This page introduces you to the VRayMtl, which is the major building block for most shading networks in V-Ray.
Overview
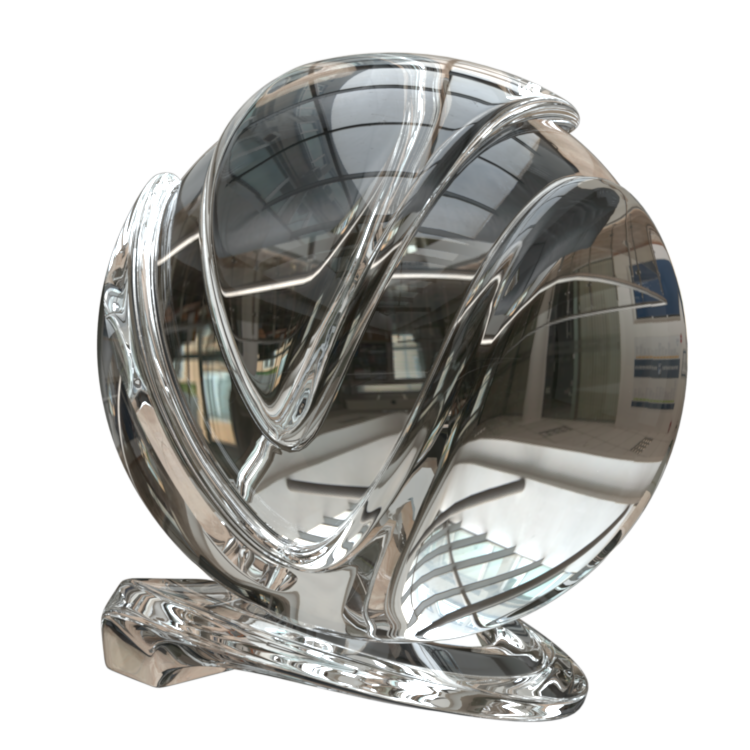
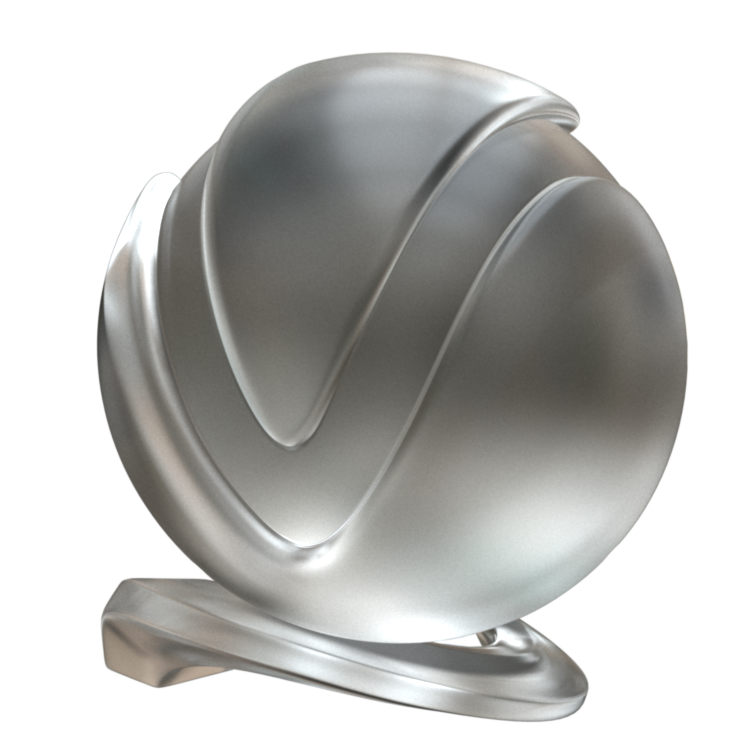
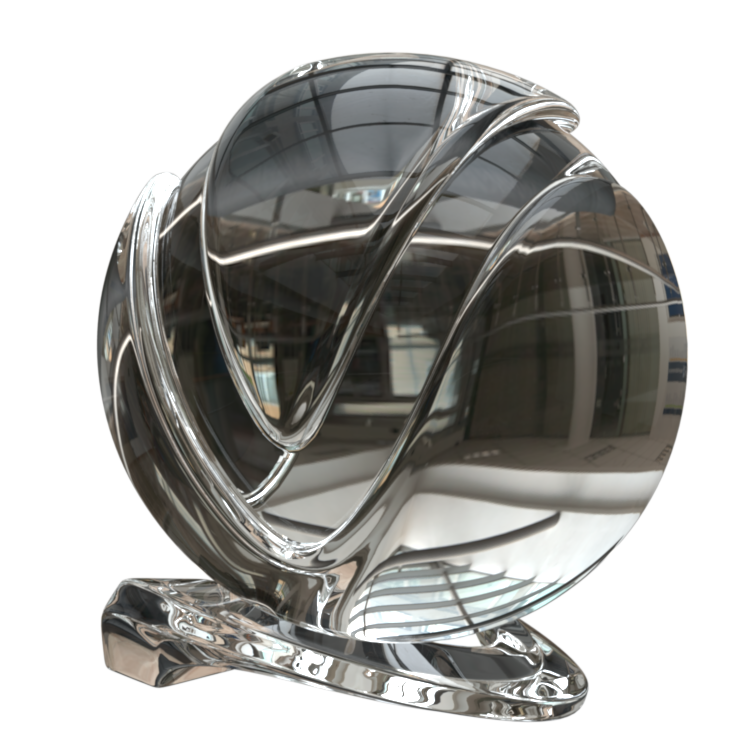
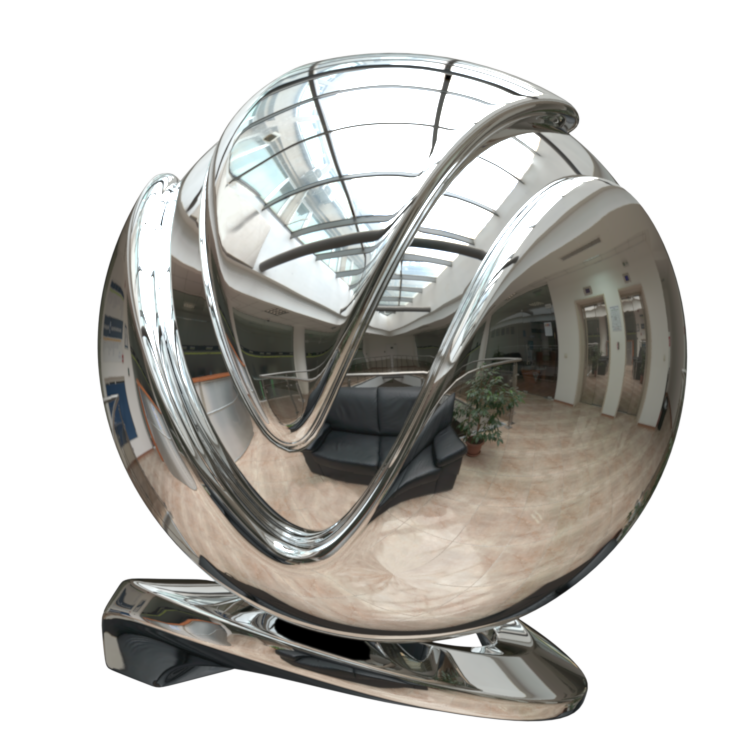
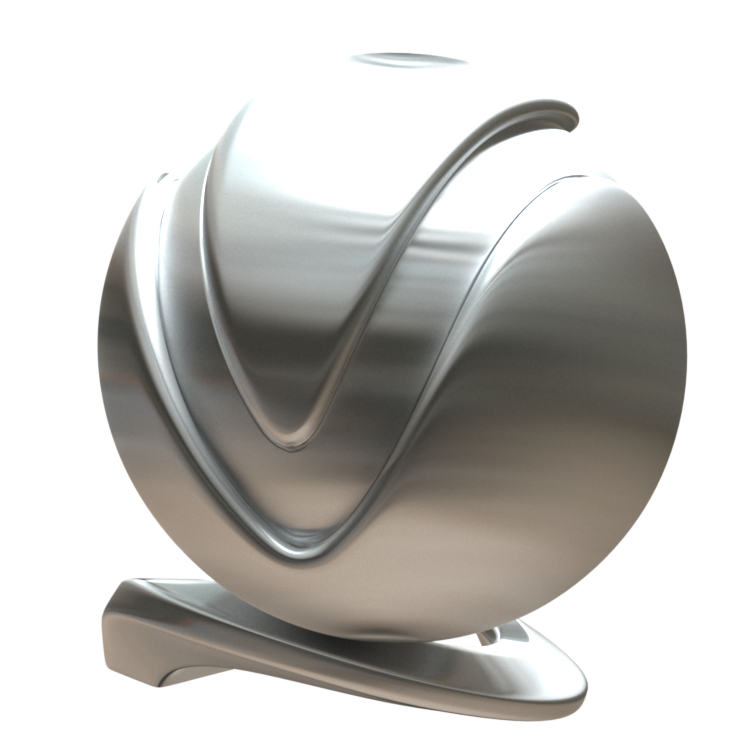
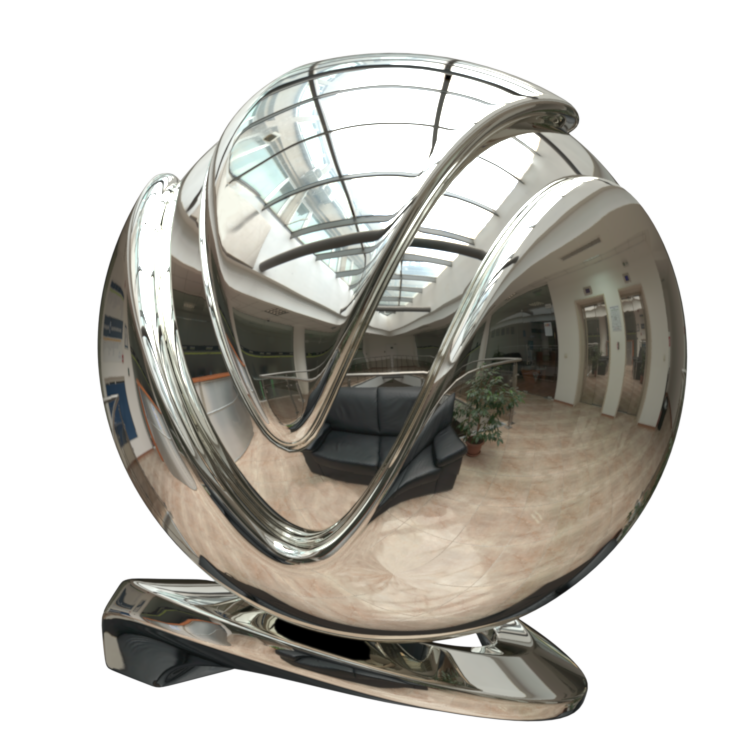
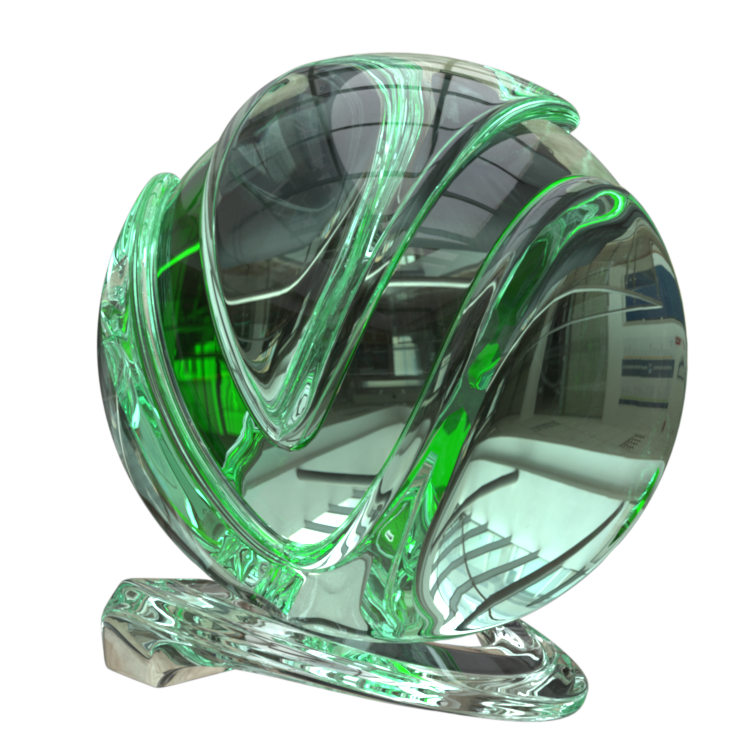
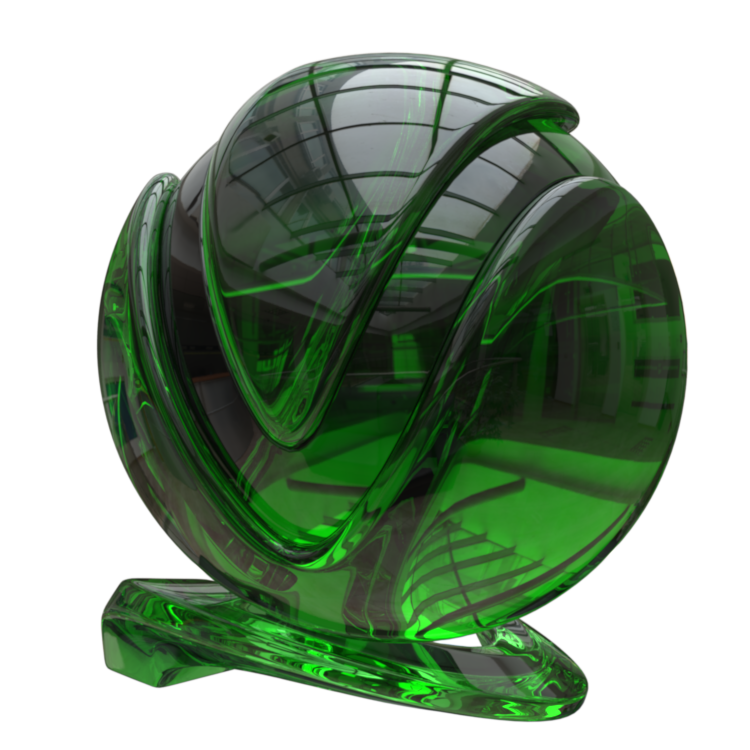
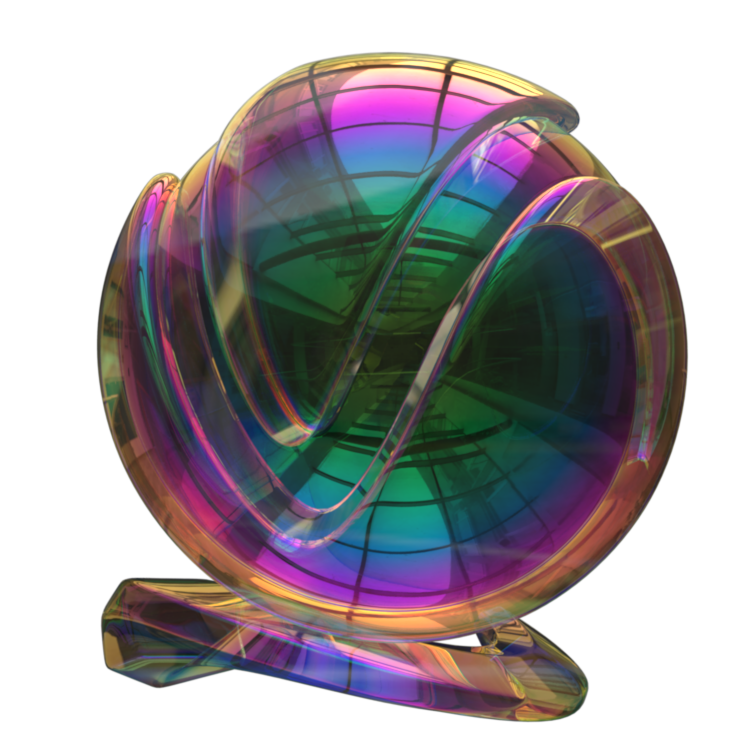
The VRayMtl is a very versatile material that allows for better physically correct illumination (energy distribution) in the scene, faster rendering, and more convenient reflection and refraction parameters. This material can be easily set up to simulate a huge variety of surfaces from plastics to metals to glass and more by adjusting a handful of parameters.
Furthermore, with the VRayMtl you can apply different texture maps, control the reflections and refractions, add bump and displacement maps, force direct GI calculations, and choose the BRDF for how light interacts with the surface material.
Read more about the Basic Parameters that control properties like the diffuse and opacity colors, or the articles on Reflection, Coat Layer, Refraction, Sheen Layer, Bump and Normal Mapping and the Options of VRayMtl.
For advanced information on the V-Ray Material structure, see the V-Ray Material Structure page.
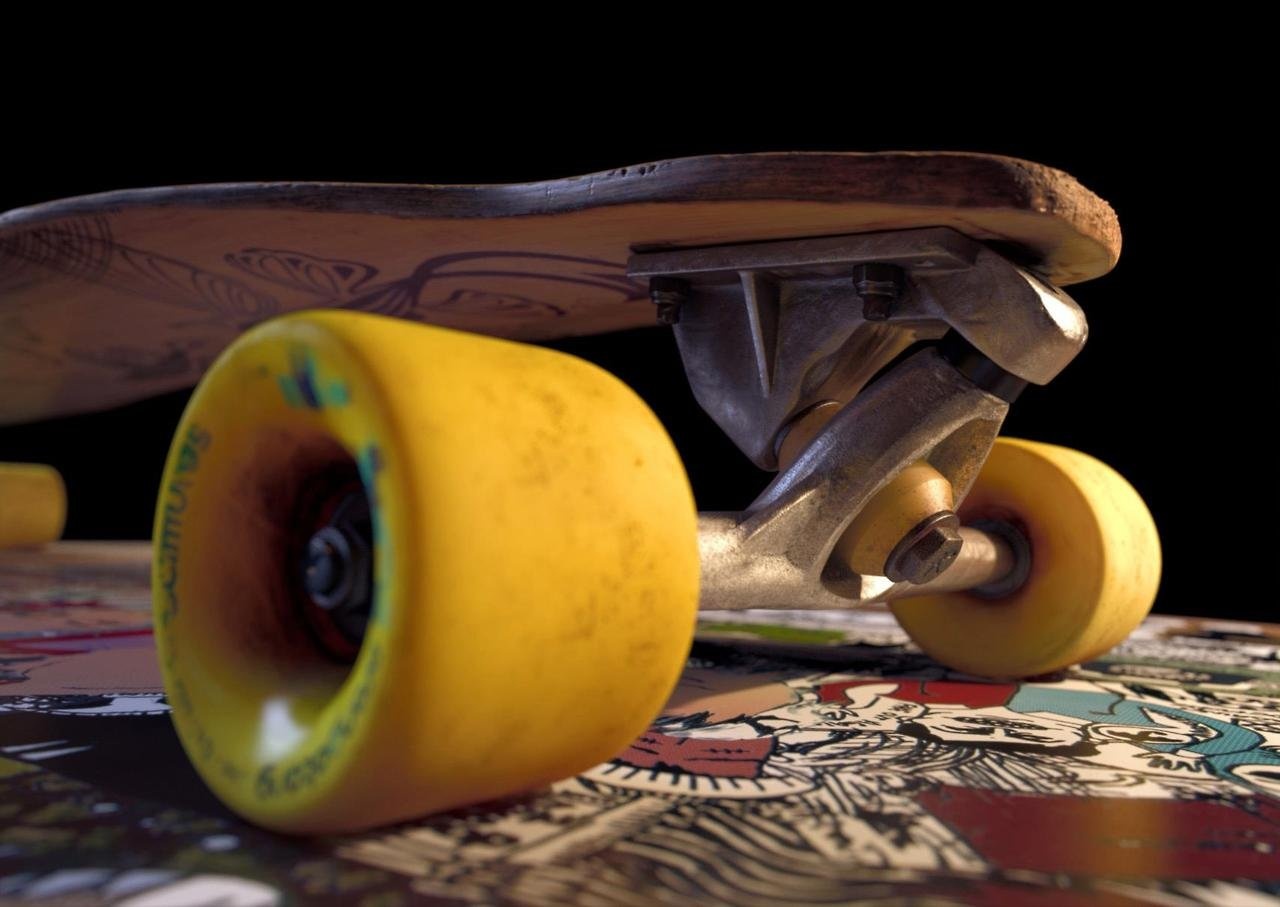
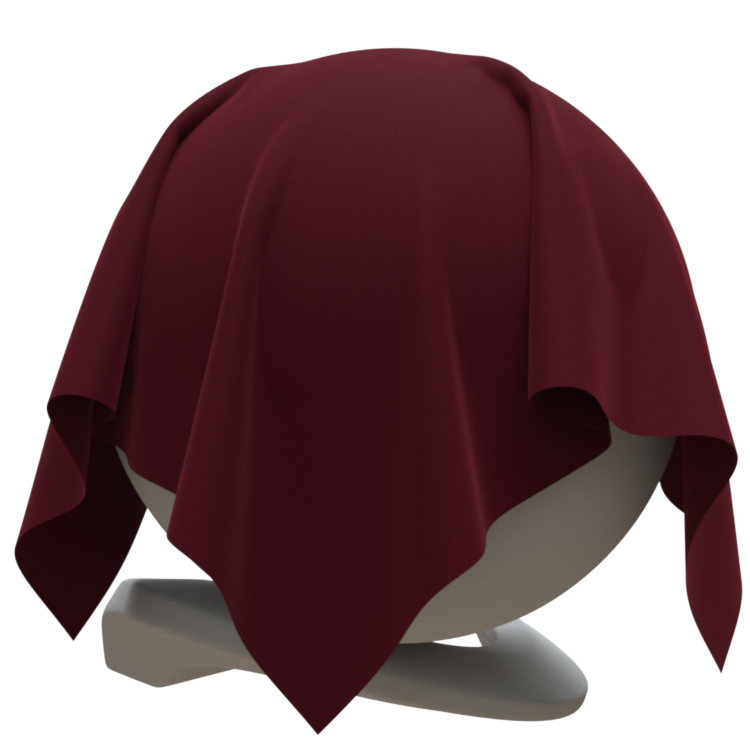
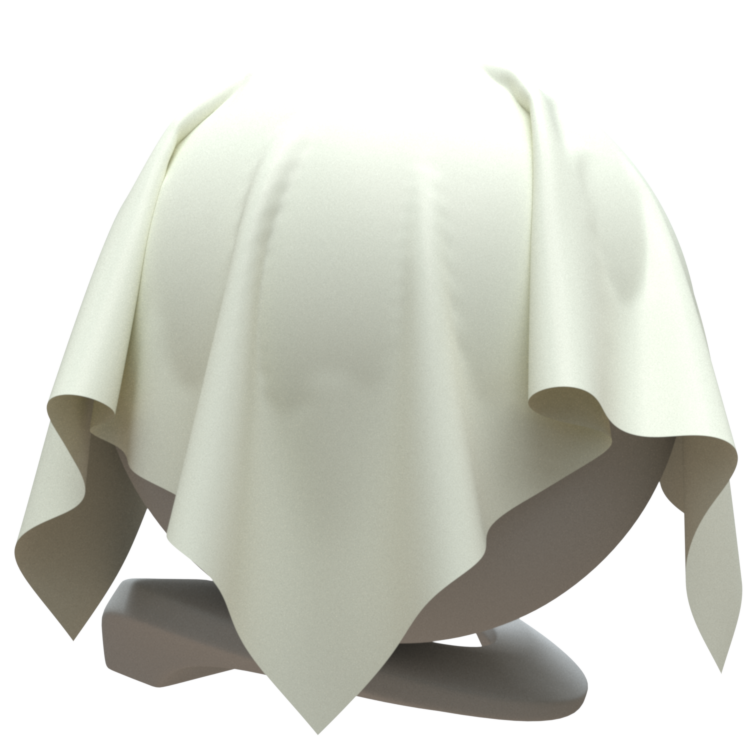
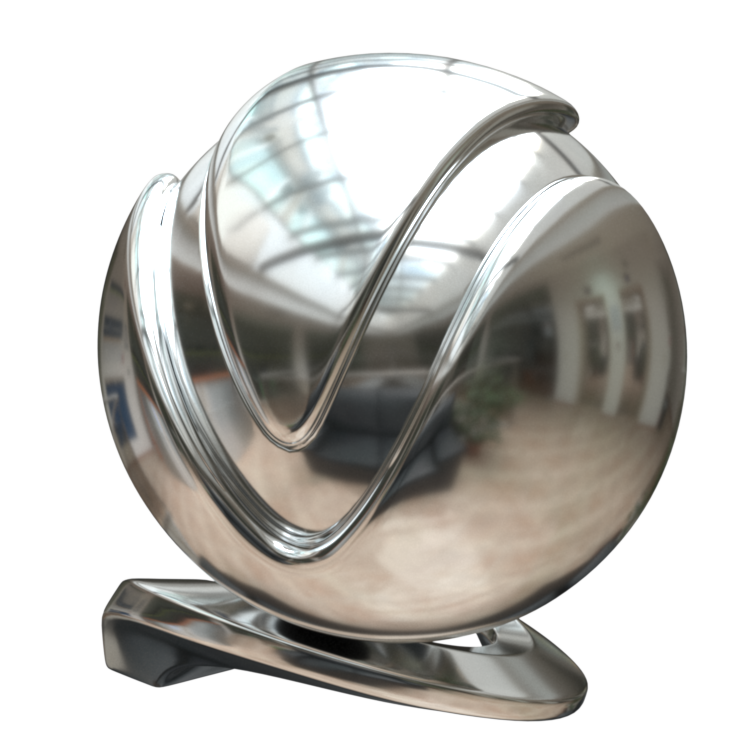
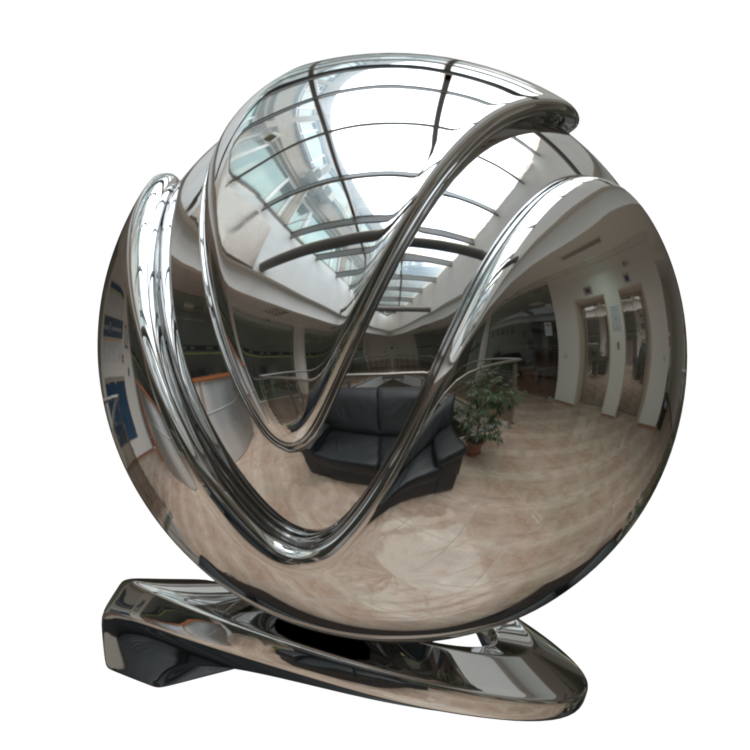
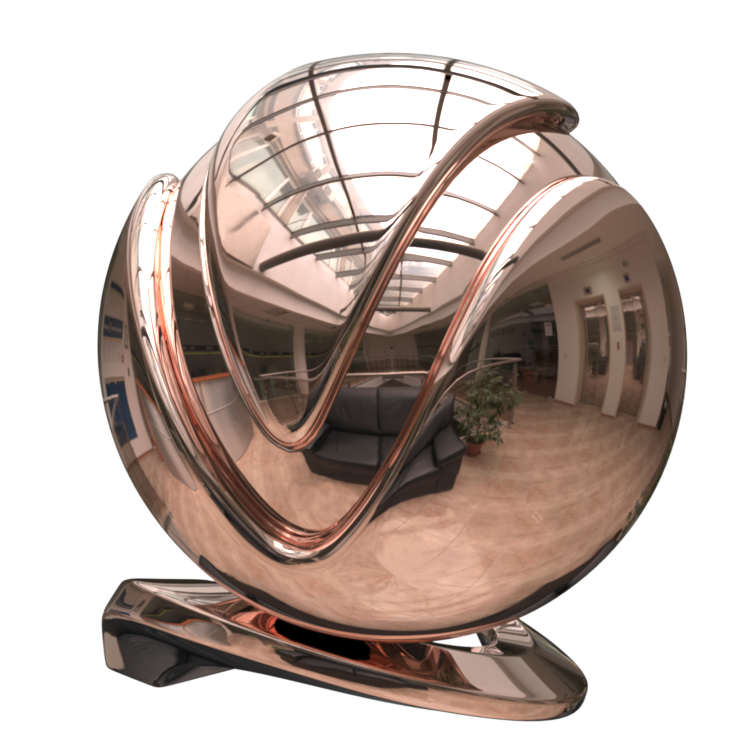
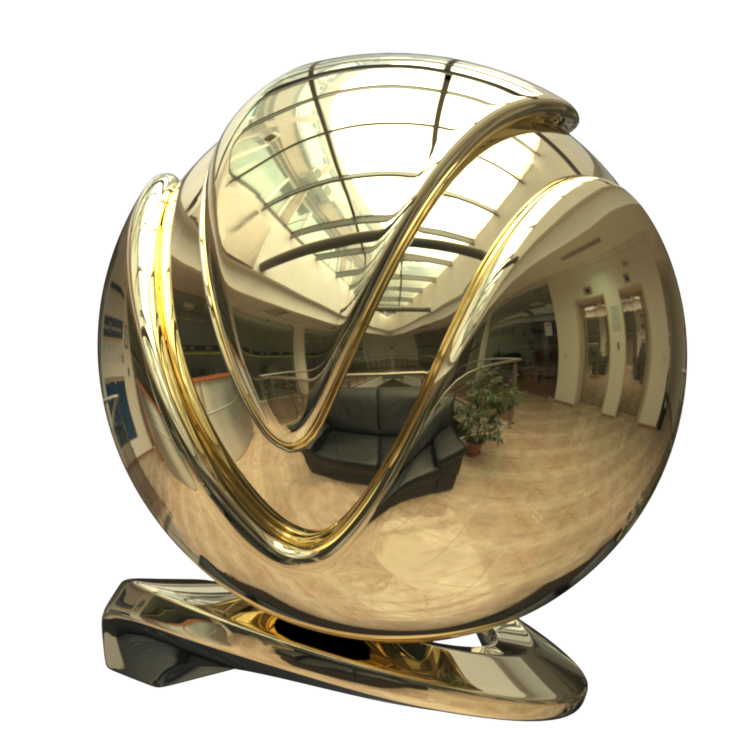
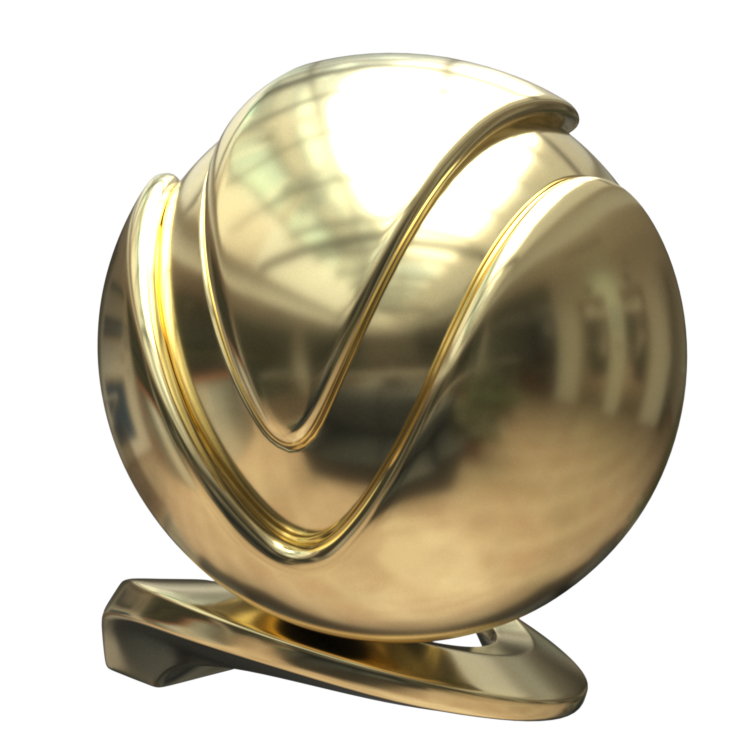
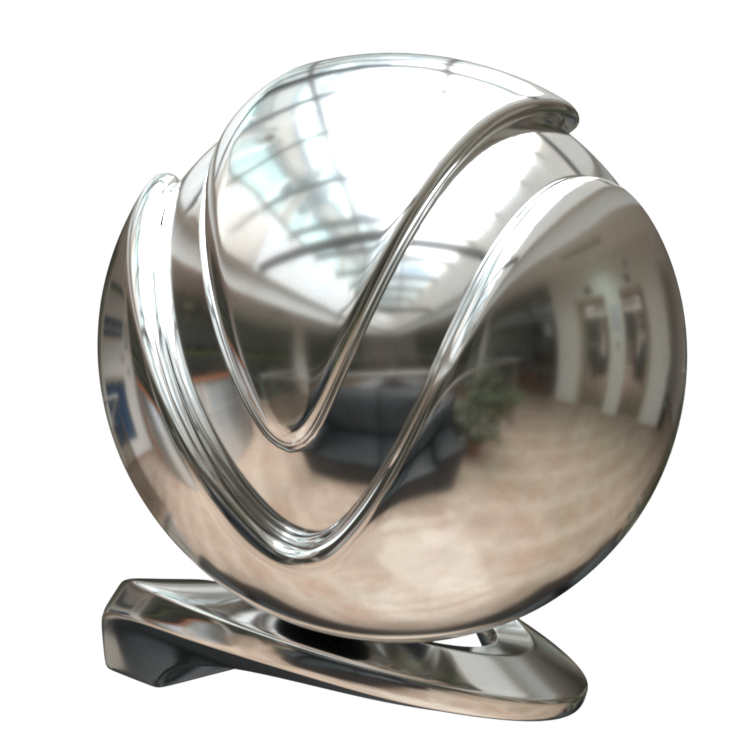
Image courtesy of Mathew Monro
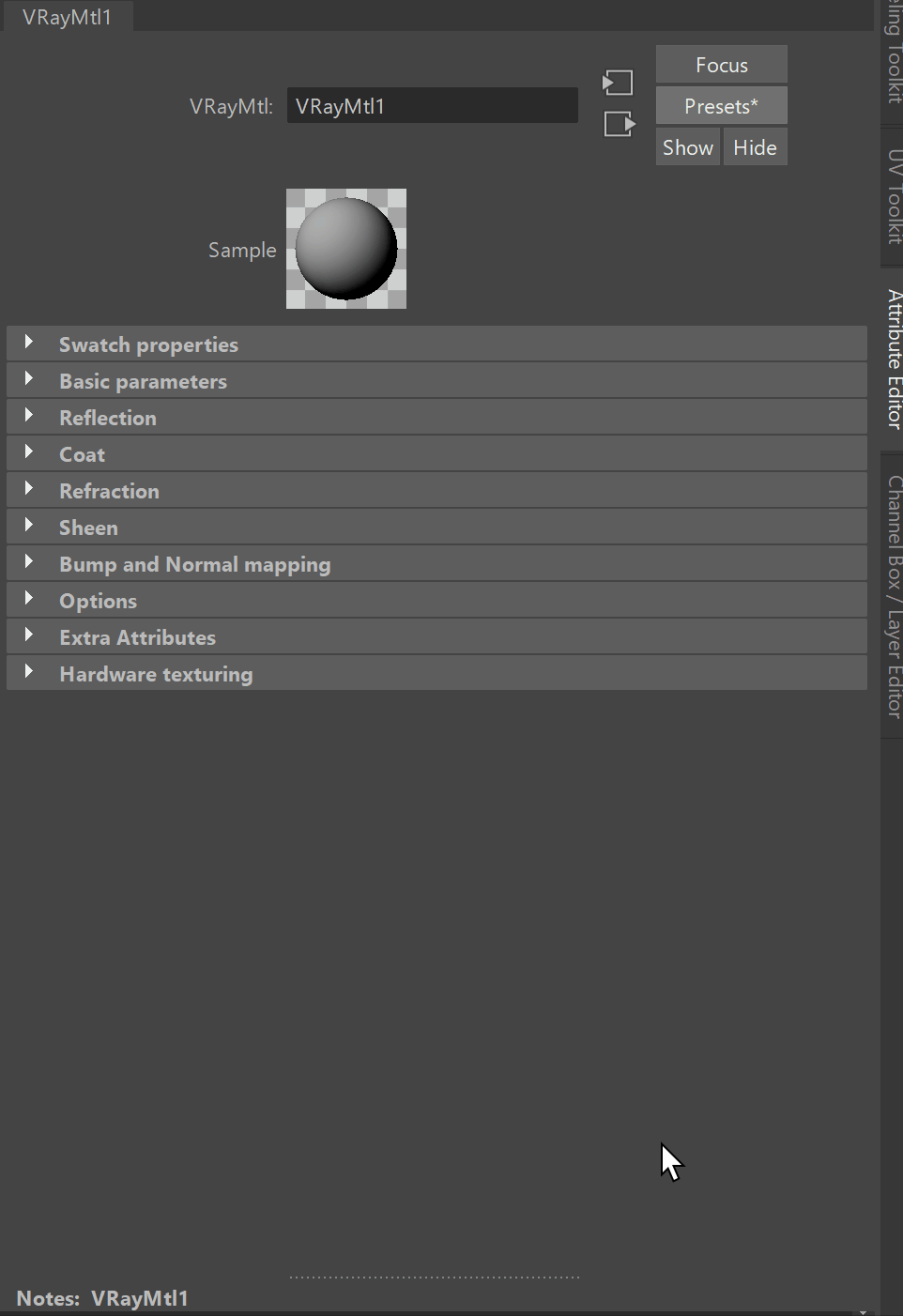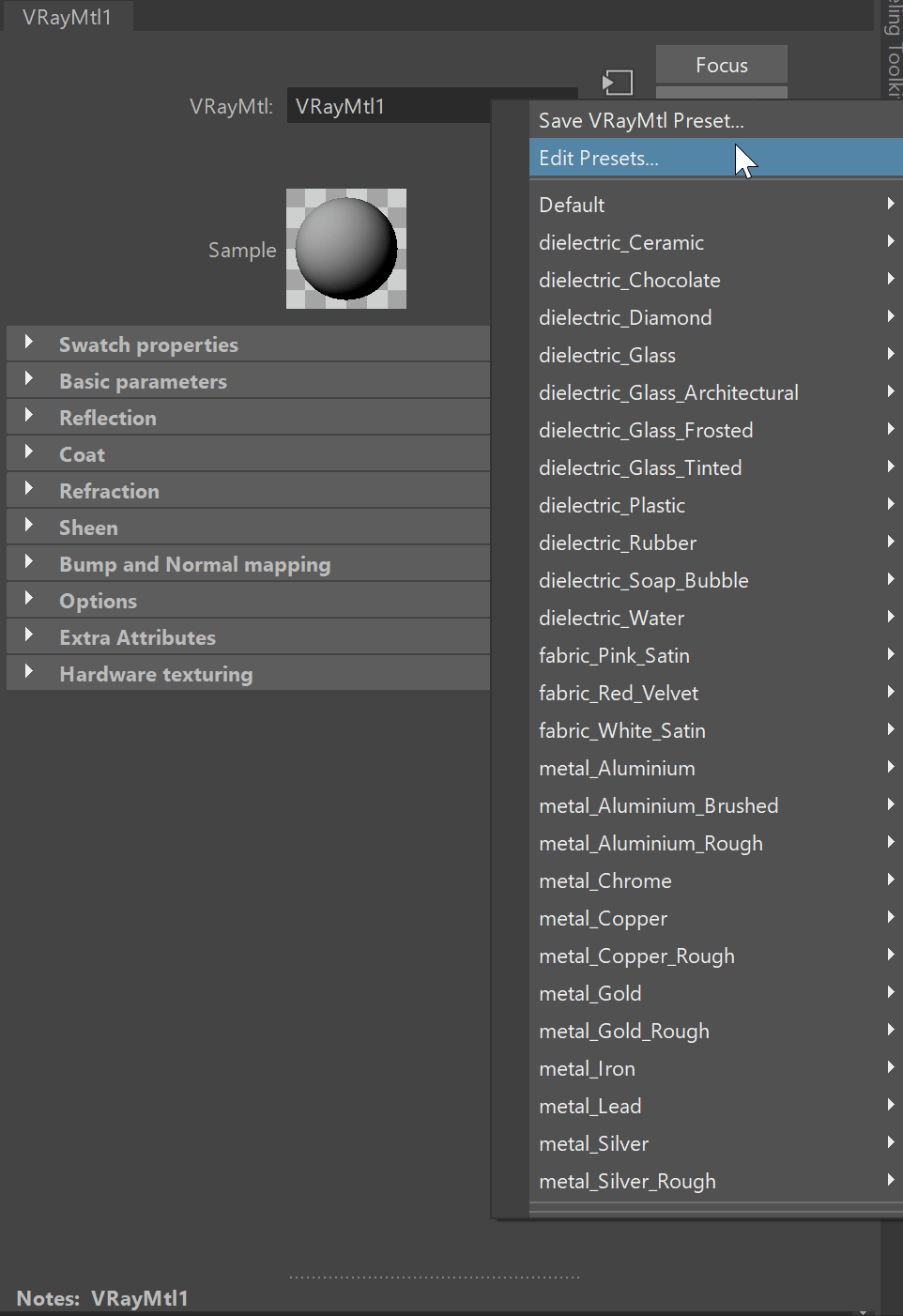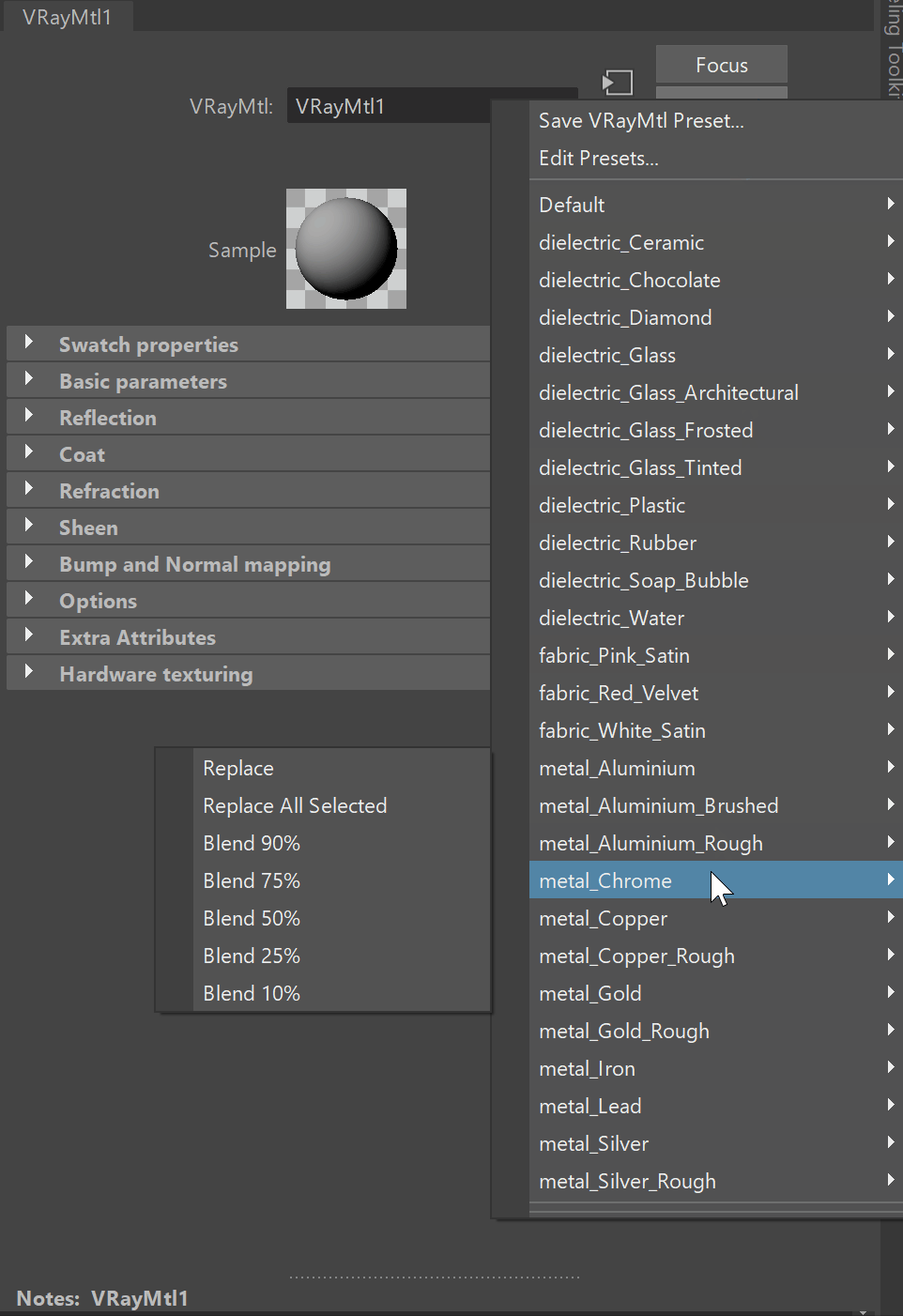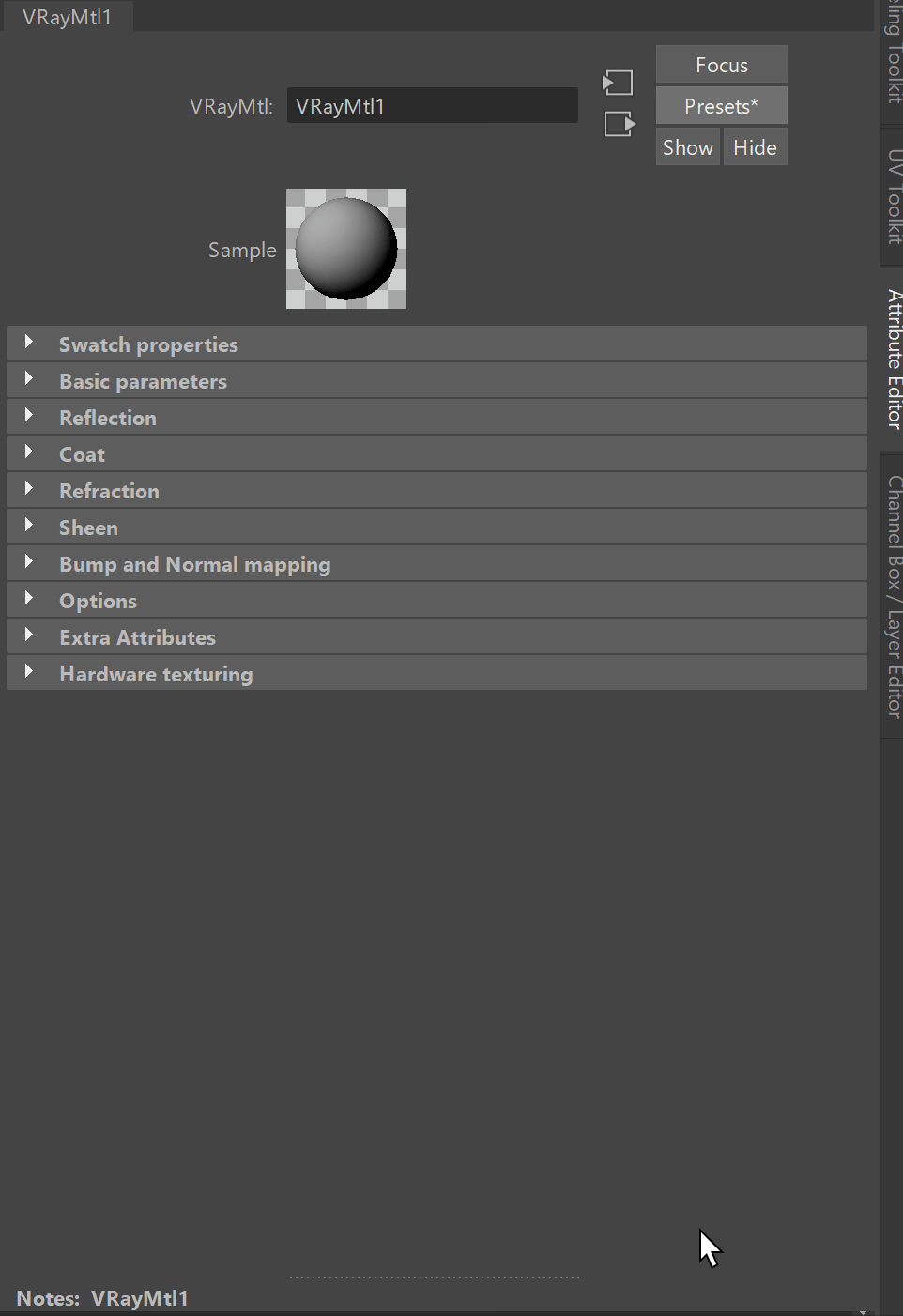
Presets
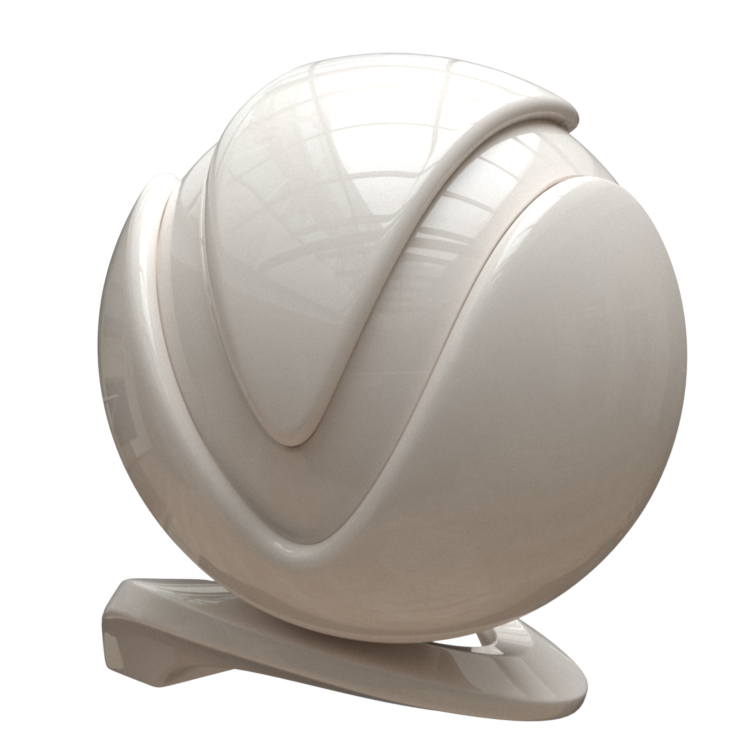
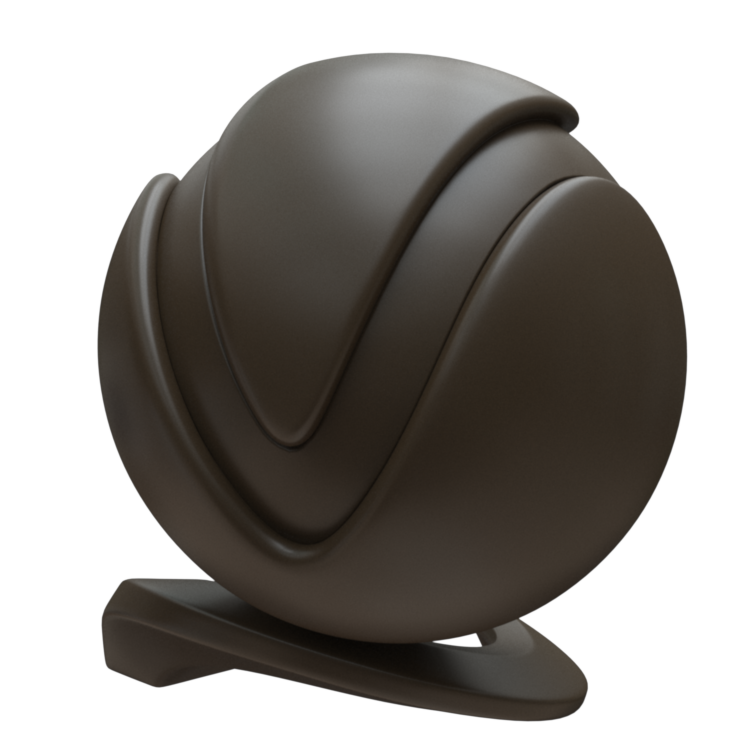
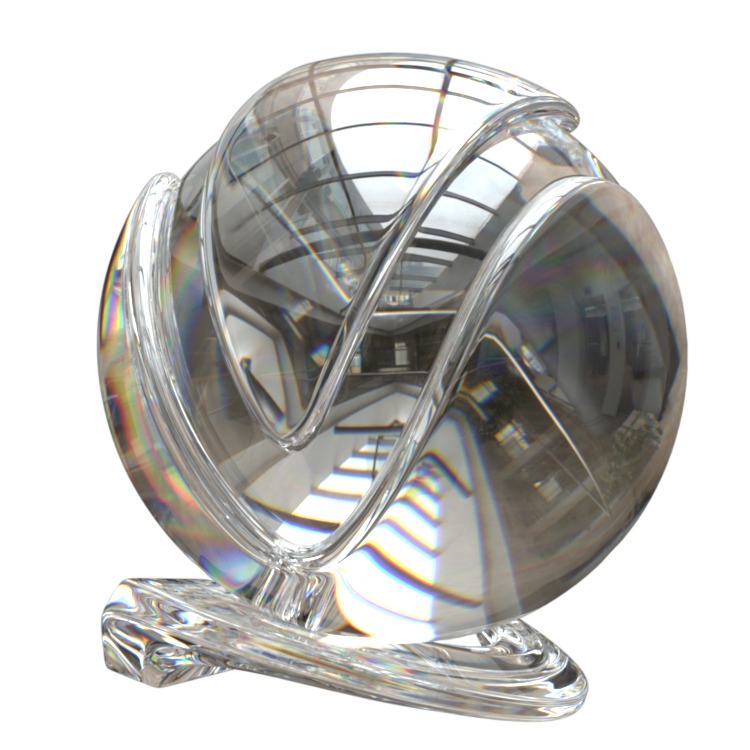
Presets – Available in the Maya Node Preset menu, the VRayMtl presets offer values for commonly used materials. See the VRayMtl Presets example below for more information.
Example: VRayMtl Presets
Non-realistic material presets, such as Chocolate, Plastic, Ceramic, and Rubber are ‘quick’ compared to their realistic (SSS-enabled) counterparts. They can be used for generic plastic for the plastic backs of computer monitors or laptops in a meeting room, or for the car tires in a scene where the cars are somewhere in the distance, etc.
Each V-Ray Material rollout has its own dedicated page listed below: