directional Illumination Method may also produce a faceted look on low-poly objects.
Uniform – Scatters light uniformly inside the material. Useful for recreating skin and such translucent materials.
Amount – Blends between full scattering and pure refraction.
Fog color – Controls the absorption of the material.
Depth (m) – Controls the strength of the fog effect. Higher values reduce the effect of the fog, making the material more transparent. Smaller values increase the fog effect, making the material more opaque.
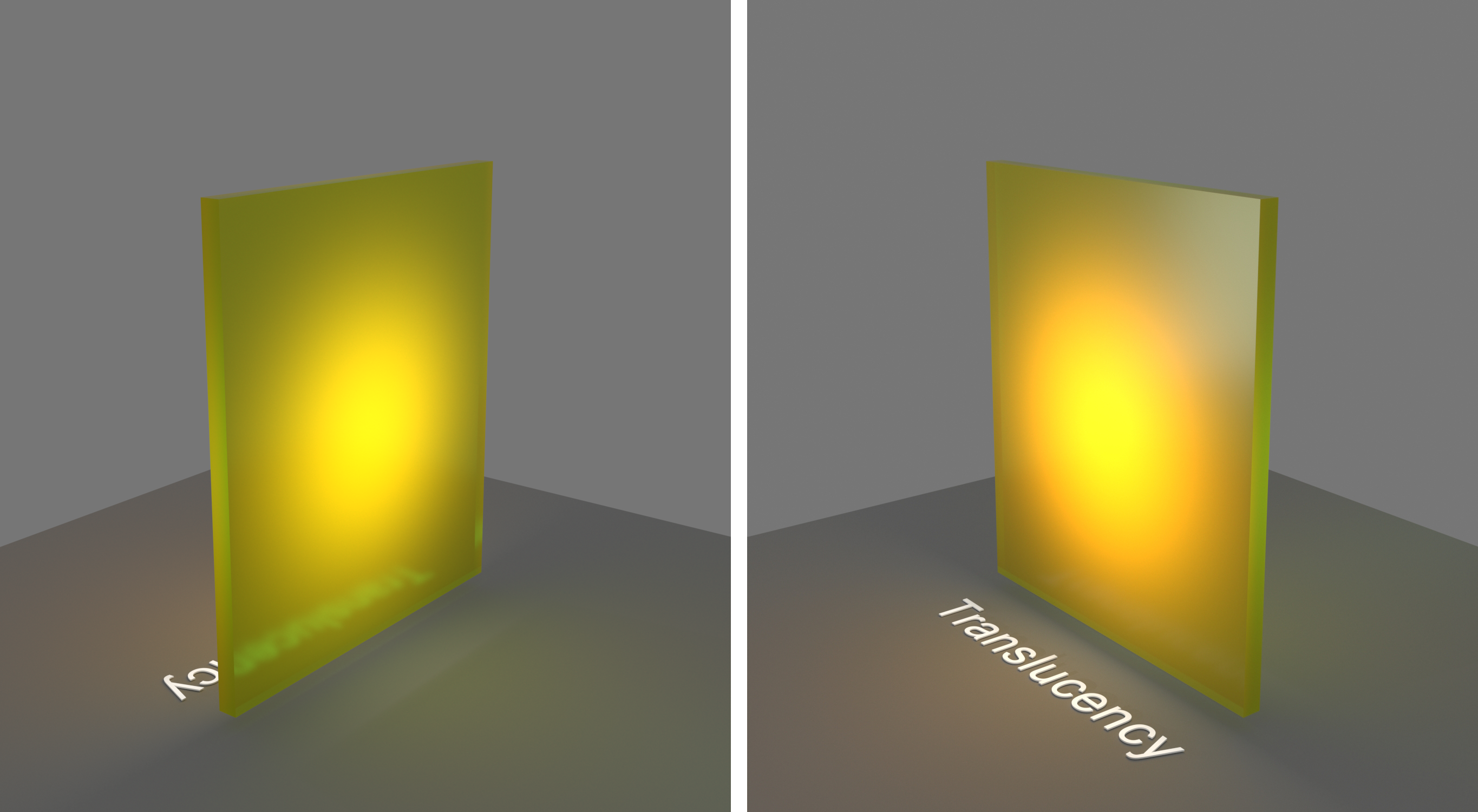
Scatter Color – Filter color for the translucency effect. See the Scatter Color example below.
SSS
Method – Determines how illumination is computed for sub-surface scattering. This option is not supported on V-Ray GPU.
Directional – Scatters more light in the direction from which a light source illuminates the surface. This method requires the Affect Shadows option to be enabled so that shadows extend below the surface. Directional Illumination Method may also produce a faceted look on low-poly objects.
Uniform – Scatters light uniformly inside the material. Useful for recreating skin and such translucent materials.
Amount – Blends between the diffuse color of the material and the SSS effect by reducing the diffuse component of the material and replacing it with the sub-surface scattering effect.
Scatter Radius – Controls how far each of the red/green/components travels inside the volume.
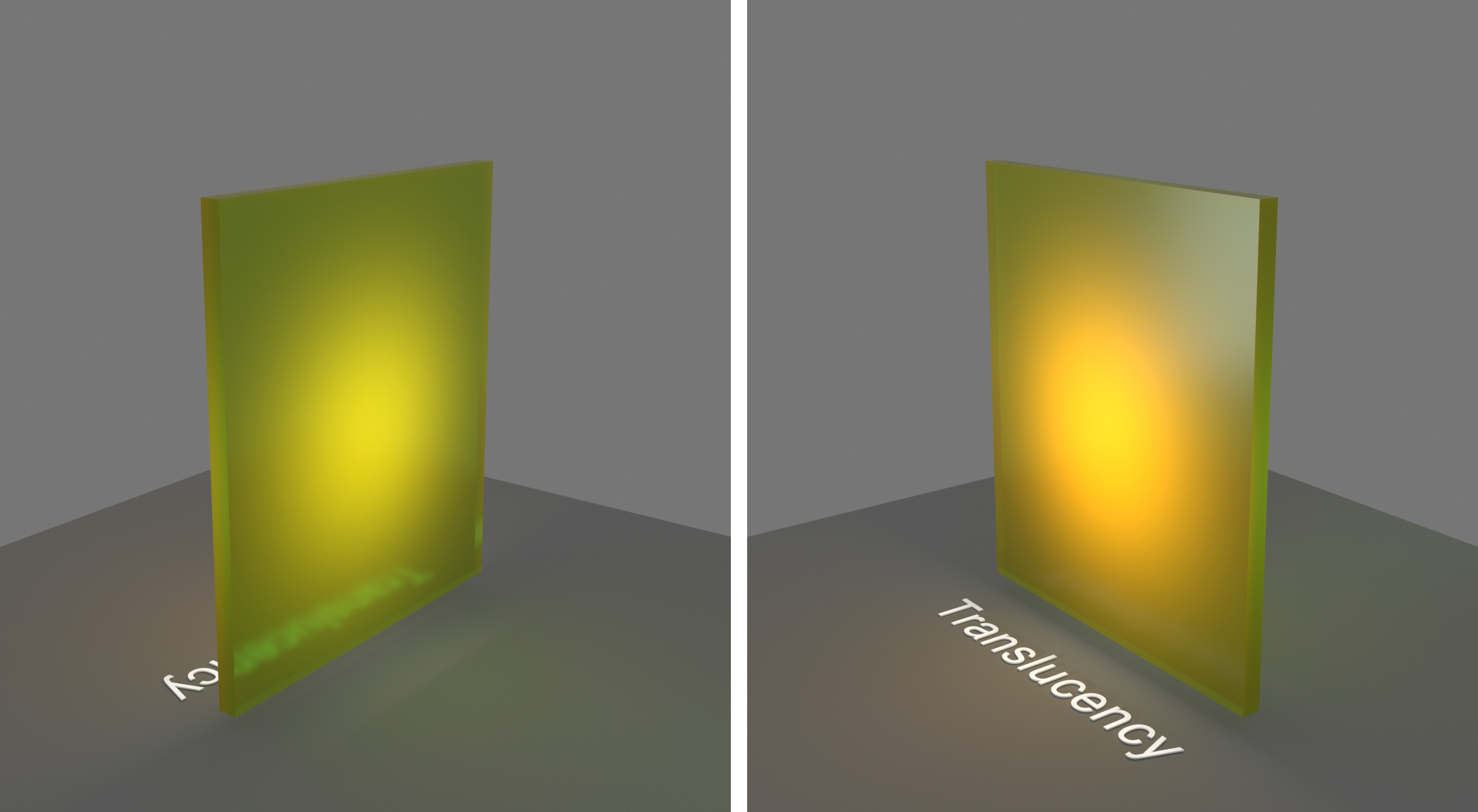
Scale (cm) – Controls the strength of the SSS effect. See the Scale (cm) example below.
SSS Color – Determines the overall surface appearance.
None
Volume translucency mode
SSS translucency mode
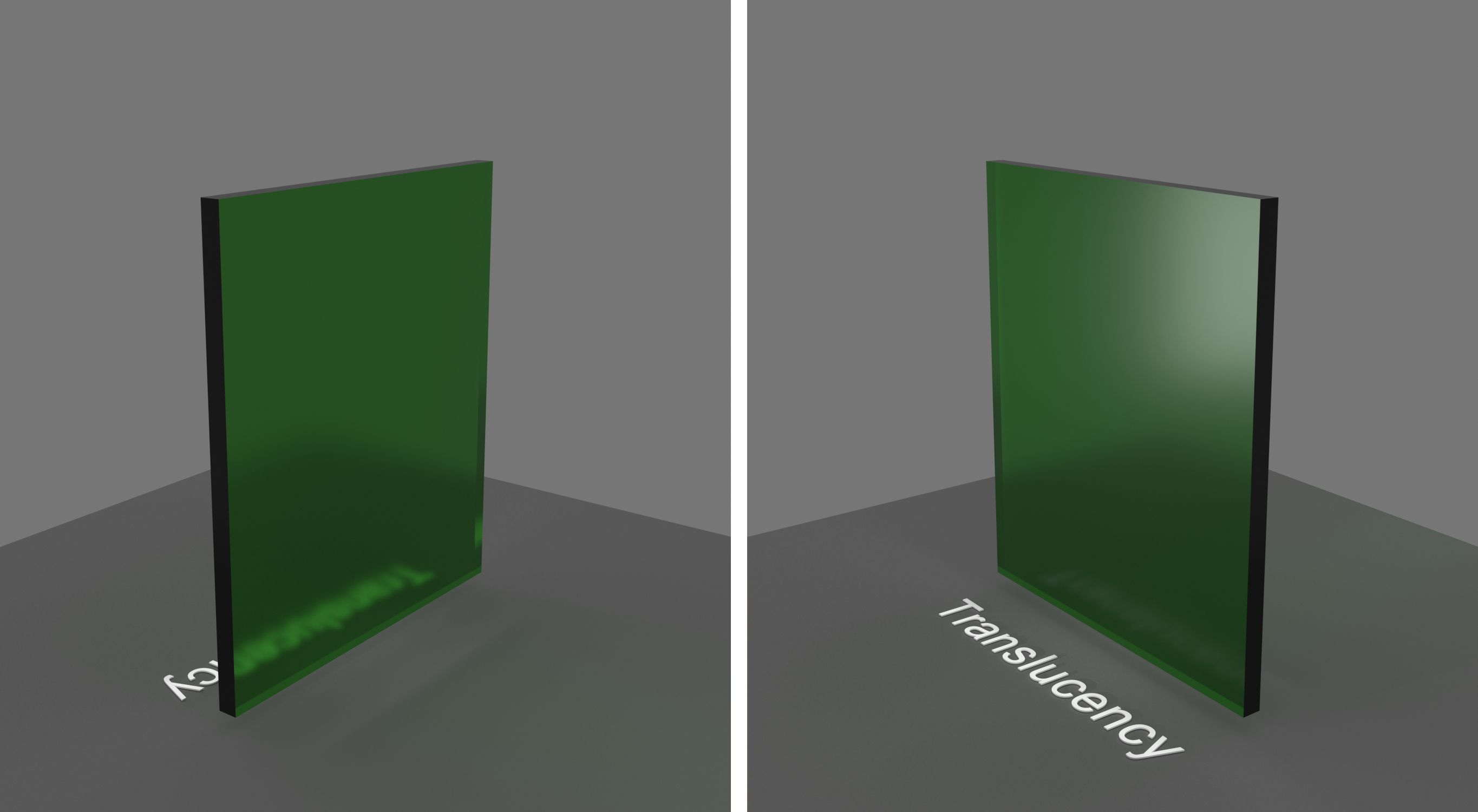
Example: Fog Depth
This example demonstrates the effect of the Depth parameter. Translucency is set to None.
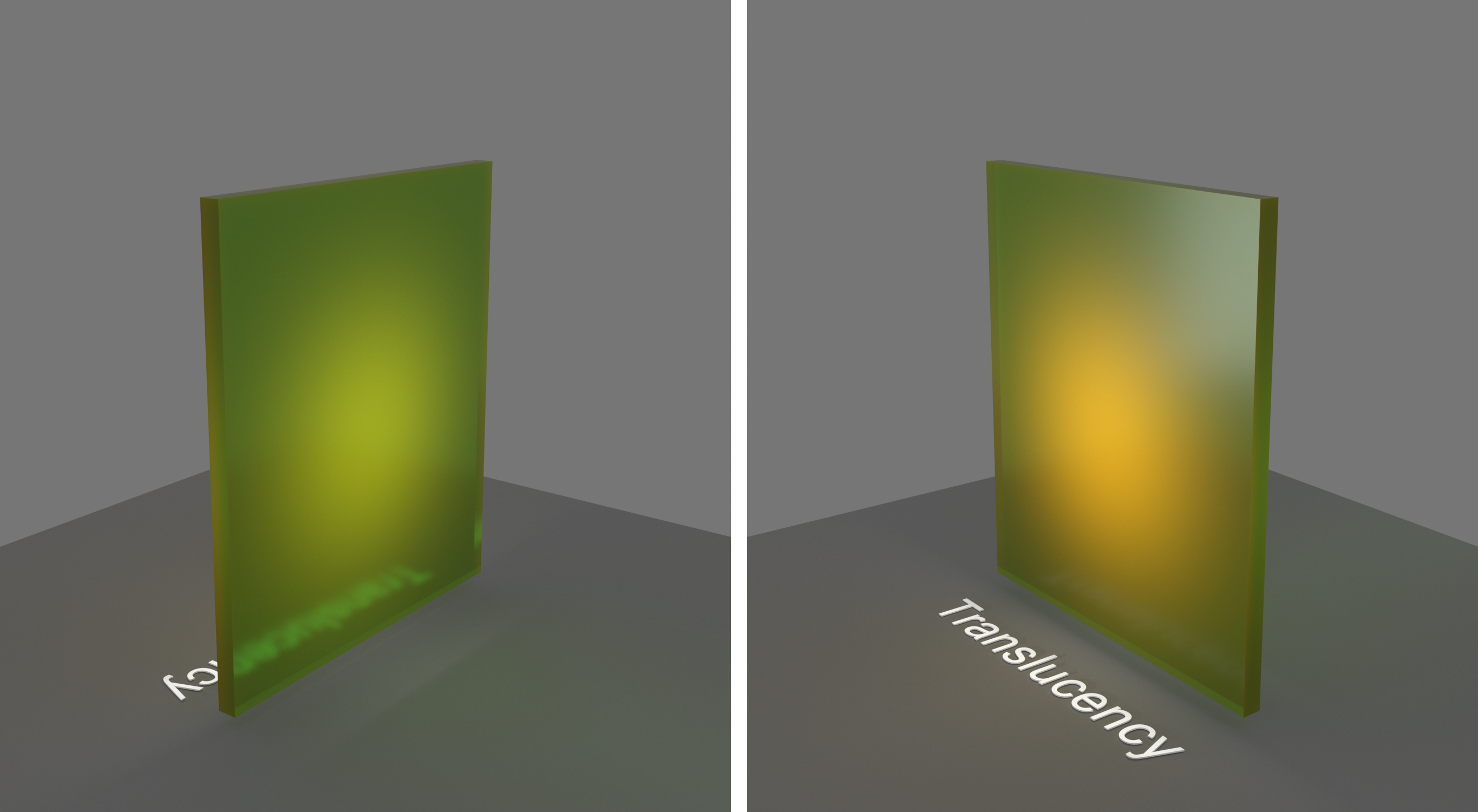
Example: Fog Color
This example demonstrates the effect of the Fog color parameter. Notice that we are changing
the hue value of the Fog color. Translucency is set to None.
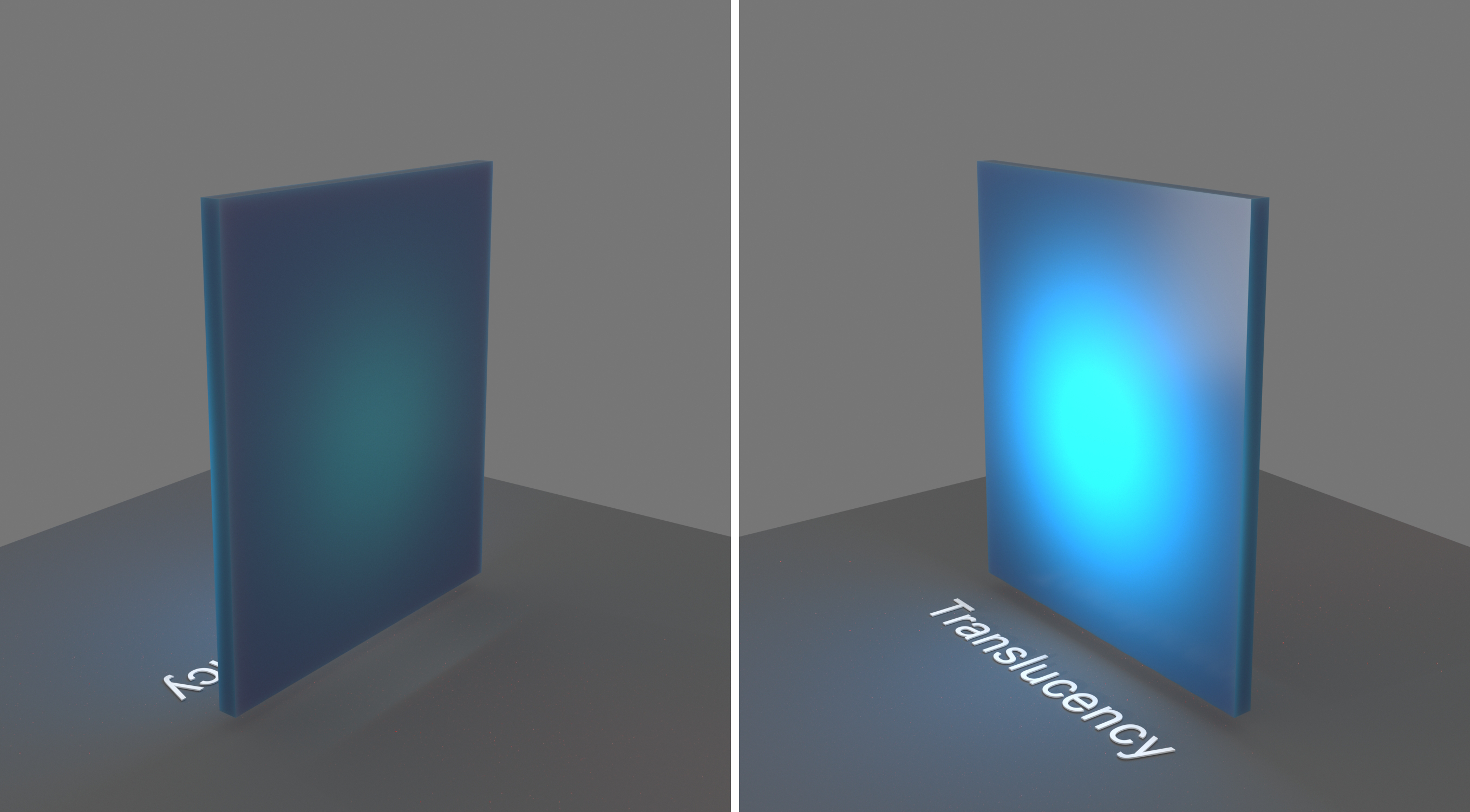
Example: Scatter Color
This example demonstrates the effect of the Scatter color parameter. Translucency is set to
Volumetric.
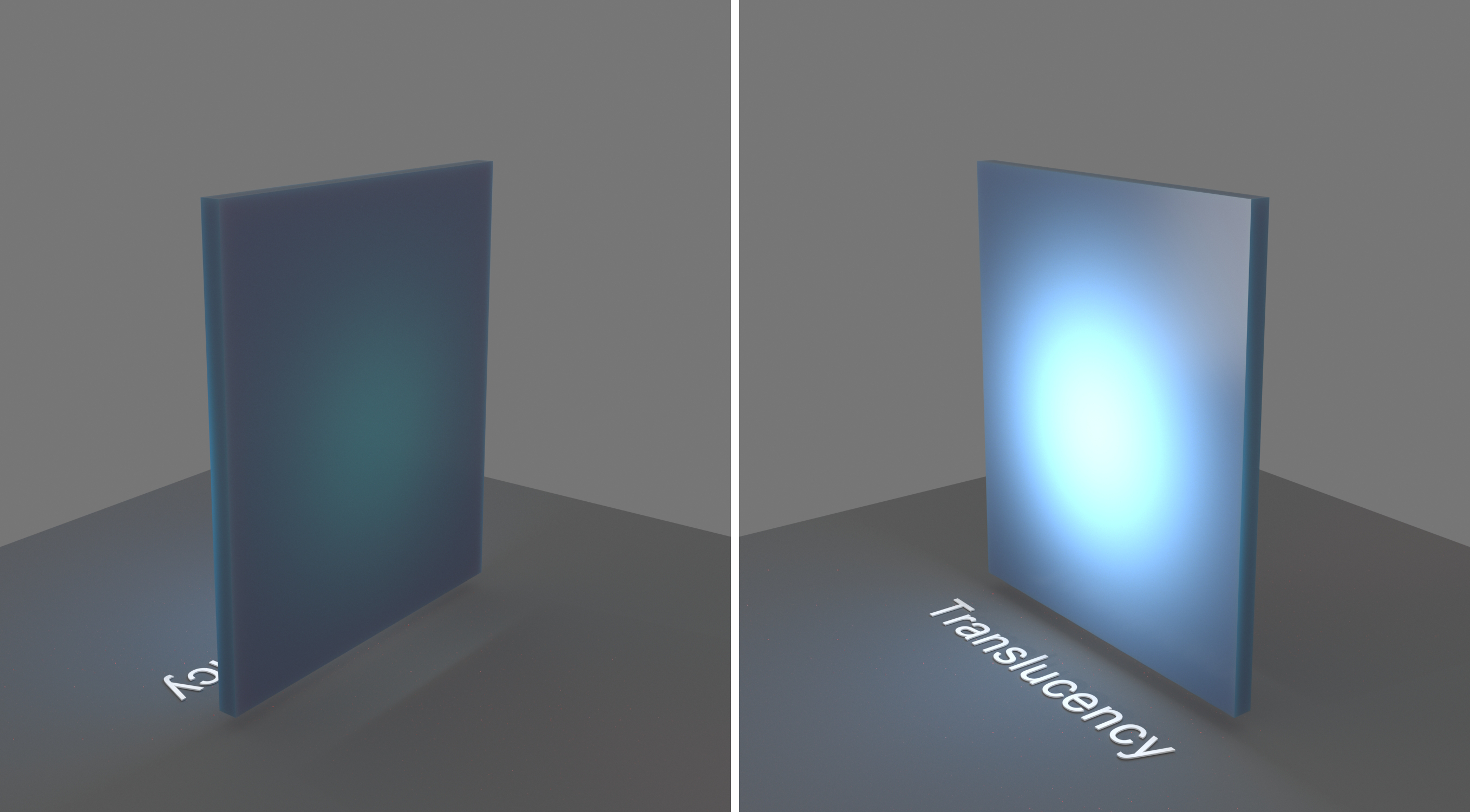
Example: Scale (cm)
This example demonstrates the effect of the Scale (cm) parameter. Translucency is set to SSS.