This page provides information about V-Ray Scatter in V-Ray for SketchUp.
Overview
The V-Ray Scatter tool creates instances of objects using the surfaces and edges of other objects or splines to generate points.
UI Paths
||Asset Editor|| > Geometries (right-click) > Scatter
||Asset Editor|| > Create Asset (left-click) > Geometries > Scatter
||V-Ray Objects Toolbar|| > Scatter over Selection
||V-Ray Objects Toolbar|| > Scatter Viewer
SketchUp Menus Ribbon
||Extensions|| > V-Ray > Objects > Scatter over Selection
||Extensions|| > V-Ray > Objects > Scatter Viewer
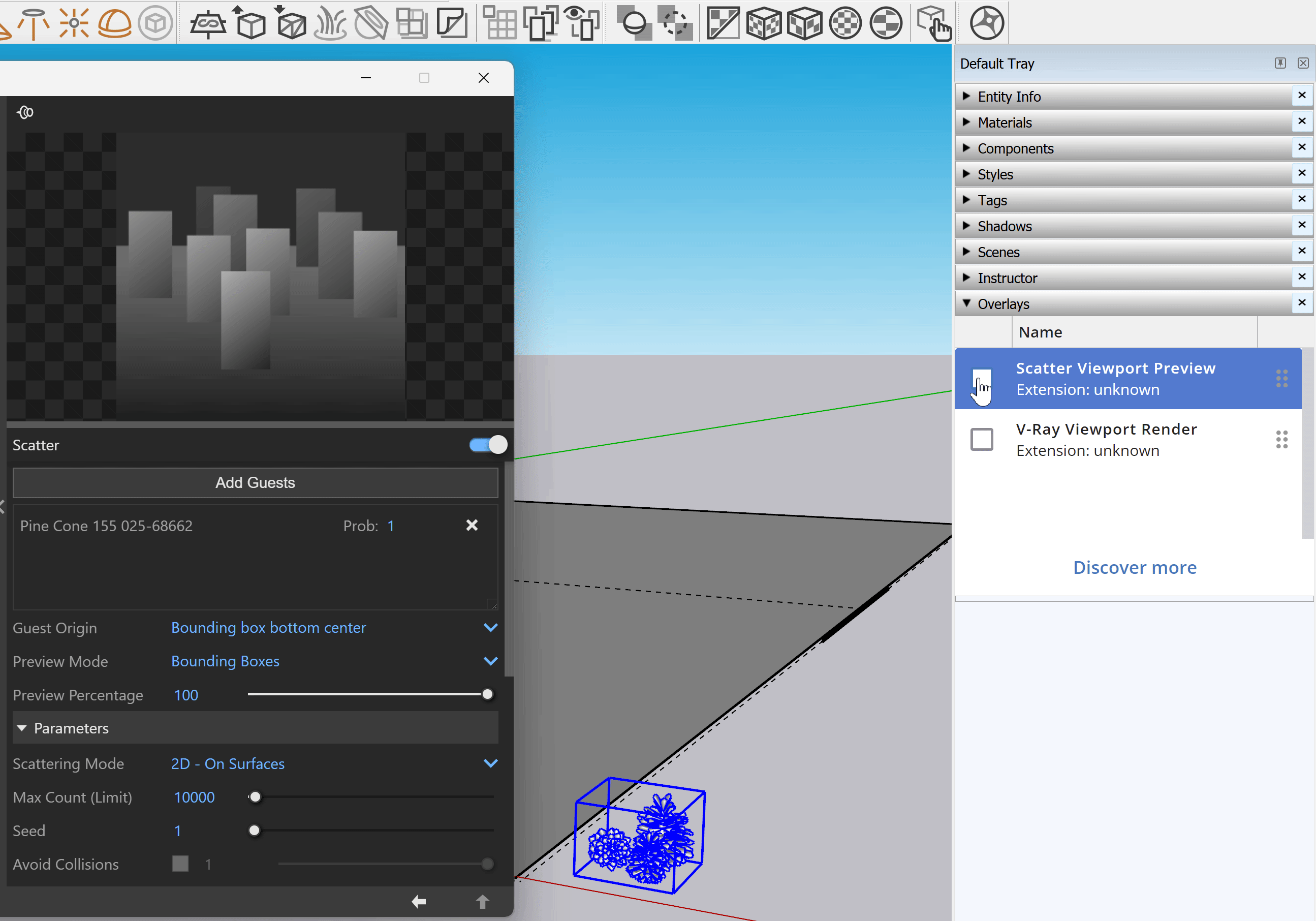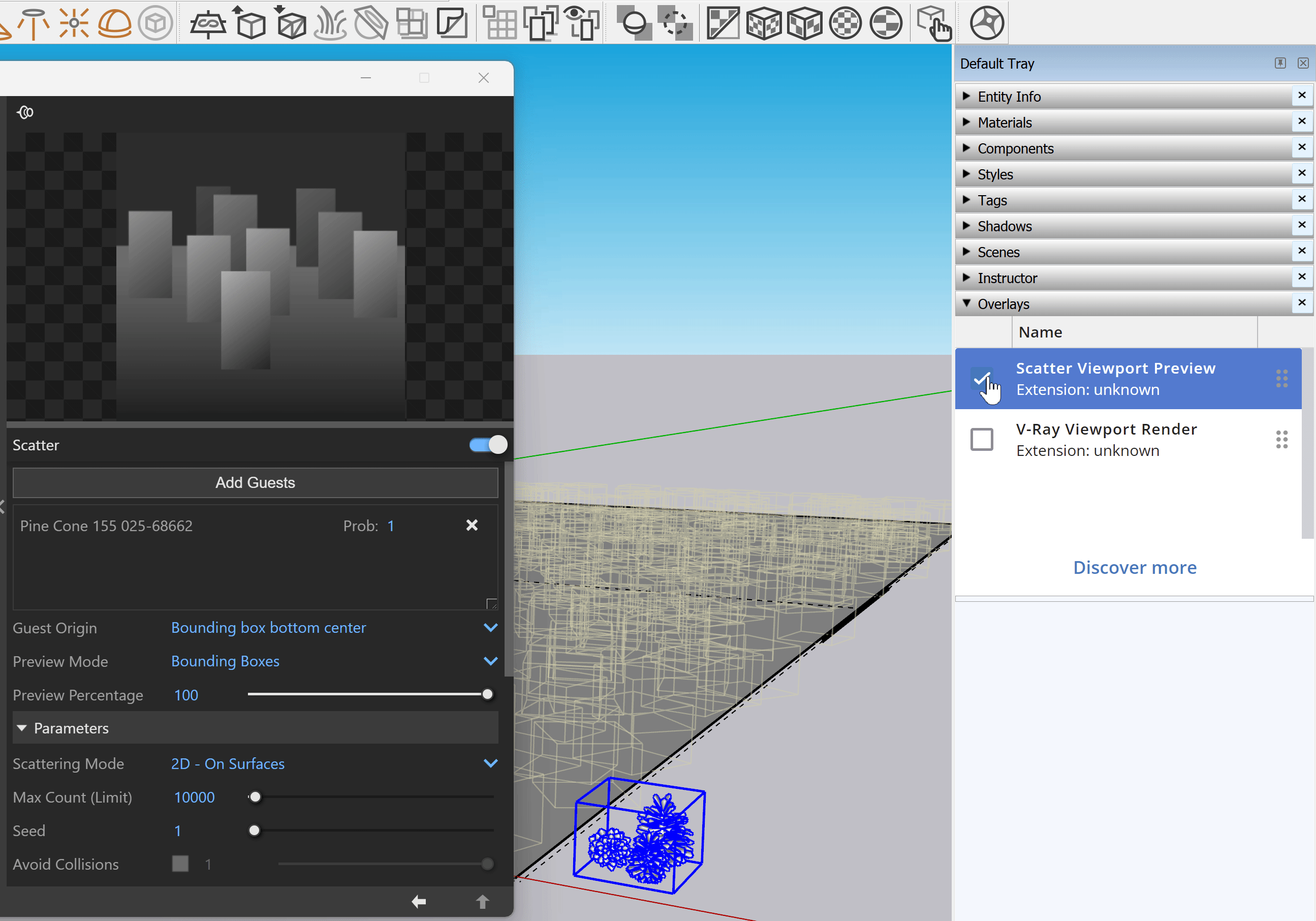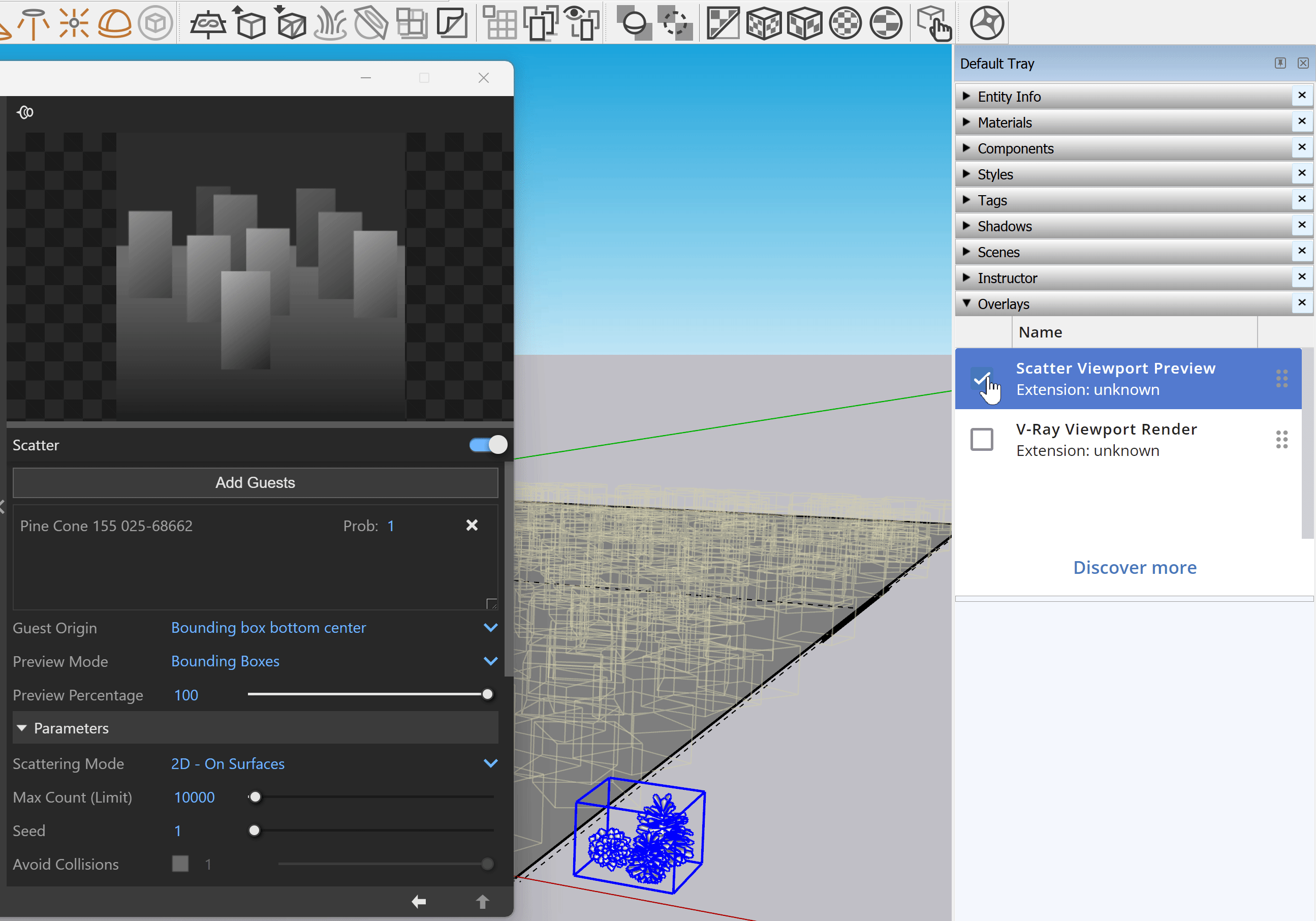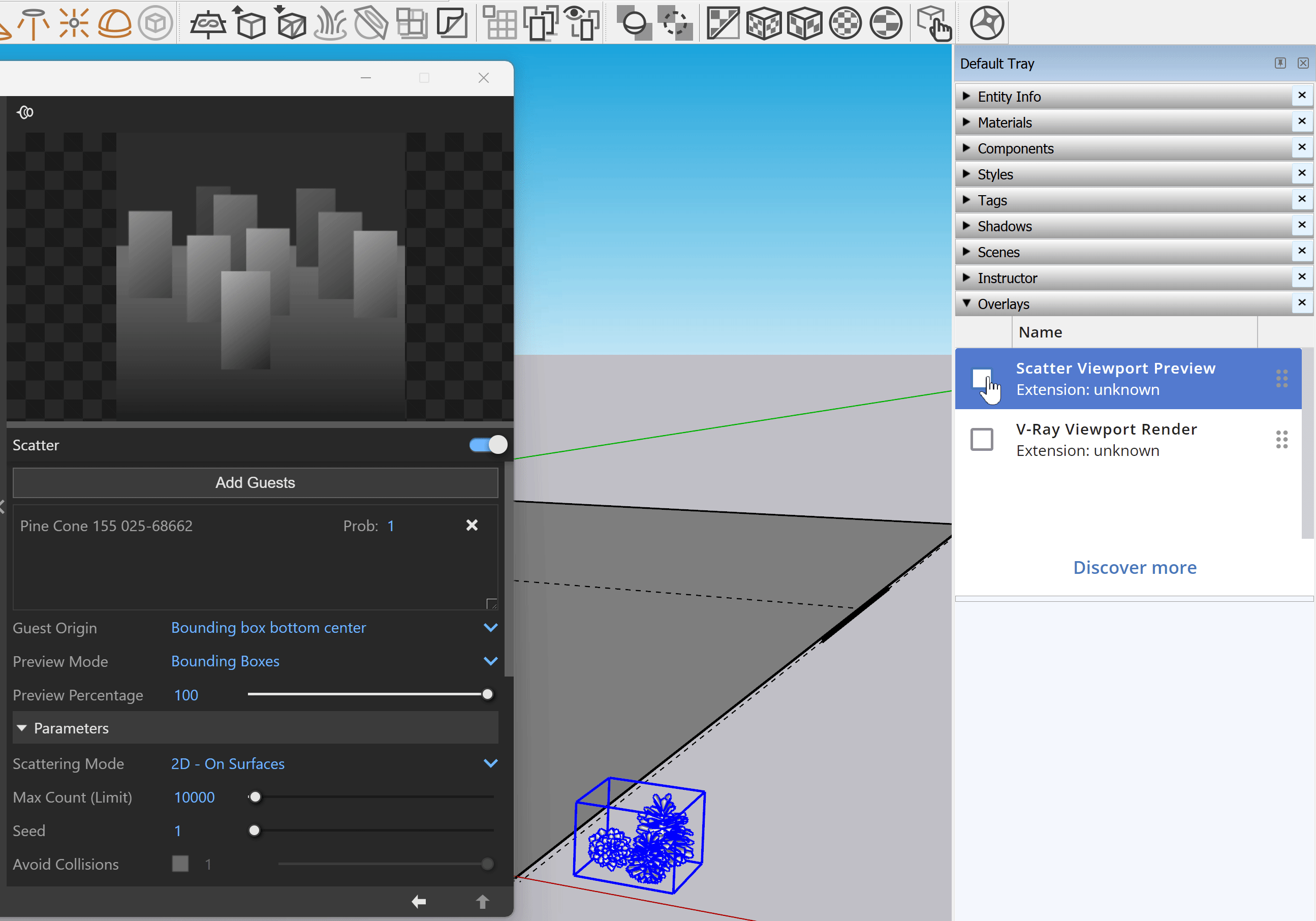
Accessing Scatter Viewport Preview from the V-Ray Toolbar or the V-Ray Menu in Sketchup 2023 or later versions opens the following notification.
||Window|| > Default Tray > Overlays > Scatter Viewport Preview
Scatter Workflow
V-Ray Scatter consists of two types of objects – Host objects, and Guest objects that are scattered over the Host object's surface. There are several ways to create Scatter Host and Guest objects.
Creating Scatter Host Objects
- Select an object in the viewport. Click the Scatter over Selection button from the V-Ray Geometry Toolbar. The button is inactive until an object is selected in the viewport window.
- Select an object in the viewport. Go to the Extensions menu > V-Ray > Objects > Scatter over Selection.
- Select an object in the viewport. Open the Asset Editor > Geometry > Scatter and use the Apply to Selection option.
To remove the Scatter from an object, use the Remove from Selection context option.
Creating Scatter Guest Objects
Add Guests – Select an object in the viewport and use the Add Guests button in the Asset Editor. The object appears under the Add Guests button.
A SketchUp component used as a Scatter guest needs to have the component instance present in the scene in order to scatter it. Deleting the instance removes the guest despite the component still being present in the SketchUp project. The extra object can be manually hidden (right-click > hide), placed in a separate hidden layer, or moved on the Scatter host surface after scattering.
Drag and drop – Drag and drop a preselected scene object from the viewport onto the Scatter Host object.
- First, make sure the Scatter over Selection is still active after Scatter is applied over the Host object.
- Then select the object that will become a Guest.
- Drag and drop it onto the Scatter Host object.
Scatter Viewport Preview Workflow
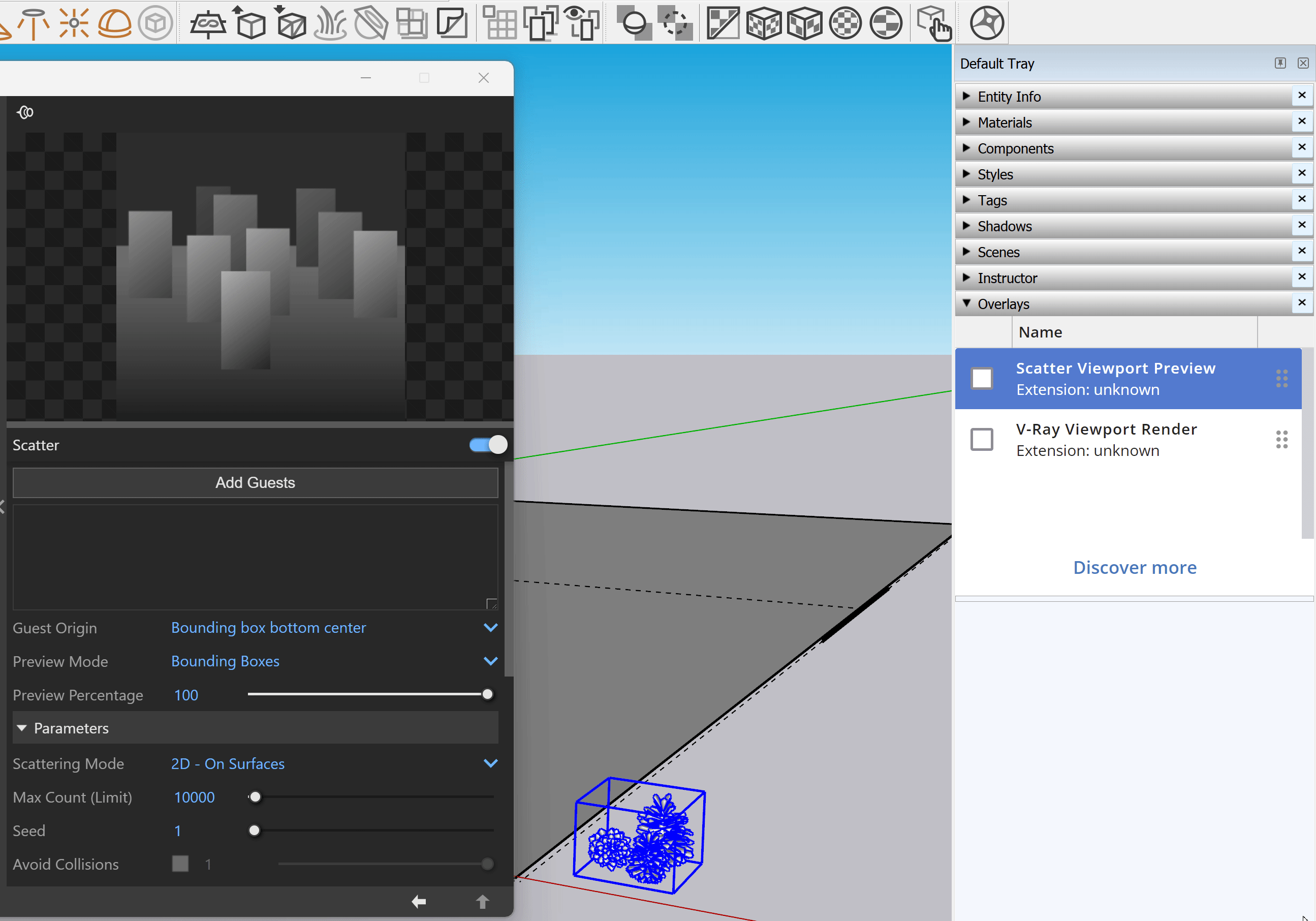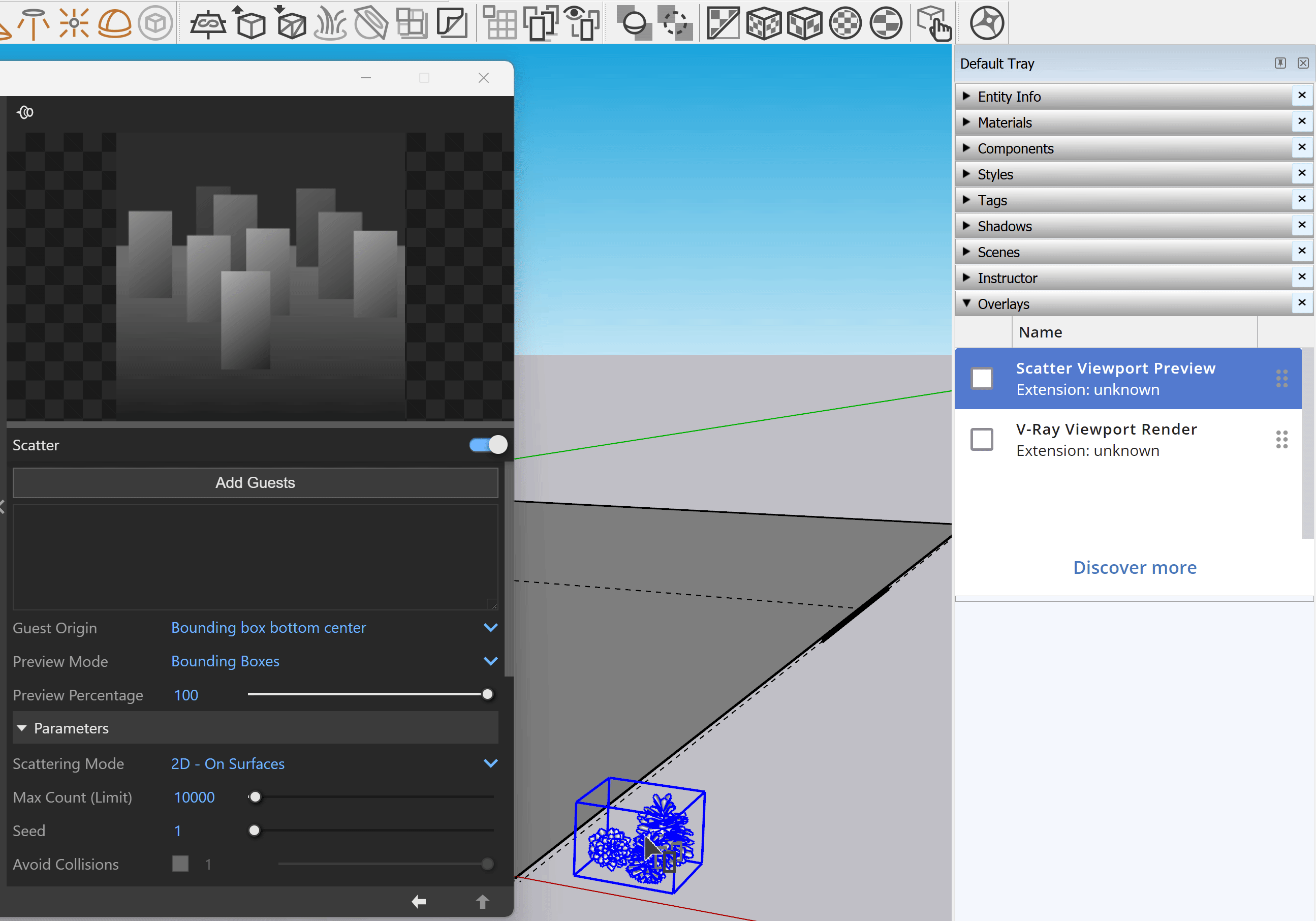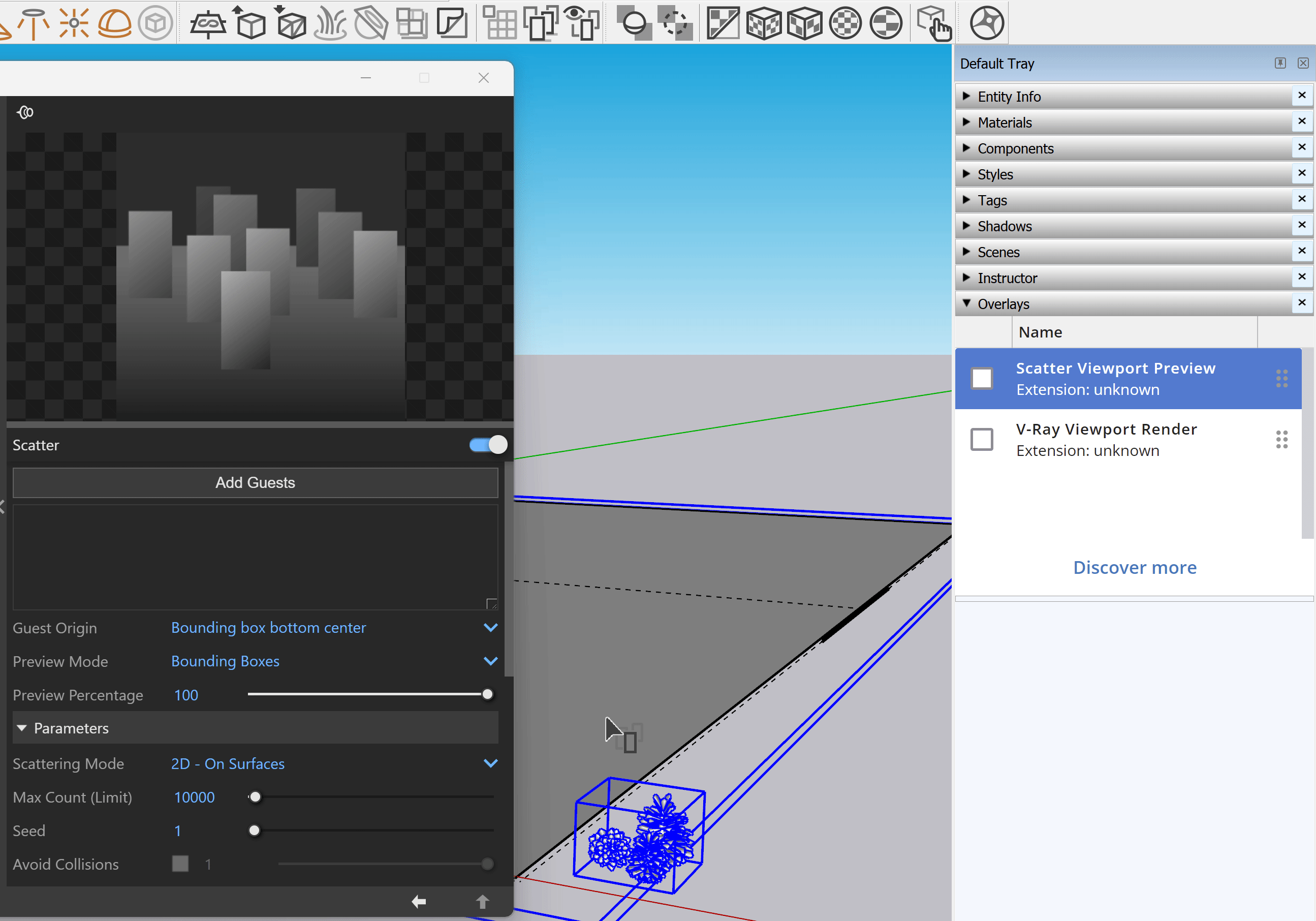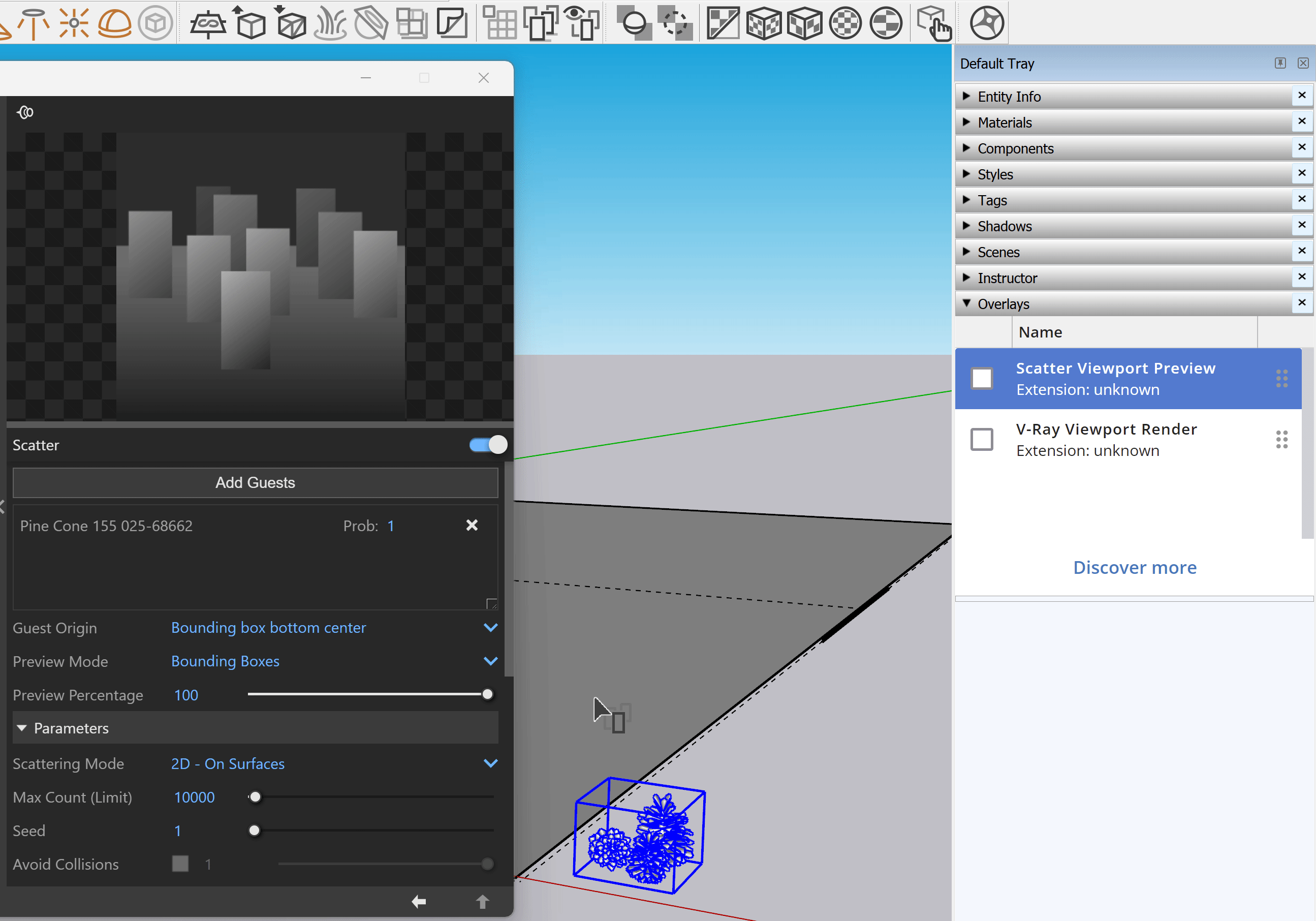
Enable the Scatter Viewport Preview from the Overlays tray in Sketchup 2023 or later versions. This provides a visual representation of the scattered objects in the viewport.
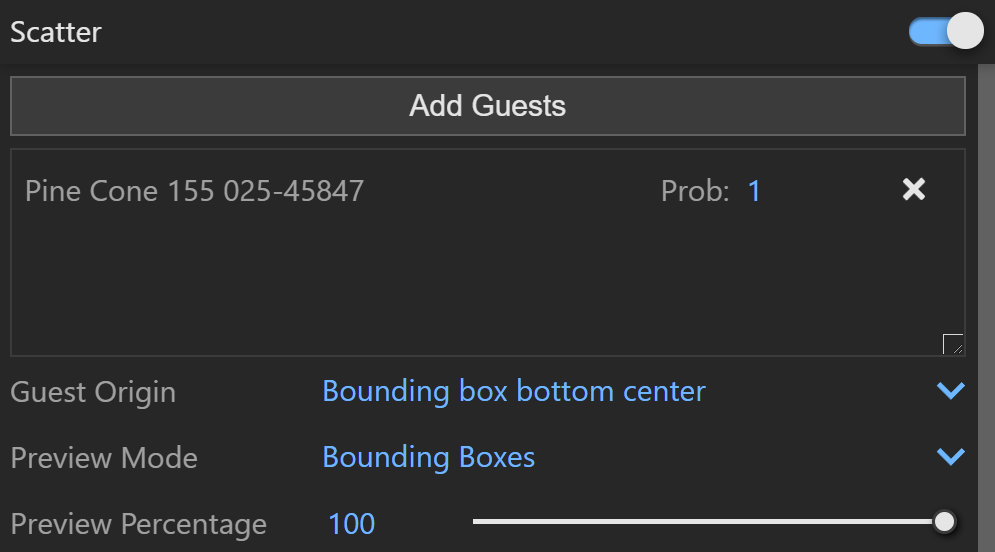
Scatter
Scatter – Enables Scatter.
Add Guests – Adds the currently selected scene objects to the Guests list. The objects in this list are scattered on the base geometry.
Probability – Determines the relative probability of the guest to appear. See the Probability examples below.
Guest Origin – Determines how the objects are positioned relative to the random Scatter points.
Bounding box bottom center – The bounding box bottom center of the object.
Bounding box volume center – The bounding box volume center snaps to the instance.
Object origin – The original object origin point snaps to the instance point.
Preview Mode – Changes between a bounding box or point preview for the instances. Note that the origin of the guest determines the point positions. See the Preview Mode examples below.
Preview Percentage – Limits the number of previews displayed in the viewport. See the Preview Percentage example below.
Example: Probability
This is an example of introducing multiple Guest objects with different probability settings to one Host object.
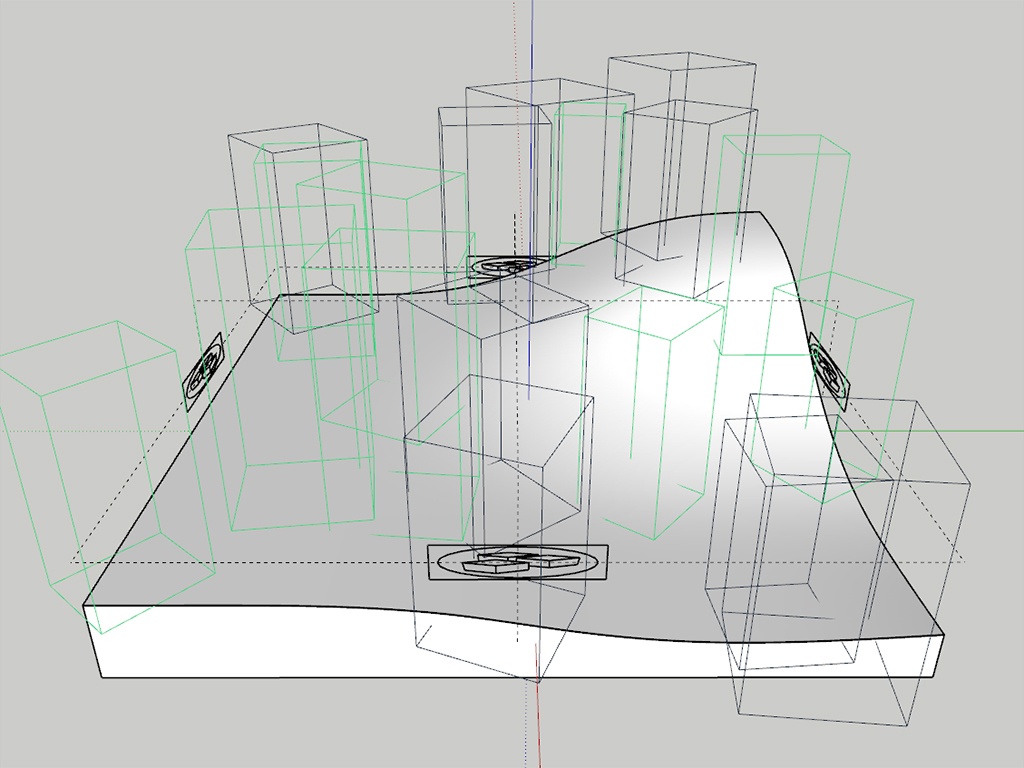
Example: Preview Mode
This example shows the different preview modes.
Scatter Guest Objects
Scatter Host Object
Point Preview
Bounding Box Preview
Example: Preview Percentage
This example shows how the Preview Percentage changes the number of previews displayed in the viewport
Parameters
Scattering Mode – Specifies the guest objects scattering mode.
1D - On Splines – Objects are scattered along splines. When a mesh is added to the guests' list, the items are scattered along all mesh edges.
2D - On Surfaces – Objects are scattered on surfaces. It doesn't matter if the surface is horizontal, vertical, or if it is a complex 3D object
3D - In a Bounding Box – Objects are scattered inside the object's bounding box. Keep in mind that bounding boxes are cube-shaped. Using this mode on a round object, scatters instances in a cube around it.
Max Count (Limit) – Limits the maximum number of instances. See the Max Count (Limit) example below.
Seed – Controls the random Scatter seed.
Avoid Collisions – When enabled, instances colliding with each other get discarded. See the Avoid Collisions example below.
Example: Max Count (Limit)
Max Count (Limit) is a limit to help avoid creating too many instances and overloading the system. This option has no effect if the Instance Count value is lower than the Max Count value. Depending on the hardware, this limit can be adjusted to ensure smooth performance and avoid excessive memory consumption. At Instances Count - 100, the scattered objects do not exceed the Max Count (Limit) - 50 and the render is the same as when the Instances Count is 50. Scattering Mode = 2D On Surfaces; Max Count (Limit) = 50.
Example: Multiple Objects as One - Combined Surface Area
Scatter treats multiple host objects as one with combined surface area (or volume). If you set Scatter to produce 100 instances of a guest object over two host objects, it does not produce 100 for each host. Instead, it produces 100 randomly distributed instances over both host objects' combined surface area (or volume).
Example: Avoid Collisions
This example shows how the Avoid Collisions function works. Higher values result in larger distance between instances.
Notes
- V-Ray 6 provides the option for multiple special objects to be added in combination with a single group/component. This allows for Fur, Scatter, and Displacement special objects to be used simultaneously. Multiple Fur and Scatter assets can be added to a single object.
- Special objects can be removed from geometry by double-clicking on the group/component, selecting the special object's widget, and then selecting the Erase option from the context menu (right-click to open the context menu).
- When Mesh Light or Clipper are applied, no other special objects are allowed.
- The Scatter Density map currently does not support raytraced textures.
- Curve objects need to be grouped via G shortcut on windows or command + G on macOS to be added as Scatter Area Modifiers.
- If Scatter is applied to a spline closing a face, its segments (edges of the face) are treated as individual splines.
- Apply a material with 0 opacity for host objects that you don’t want visible in the rendered image.
- Scene units in SketchUp are always calculated in inches.
Rollouts
Each Scatter rollout has its own dedicated page listed below: