This page provides information on the advanced options of the Surface Scattering in Maya.
Edge Trimming
Enable Edge Trimming – Toggles the Edge Trimming function, which "trims the edges" of the Scater geometry, removing any instances that scatter outside of the Target Objects or the Include/Exclude Objects.
The typical use cases of Edge Trimming include:
- Grass lawns - in case of using large grass clumps, no individual grass blades will be growing outside of the defined area.
- Carpets - in case of using large clumps of strands, no individual strands will be placed outside of the carpet area.
- Pebbles, rocks, bark chippings, or any other objects which you need to distribute within some specific boundary and make sure no instances stick outside of that boundary (determined based on the mesh element pivot precision).
In addition to making the scattering look more refined and natural, the edge trimming feature boosts performance by removing some of the instances you save from RAM and making parsing time shorter.
See the example for more.
Edge Trimming V-Ray Proxy Files
V-Ray Proxy files are often created in other software, not Maya. This may result in their axes having a different orientation than the native Maya one. Having axes with a different orientation obstructs Chaos Scatter from trimming the instances properly. This is the case for all Chaos Cosmos assets and proxies created in V-Ray for 3ds Max. You need to adjust their axes if you want to scatter such proxy files and use Edge Trimming. To do so:
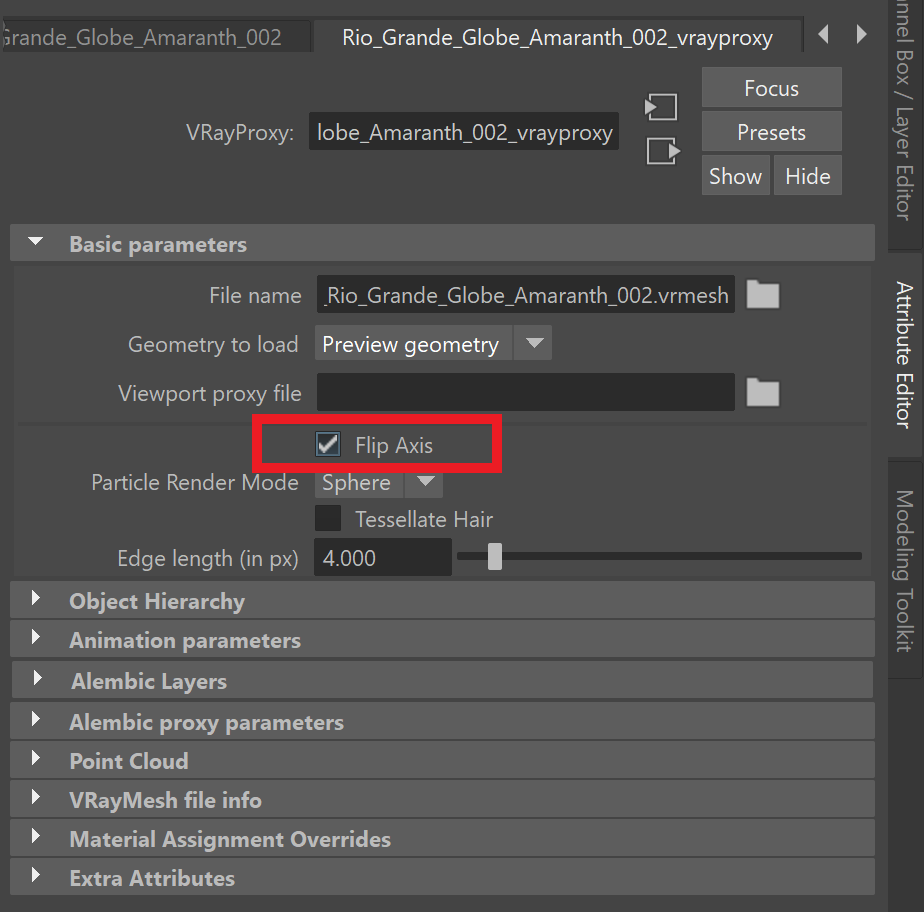
- Go to the proxy object's attributes, and in the Basic Parameters rollout, enable the Flip Axis option.
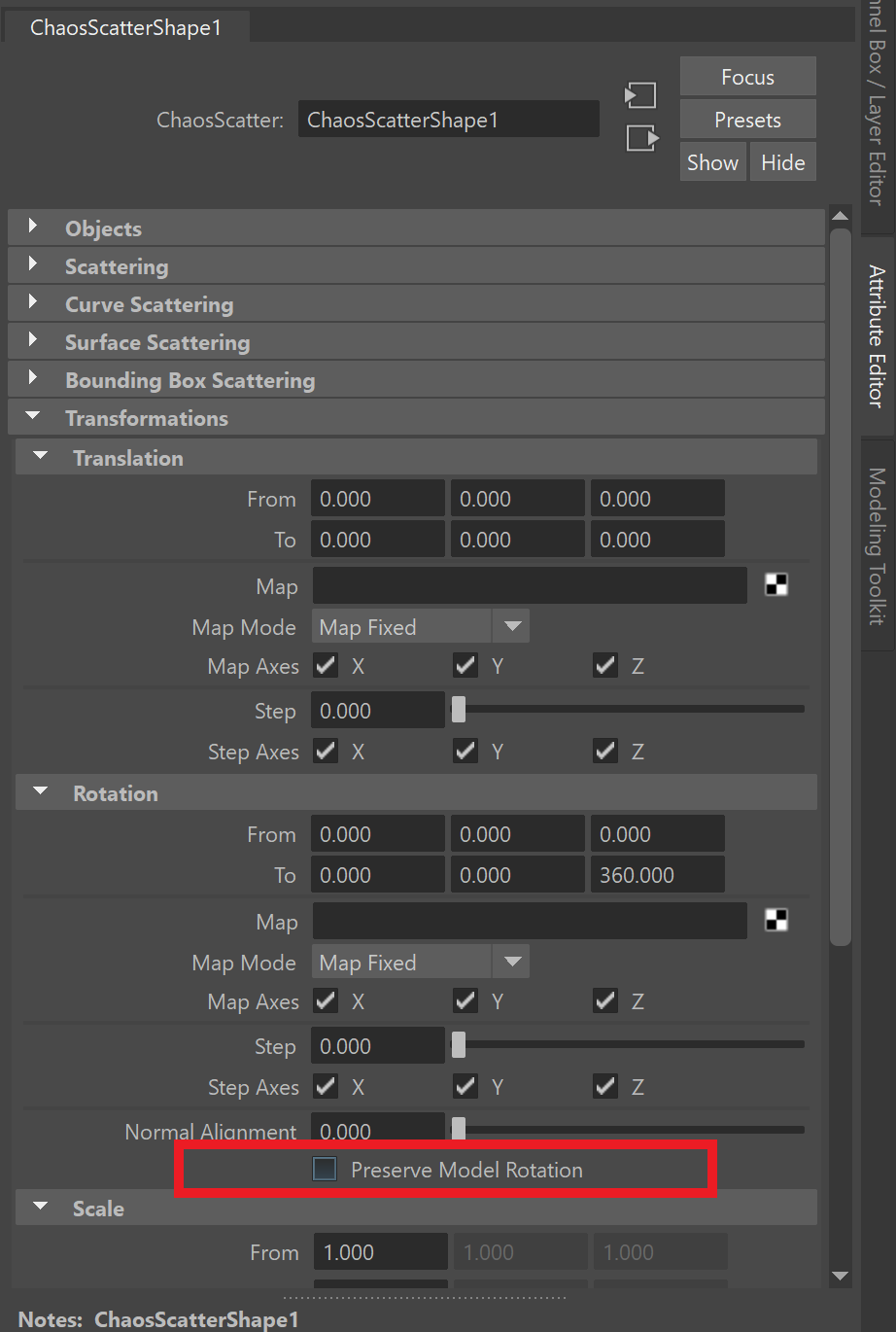
- In the Scatter Object's attributes, go to the Transformations rollout > Rotation and disable the Preserve Model Rotation option.
Enable the Proxy's Basic Parameters > Flip Axis
Disable the Scatter object's Translations > Rotation > Preserve Model Rotation option
Example: Enable Edge Trimming
Turning on the Edge Trimming function deletes all grass strands that are outside of the Target Object, creating a clean line, imitating that the grass has been professionally cut.
Slope Limitation
Slope Limitation limits scattering only to 'slopes' at certain angles. It can be used to create realistic spread of trees on curved surfaces, for instance. The lower the Angle range is set, the smaller the angle at which scattering stops.
Up Axis – The angles are measured either between the Local Up Axis and the surface normal, or the World Up Axis and the surface normal. You can select which up normal to use:
Local – When enabled, the Slope Limitation is measured according to the up vector of each individual Targets object.
World – When enabled, the Slope Limitation is measured according to the world Y-axis up vector for all Targets objects in the scene.
See the Slope Limitation Up Axis example for more information.
Min Angle/Max Angle – Defines a range of angles to which the scattering is limited. Instances outside of this range get filtered out. See the Min/Max Angle example below for more information.
When using the Local Up Axis, freeze the scale of the model.
Example: Slope Limitation Up Axis
The Local and World Slope Limitations determine the up-vector. The Local option uses the normals of the Target object; the World option uses the Y-axis of the scene. In this example, the Min/Max Angle is set to 0.0°-45.0°.
Example: Min/Max Angle
The Min/Max Angles remove instances based on the angle of the underlying geometry. These options can be used to remove geometry from steep areas as well as shallow areas.
Altitude Limitations
Enable Altitude Limitations – Toggles the altitude limitations parameters on and off. Altitude defines a height range (in cm) for the scattered geometry to distribute on.
Altitude Limit Mode – Determines the coordinates space used for determining altitude.
Position Independent – The altitude of the surface points on each individual distribute-on object is evaluated relative to the object center while the object rotation and scale still affect the altitude.
World – The altitude of the surface points on each individual distribute-on object is evaluated in world space (after all transforms).
Min Altitude – Determines the minimum altituge range for the scatter objects. Objects below this threshold are not rendered.
Max Altitude – Determines the maximum altitude range for the scatter objects. Objects above this threshold are not rendered. See the example for more information.
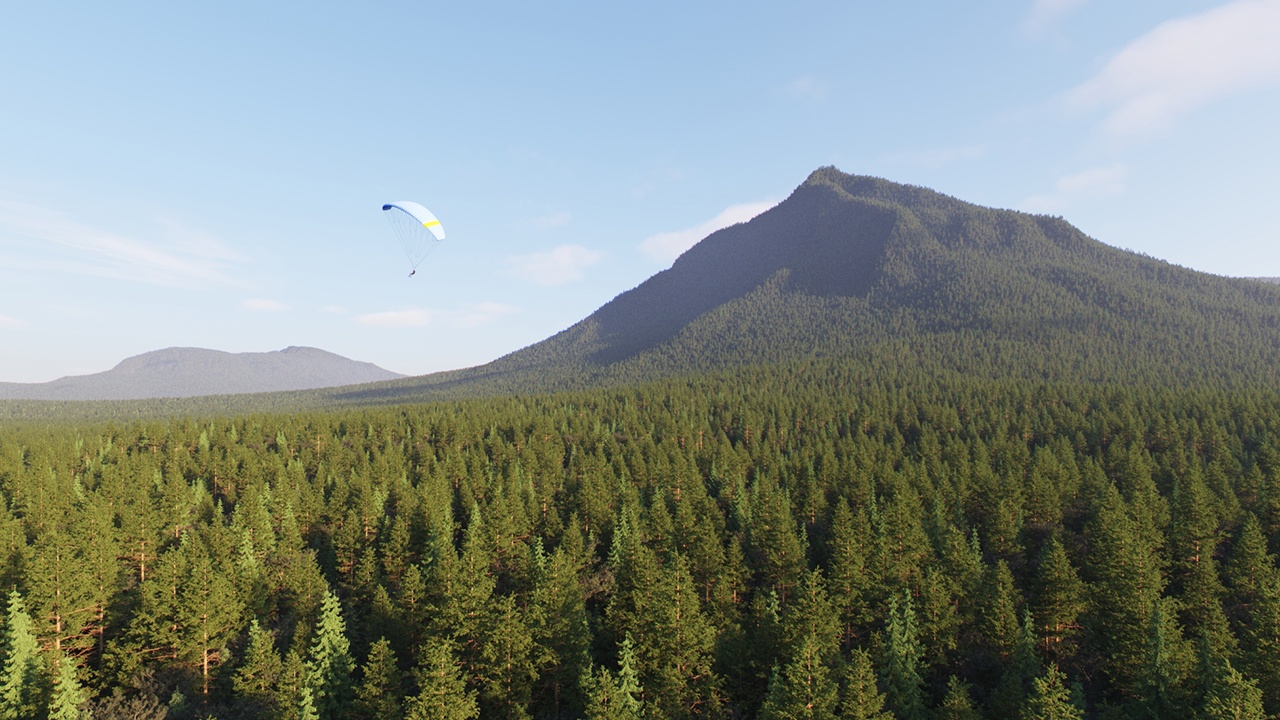
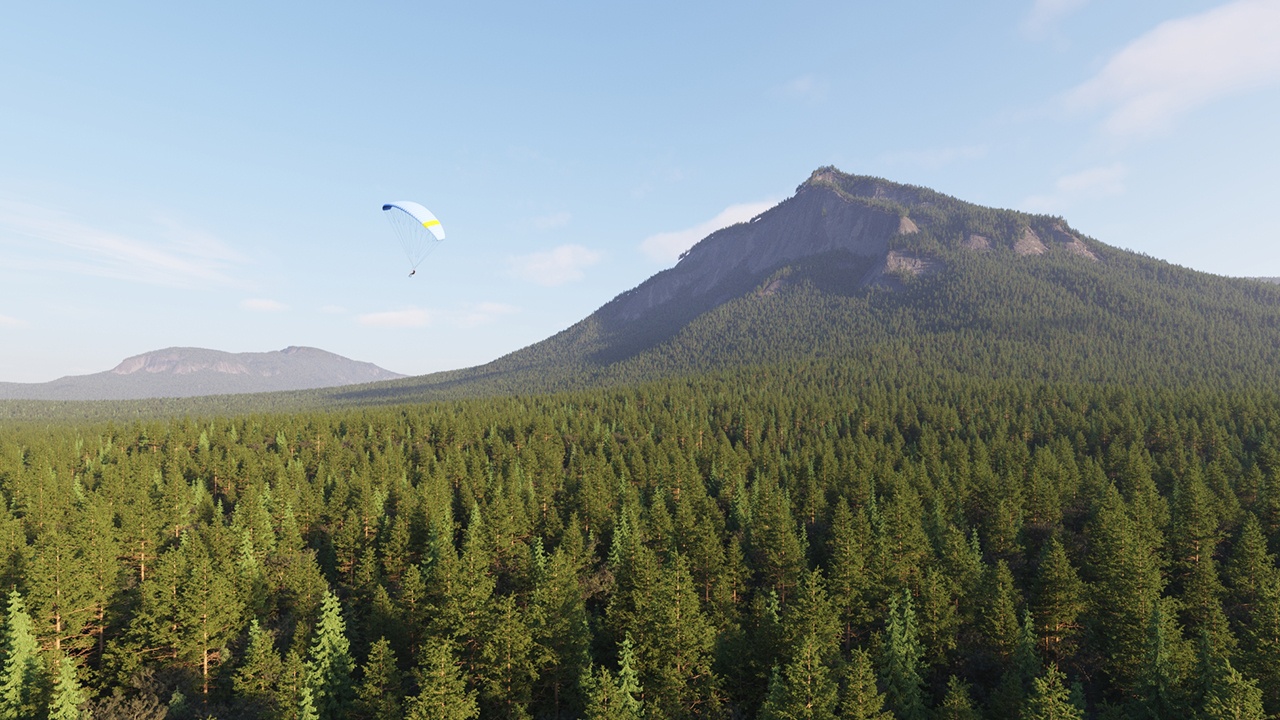
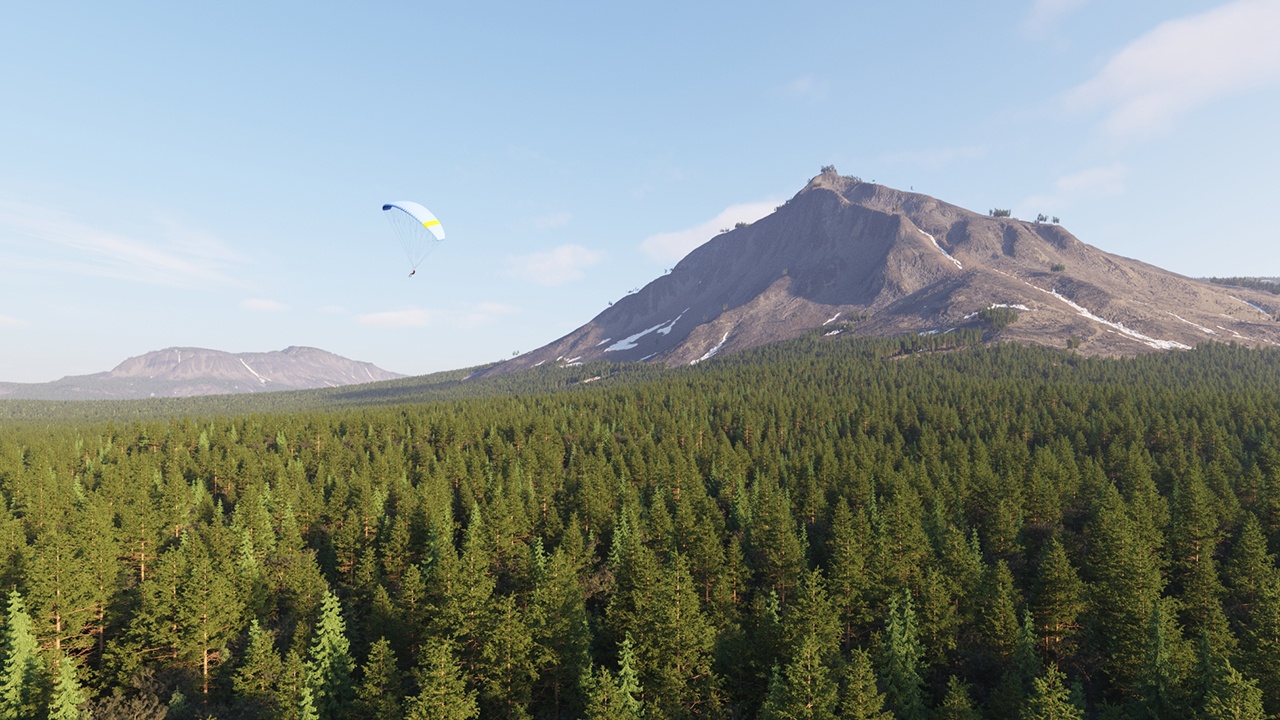
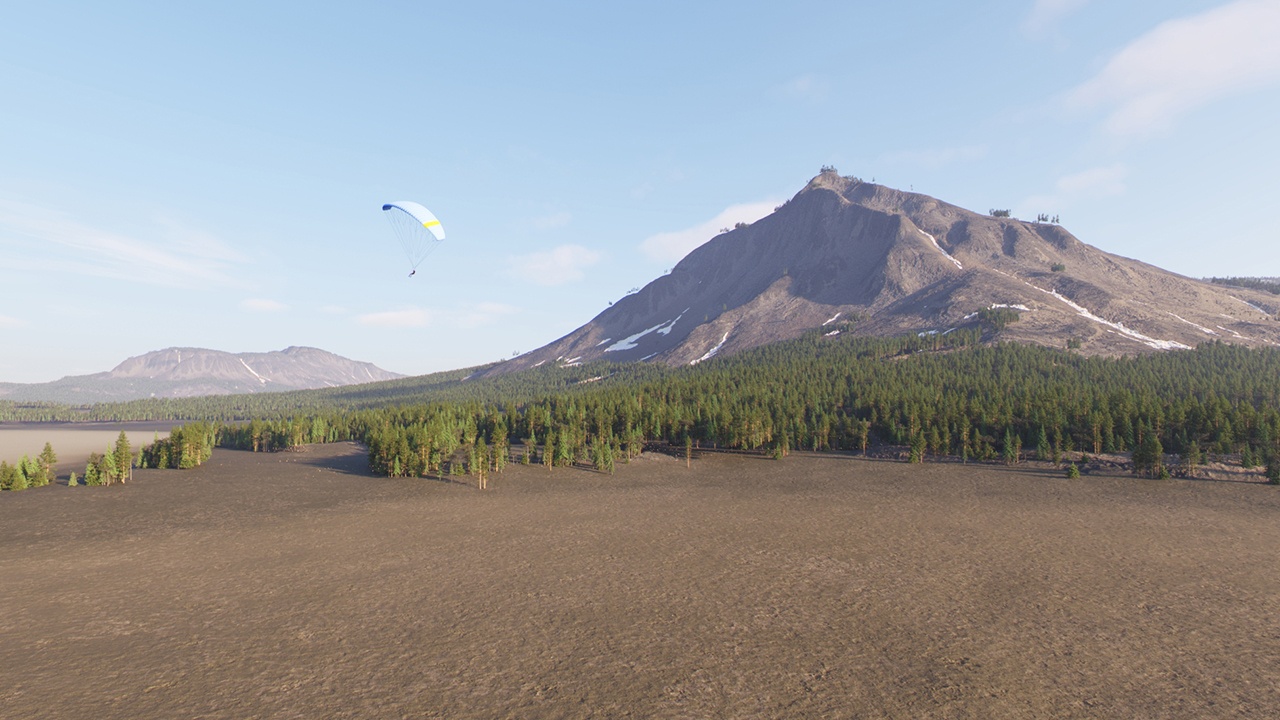
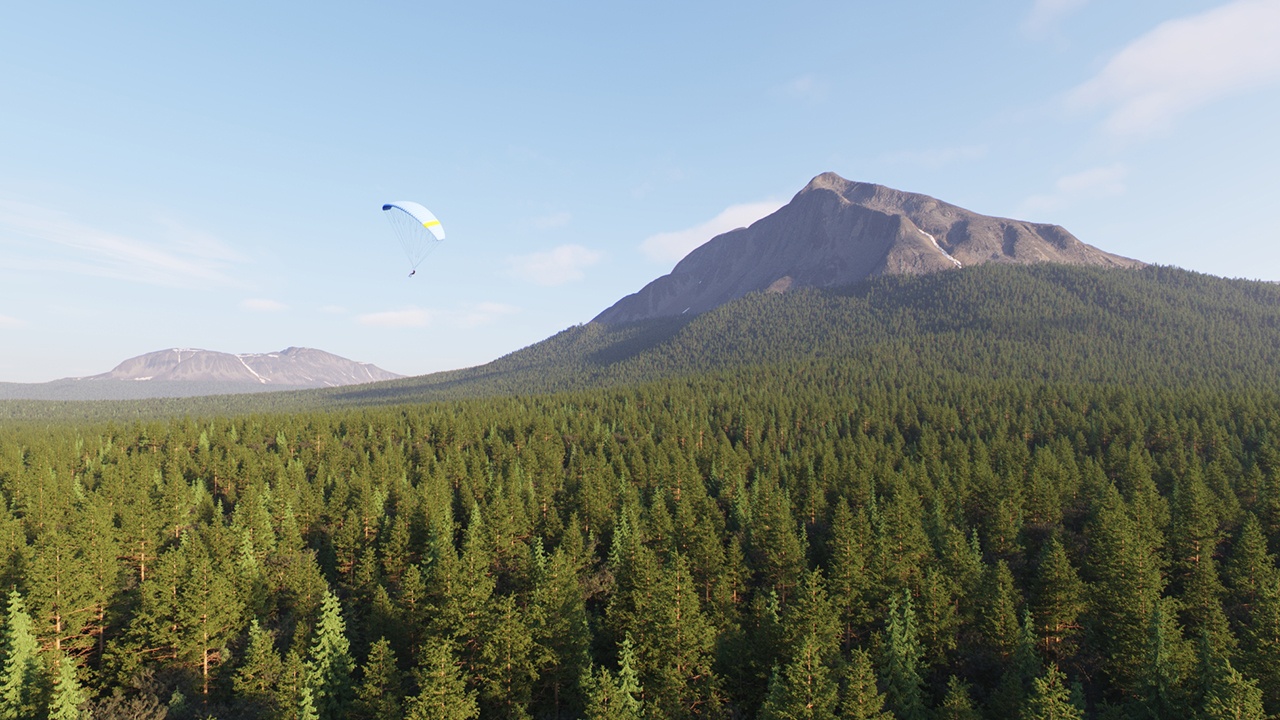
Example: Altitude Limitation
Setting the Max Altitude to 5000.000 cm (500m) limits the scattered trees to that height.
Falloff Curve
The Falloff Curve specifies the density of the scattered objects depending on their altitude.
Lowering the point on the left side of the curve results in lowering the density of the objects closer to the minimum altitude range. Lowering the point on the right side of the curve results in lowering the density of the objects close to the maximum altitude range.
The Expand button opens the Falloff Curve in a separate window.